
HMS Abelia was a Flower-class corvette that served in the Royal Navy and was built by Harland and Wolff in 1941.

HMS Penelope was an Arethusa-class light cruiser of the Royal Navy. She was built by Harland & Wolff ; her keel was laid down on 30 May 1934. She was launched on 15 October 1935, and commissioned 13 November 1936. She was torpedoed and sunk by German U-boat U-410 near Naples with great loss of life on 18 February 1944. On wartime service with Force K, she was holed so many times by bomb fragments that she acquired the nickname "HMS Pepperpot".

HMS Anchusa was a Flower-class corvette that served in the Royal Navy.

HMS Black Prince was a Dido-class light cruiser of the Royal Navy, of the Bellona subgroup. The cruiser was commissioned in 1943, and served during World War II on the Arctic convoys, during the Normandy landings, and as part of the British Pacific Fleet. In 1946, the cruiser was loaned to the Royal New Zealand Navy, becoming HMNZS Black Prince. The cruiser was docked for modernisation in 1947, but in April, her sailors walked off the ship as part of a series of mutinies in the RNZN. The shortage of manpower resulting from these mutinies meant that the modernisation had to be cancelled, and Black Prince was placed in reserve until 1953. She returned to service after refitting with simplified secondary armament with a single quad "pom pom" in Q position and eight Mk3 40mm Bofors guns. The ship was decommissioned again two years later, and returned to the Royal Navy in 1961. Black Prince did not re-enter service, and was towed from Auckland to Osaka for scrapping in 1962.
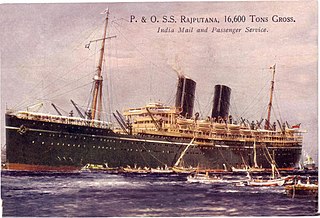
SS Rajputana was a British passenger and cargo carrying ocean liner. She was built for the Peninsular & Oriental Steam Navigation Company at the Harland and Wolff shipyard at Greenock on the lower River Clyde, Scotland in 1925. She was one of the P&O R-class liners from 1925 that had much of their interiors designed by Lord Inchcape's daughter Elsie Mackay. Named after the Rajputana region of western India, she sailed on a regular route between England and British India.

Vasilissa Olga was the second and last destroyer of her class built for the Royal Hellenic Navy in Great Britain before the Second World War. She participated in the Greco-Italian War in 1940–1941, escorting convoys and unsuccessfully attacking Italian shipping in the Adriatic Sea. After the German invasion of Greece in April 1941, the ship escorted convoys between Egypt and Greece until she evacuated part of the government to Crete later that month and then to Egypt in May. After the Greek surrender on 1 June, Vasilissa Olga served with British forces for the rest of her career.

The Shoreham-class sloops were a class of eight warships of the Royal Navy built in the early 1930s.

HMS Ceres was a C-class light cruiser of the Royal Navy. She was the name ship of the Ceres group of the C-class of cruisers.

HMS Mallow was a Flower-class corvette commissioned into the Royal Navy that served as a convoy escort during World War II; with the Royal Navy in 1940–1944, and with the Royal Yugoslav Navy-in-exile in 1944–1945. In Yugoslav service she was renamed Nada. Her main armament was a single 4-inch (102 mm) Mk IX naval gun, although a significant number of secondary and anti-aircraft guns were added towards the end of the war. During the war she escorted a total of 80 convoys whilst in British service, sinking one German U-boat, and escorted another 18 convoys whilst in Yugoslav service. After the war she served in the fledgling Yugoslav Navy as Nada then Partizanka, before being returned to the Royal Navy in 1949. Later that year she was transferred to the Egyptian Navy in which she served as El Sudan until she was decommissioned in 1975.

HMS Bryony was a Flower-class corvette that served in the Royal Navy and Royal Norwegian Navy.

HMS Peony was a Flower-class corvette of the Royal Navy. In 1943 she was transferred to the Royal Hellenic Navy as RHNS Sachtouris, serving throughout World War II and the Greek Civil War. She was returned to the Royal Navy in 1951 and scrapped in April 1952.
HMS Arabis was a Flower-class corvette of the Royal Navy. The ship was commissioned into the Royal Navy as HMS Arabis. She was transferred to the United States Navy in 1942, serving as USS Saucy. Returned to the United Kingdom in 1945, she was recommissioned into the Royal Navy as HMS Snapdragon.

HMS Hyacinth was a Flower-class corvette of the Royal Navy. She served during the Second World War and achieved three victories over enemy submarines in a highly successful career. Only Sunflower managed to repeat such success among her sister ships. She went on to serve in the Royal Hellenic Navy as RHNS Apostolis, was returned to the Royal Navy in 1952 and scrapped in the same year.
HMS Royal Scotsman, originally the MV Royal Scotsman, was an LSI of the British Royal Navy that served during World War II. A former passenger ferry, she saw action in the Mediterranean during the invasions of North Africa, Sicily and Italy. It was later purchased in 1967 by the Church of Scientology and renamed the MV Apollo, and became the headquarters of the Church of Scientology, the founding flagship of the Sea Org, and the personal residence of L. Ron Hubbard until 1975.
HMS Calendula was a Flower-class corvette, built for the Royal Navy during the Second World War, and was in service in the Battle of the Atlantic. In 1942 she was transferred to the United States Navy as part of the reverse Lend Lease arrangement and renamed USS Ready, one of the Temptress-class gunboats. With the end of hostilities she was returned to the Royal Navy and sold into mercantile service.

HMS Hurworth was a Second World War Type II Hunt-class escort destroyer of the British Royal Navy. She spent most of her career in the Mediterranean. She was lost to a mine in the Aegean Sea in 1943.

HMS Rhododendron was a Flower-class corvette that served with the Royal Navy during the Second World War. She served as an ocean escort in the Battle of the Atlantic.

HMS Alisma was a Flower-class corvette that served in the Royal Navy.

HMS Dunvegan Castle was a UK ocean liner that was converted into an armed merchant cruiser (AMC) in the Second World War. Harland and Wolff built her and her sister ship Dunnottar Castle in Belfast in 1936.
HMS Erica was a Flower-class corvette that served in the Royal Navy and was built by Harland and Wolff in 1941. She was named after Erica. Commissioned in 1940 and sunk by a mine on 9 February 1943.
















