Related Research Articles

Aquarius is a constellation of the zodiac, between Capricornus and Pisces. Its name is Latin for "water-carrier" or "cup-carrier", and its old astronomical symbol is (♒︎), a representation of water. Aquarius is one of the oldest of the recognized constellations along the zodiac. It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It is found in a region often called the Sea due to its profusion of constellations with watery associations such as Cetus the whale, Pisces the fish, and Eridanus the river.
Mu Arae, often designated HD 160691, officially named Cervantessur-VAN-teez, is a main sequence G-type star approximately 50 light-years away from the Sun in the constellation of Ara. The star has a planetary system with four known extrasolar planets, three of them with masses comparable with that of Jupiter. Mu Arae c, the innermost, was the first hot Neptune or super-Earth discovered.
HD 330075 is a star in the southern constellation of Norma. It has a yellow hue and an apparent visual magnitude of 9.36, which makes it too faint to be seen with the naked eye – it is visible only with telescope or powerful binoculars. Parallax measurements provide a distance estimate of 148 light years from the Sun, and it is drifting further away with a radial velocity of 62 km/s. The star is estimated to have come as close as 111.5 light-years some 409 million years ago.
HD 179949 is a 6th magnitude star in the constellation of Sagittarius. It is a yellow-white dwarf, a type of star hotter and more luminous than our Sun. The star is located about 90 light years from Earth and might be visible under exceptionally good conditions to an experienced observer without technical aid; usually binoculars are needed.

OGLE-TR-10b is an extrasolar planet orbiting the star OGLE-TR-10.
HD 217107 b is an extrasolar planet approximately 65 light-years away from Earth in the constellation of Pisces. The planet was discovered orbiting the star HD 217107 approximately every seven days, classifying the planet as a hot Jupiter. Because of the planet's somewhat eccentric orbit, scientists were able to confirm another planet within the system.
HD 2638 b is a planet of the star HD 2638. It is a typical "hot Jupiter", a planet that orbits its parent star in a very tight "torch orbit". The distance to the star is less than 1/20 Earth's distance from the Sun. One orbital revolution lasts only about three and half days.

A super-Earth is an extrasolar planet with a mass higher than Earth's, but substantially below those of the Solar System's ice giants, Uranus and Neptune, which are 14.5 and 17 times Earth's, respectively. The term "super-Earth" refers only to the mass of the planet, and so does not imply anything about the surface conditions or habitability. The alternative term "gas dwarfs" may be more accurate for those at the higher end of the mass scale, although "mini-Neptunes" is a more common term.
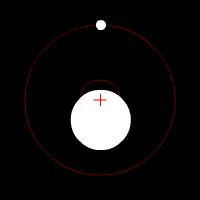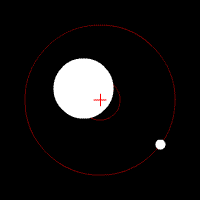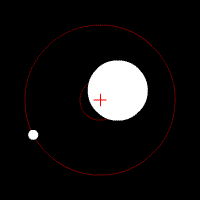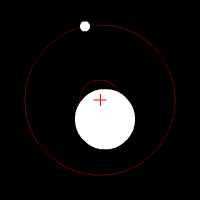
Doppler spectroscopy is an indirect method for finding extrasolar planets and brown dwarfs from radial-velocity measurements via observation of Doppler shifts in the spectrum of the planet's parent star.

