
The Sophia Amalia was a ship of the Royal Dano-Norwegian Navy named after Sophia Amalia, the wife of King Frederick III.
HDMS Søormen was a 12-gun cutter of the Royal Dano-Norwegian Navy, built in 1789. After being captured by the British in 1808 she was added to the Royal Navy as HMS Salorman. She was wrecked in 1809.

Steen Andersen Bille, was a Danish vice-admiral and minister for the navy. He was famous for his service in the Danish Royal Navy, particularly during the First Schleswig War, 1848–51.

Hans Peter Holm was a Danish naval officer who commanded vessels of the Dano-Norwegian Navy in several actions. He commanded several naval vessels during the Gunboat War. His most important action occurred in 1812 at the Battle of Lyngør when a British squadron, led by the British ship-of-the-line HMS Dictator, destroyed his vessel, HDMS Najaden. Holm sustained wounds in the battle but survived, only to drown in an accident shortly afterwards.

Battle of Rügen was a major naval battle fought on August 8, 1715 off Jasmund on the Swedish island of Rügen during the Great Northern War.

HDMS Elephanten was a ship of the line of the Royal Dano-Norwegian Navy that served from 1703 to 1728. There were three other Danish ships-of-the line of the same name, dating from 1684, 1741 and 1773. The ship was sometimes referred to as Nye Elefant to differentiate from others of similar name. For much of her service career, which coincided with the Great Northern War, Elephanten was the flagship of the Danish fleet active in the Baltic Sea.

Christian Wulff was a Danish naval officer. He commanded HDMS Bellona on her expedition to South America in 1840–41.
HDMS Friderichsværn was a Danish frigate built at Nyeholm, Copenhagen, in 1783. The British Royal Navy captured her in 1807 and took her into service as HMS Frederickscoarn. It sold her in 1814.

Frantz Christopher Henrik Hohlenberg was a Danish naval officer who specialised in ship design and had little seagoing experience. He succeeded Ernst Wilhelm Stibolt as Master Shipbuilder (fabriksmester) at the Royal Danish Dockyards in 1796. His ships included five ships of the line and 18 frigates. Three of the ships of the line and nine of the frigates were captured at the 1807 Battle of Copenhagen and subsequently added to the Royal Navy. He resigned after a controversy in 1803.
HDMS Hvide Ørn , was a light frigate designed by Frantz Hohlenberg and built in Copenhagen. She capsized and was lost with all hands off Corsica at the end of 1799. There were three previous ships bearing this name in the Danish navy. The name was after the loss of the ship retired. An 1898 model of the ship is in the collection of the Royal Danish Naval Museum.
Danish shipbuilders in the Age of Sail
This list, arranged by year, presents builders of Danish warships from the late 17th century to mid-19th century. It names the Heads of Naval Construction (Fabrikmester) and includes lesser shipbuilders to the Danish Royal Navy. It does not include purely commercial shipbuilders.
HDMS Ørnen (1694) was a frigate in the Royal Danish Navy active during the Great Northern War

Michael Bille (1680–1756) was an officer in the Danish Royal Navy during the Great Northern War. He was commissioned as a junior lieutenant in 1699, advancing steadily to become Vice admiral when he retired in 1737.

HDMS Det Store Bælt was a frigate of the Royal Dano-Norwegian Navy, launched in 1782. In 1800, she was sold to the Danish Asiatic Company and renamed Holsteen.
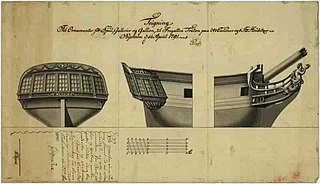
HDMS Triton was a Danish frigate launched in 1790 which operated in Danish/Norwegian home waters and in the Mediterranean in the protection of Danish merchant ships - not only from Barbary pirates but also from potential British privateers. The period in which it operated was fraught with political and practical difficulties which led to two battles at Copenhagen and other, lesser, actions.
De Fire Søstre was the name of five separate ships which served purely as merchant ships or, for part of their lives, hospital and supply ships to the Danish fleet.

HDMS Justitia was a Royal Dano-Norwegian Navy ship-of-the-line, built to a design by Henrik Gerner. Although launched in 1777, she was not fully commissioned until 1780. The British Royal Navy seized her in 1807, together with the rest of the Danish fleet after the second battle of Copenhagen. The British never commissioned Justitia. A renaming to Orford in 1809 was cancelled. She was broken up in 1817.

HDMS Justitia was a ship-of-the-line designed by Ole Judichaer built at Nyholm, Copenhagen for the Royal Danish-Norwegian Navy.

Edouard Suenson was a Danish vice admiral who was known for his participation in the First Schleswig War and Second Schleswig War where he was the main Danish commander at the Battle of Heligoland.

HDMS Slesvig (Sleswig) was a ship of the line of the Royal Danish Navy, which she served from 1725. In 1733, she was transferred to the new Danish Asiatic Company.


















