
Annibal was a 74-gun ship of the line of the French Navy, lead ship of her class. She was designed by Jacques-Noël Sané, and was one of the earliest of his works. She was built at Brest in 1778.
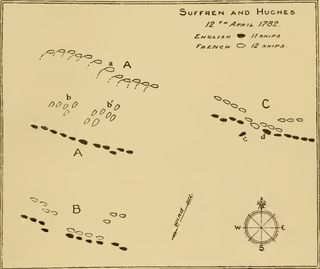
The Battle of Providien was the second in a series of naval battles fought between a British fleet, under Vice-Admiral Sir Edward Hughes, and a French fleet, under the Bailli de Suffren, off the coast of India during the Anglo-French War. The battle was fought on 12 April 1782 off the east coast of Ceylon, near a rocky islet called Providien, south of Trincomalee.

The Battle of Negapatam was the third in a series of battles fought between a British fleet, under Vice-Admiral Sir Edward Hughes, and a French fleet, under the Bailli de Suffren, off the coast of India during the American Revolutionary War. The battle was fought on 6 July 1782. Though the battle was indecisive, Suffren was stopped in his goal by Hughes and withdrew to Cuddalore, while the British remained in control of Negapatam.

The Battle of Trincomalee was fought between a British fleet under Vice-Admiral Sir Edward Hughes and a French fleet under the Bailli de Suffren off the coast of Trincomalee, then Ceylon, on 3 September 1782. It was the fourth in a series of battles fought between the two fleets off the coast of the Indian subcontinent during the American Revolutionary War.
James Alms was an officer of the Royal Navy who saw service during the War of the Austrian Succession, the Carnatic and Seven Years' War and the American War of Independence, rising to the rank of post-captain.

HMS Superb was a 74-gun Bellona-class third-rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy, designed by Sir Thomas Slade and built by Adam Hayes at Deptford Dockyard, launched on 27 October 1760 as a sister ship to HMS Dragon.
HMS Exeter was a 64-gun third rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy, launched on 26 July 1763 at Chatham Dockyard.

HMS Sultan was a 74-gun third rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy, launched on 23 December 1775 at Harwich. Built to take part in the American Revolutionary War, her departure was delayed due to a shortage of crew and it was 9 June 1778 before she finally sailed as part of a squadron led by Rear-Admiral John Byron. In September she was with Richard Howe's fleet, blockading the French in Boston and in 1779, transferred to the West Indies, where she took part in the Battle of Grenada that July. Almost a year later, on 20 June 1780, she was involved in a short action off the coast of the Dominican Republic with a superior French force.

HMS Monmouth was an Intrepid-class 64-gun third rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy, built by Israel Pownoll and launched on 18 April 1772 at Plymouth. Being relatively compact in relation to her gun power, she was affectionately known as the "Little Black Ship".
Admiral Robert Montagu was a Royal Navy officer who became Commander-in-Chief of the Jamaica Station.

Sphinx was a two-deck 64 gun ship of the French Navy. She was built at Brest to plans by Ollivier Fils and launched in 1776. She took the name of a recently retired 64-gun ship with the same dimensions. She fought in the American War of Independence, most notably in Suffren's campaign in the Indian Ocean.

Armand de Saint-Félix was a French Navy officer and admiral.
Bernard-Marie Boudin de Tromelin was a French Navy officer.
The action of 12 August 1782 was a minor single-ship action that opposed the French 32-gun frigate Bellone to the British 28-gun HMS Coventry in the run-up to the Battle of Trincomalee. Although both ships were frigates, Bellone belonged to the Iphigénie class and was a comparatively large frigate for her time, carrying a battery of 18-pounder long guns, while Coventry was a sixth-rate armed only with 9-pounder long guns. Furthermore, Bellone had the advantage of the wind. The nominal crew of Coventry was about tho thirds of that of Bellone, but in the occasion it was reinforced by the troops she was carrying. In spite of these overwhelming odds, Coventry managed to inflict heavy casualties on Bellone, and most decisively to shoot most of the senior staff. The resulting confusion on Bellone allowed Coventry to escape to Madras.
René Joseph Bouvet de Précourt was a French Navy officer. He was captain of the 64-gun Ajax in Suffren's squadron in the Indian Ocean during the War of American Independence, and fought at the Battle of Sadras on 17 February 1782.
Jean Baptiste Christy de La Pallière was a French Navy officer. He notably he captained the 74-gun Orient at the Battle of Sadras on 17 February 1782, at the Battle of Providien on 12 April 1782, at the Battle of Negapatam on 6 July 1782, and at the Battle of Trincomalee from 25 August to 3 September 1782.
Anne René Augustin de Roscanvec de La Landelle was a French Navy officer. He notably captained the 64-gun Bizarre at the Battle of Sadras on 17 February 1782, at the Battle of Providien on 12 April 1782, at the Battle of Negapatam on 6 July 1782, and at the Battle of Trincomalee from 25 August to 3 September 1782.
Charles Gaspard Hyacinthe de Forbin La Barben was a French Navy officer. He fought in the Indian Ocean under Suffren during the War of American Independence, captaining the 64-gun Vengeur at the Battle of Porto Praya on 16 April 1781, the Battle of Sadras on 17 February 1782, the Battle of Providien on 12 April 1782, the Battle of Negapatam on 6 July 1782, and the Battle of Trincomalee from 25 August to 3 September 1782. He was one of the officers that Suffren dismissed in the wake of the Battle of Trincomalee.
Félix d'Hesmivy de Moissac was a French Navy officer. He fought in the War of American Independence, earning a founding membership in the Society of the Cincinnati, and taking part in the French operations in the Indian Ocean as Suffren's flag captain.
François-Josué de la Corne de Chapt (1750–1800) was a Canadian who served as an officer in the French Navy. He served in the War of American Independence.