HD 2039 is a yellow dwarf or yellow subgiant star in the constellation Phoenix. The star is not visible to the naked eye, and lies 280 light years away from the Sun. HD 2039 is a relatively stable star, and an exoplanet at least three times the mass of the planet Jupiter has been discovered in its orbit; this exoplanet, known as HD 2039 b, was the 100th exoplanet to be discovered.
HD 8574 b is an extrasolar planet discovered in 2001 by a team of European astronomers using Doppler spectroscopy as part of the ELODIE Planet Search Survey, and was published in a paper with five other planets. HD 8574 b is in the orbit of host star HD 8574. The planet is at most two times the mass of Jupiter, orbiting every 227 days at three quarters of the distance between the Earth and Sun. HD 8574 b has a very elliptical orbit, far more than that of Jupiter.
HD 93083 b is an extrasolar planet orbiting the K-type subgiant star HD 93083 in Antlia constellation. It is probably much less massive than Jupiter, although only the minimum mass is known. The planet's mean distance from the star is about half that of Earth, and the orbit is slightly eccentric. This planet is another discovery by the HARPS search team.
HD 47186 is a star located approximately 129 light-years away in the constellation of Canis Major. It is a G6V star with the characteristics very similar to the Sun, but it is 1.7 times more metal-rich. In 2008, two extrasolar planets were discovered orbiting the star.
HD 154672 is a yellow subgiant. It is about 65 parsecs away from the Sun that is larger than, but of a similar mass to, the Sun. However, HD 154672 is much older. The star is very metal-rich, which is one of the reasons why it was targeted for a planet search by the N2K Consortium, which discovered the gas giant planet HD 154672 b using Doppler Spectroscopy; the discovery was reported in October 2008. The N2K collaboration chose HD 154672 primarily because it aimed to discover the correlation between a star's metallicity and the mass of orbiting planets.
HD 154672 b is an extrasolar planet located approximately 210 light-years away in the constellation of Ara, orbiting the metal-rich and aged star HD 154672. This planet has a minimum mass five times that of Jupiter and orbits at about 60% the distance between the Earth to the Sun. Its orbit is very elliptical, which causes temperatures on the planet to vary significantly as it proceeds along its orbit. This planet was discovered in Las Campanas Observatory on September 5, 2008 using the radial velocity method. Along with HD 205739 b, the planets were the first to be discovered by the N2K Consortium using the Magellan Telescopes.
HD 205739 b is an extrasolar planet located approximately 350 light-years away
HD 153950 b is an extrasolar planet located approximately 162 light-years away. This planet was discovered on October 26, 2008 by Moutou et al. using the HARPS spectrograph on ESO's 3.6 meter telescope installed at La Silla Observatory in Atacama desert, Chile.
HD 215497 is a single star in the southern constellation of Tucana. It has an orange hue with an apparent visual magnitude of 8.96, which is too dim to be viewed with the naked eye. A 2015 survey ruled out the existence of any stellar companions at projected distances from 26 to 300 astronomical units. Based on parallax measurements, it is located at a distance of 132 light years from the Sun. The star is drifting further away with a radial velocity of +49 km/s, having come as close as 45 light-years some 774,000 years ago. The absolute magnitude of this star is 5.77.

An exoplanet is a planet located outside the Solar System. The first evidence of an exoplanet was noted as early as 1917, but was not recognized as such until 2016; no planet discovery has yet come from that evidence. What turned out to be the first detection of an exoplanet was published among a list of possible candidates in 1988, though not confirmed until 2003. The first confirmed detection came in 1992, with the discovery of terrestrial-mass planets orbiting the pulsar PSR B1257+12. The first confirmation of an exoplanet orbiting a main-sequence star was made in 1995, when a giant planet was found in a four-day orbit around the nearby star 51 Pegasi. Some exoplanets have been imaged directly by telescopes, but the vast majority have been detected through indirect methods, such as the transit method and the radial-velocity method. As of 1 July 2022, there are 5,108 confirmed exoplanets in 3,779 planetary systems, with 826 systems having more than one planet. This is a list of the most notable discoveries.
Kepler-39b, is a confirmed extrasolar object discovered orbiting the F-type star Kepler-39. It is eighteen times more massive than Jupiter, and is about five fourths its size. The planet orbits its host star at about 15% of the average distance between the Earth and Sun. Kepler-39b's host star was investigated by European astronomers along with three other stars, including the host star of Kepler-40b, using equipment at the Haute-Provence Observatory in France. Collection and analysis of data in late 2010 led to the confirmation of Kepler-39b. The discovery paper was published in a journal on June 6, 2011.
References
- 1 2 Pepe, F.; et al. (2004). "The HARPS search for southern extra-solar planets I. HD 330075 b: A new "hot Jupiter"". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 423 (1): 385–389. arXiv: astro-ph/0405252 . Bibcode:2004A&A...423..385P. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20040389.