
HMS Quorn was a Hunt-class destroyer of the Royal Navy, built in 1940 and sunk off the Normandy coast on 3 August 1944. The class were named after British fox and stag hunts, in this case, the Quorn Hunt, predominantly based in Leicestershire.

HMS Quail was a Q-class destroyer of the Royal Navy. She served during the Second World War but her career lasted less than a year before she was damaged by a mine and withdrawn from active service.

HMS Tynedale was a Hunt-class destroyer of the first subgroup which served during the Second World War. She was sunk by the U-593 on 12 December 1943.

HMS Mendip (L60) was a Hunt-class destroyer of the Royal Navy. She was a member of the first subgroup of the class. The ship is notable for seeing service in the navies of three other nations after her use by the Royal Navy. She saw service in the Second World War and later as an Egyptian Navy ship in the Suez Crisis. She was captured in battle on 31 October 1956 by the Israeli Navy and re-commissioned as INS Haifa (K-38).

HMS Brecon was a Hunt-class destroyer of the Royal Navy that saw service in the Second World War, one of two ships in the fourth subgroup of the class, built to a radically different design from other ships in the Hunt class.

The second HMS Hambledon was a Hunt-class destroyer of the Royal Navy in commission from 1940 to 1945. She was a member of the first subgroup of the class, and saw service throughout World War II.
HMS Blencathra (L24) was a Hunt-class destroyer of the Royal Navy in commission from 1940 to 1948. She was a member of the first subgroup of the class, and saw service through most of World War II.

The second HMS Exmoor (L08), ex-HMS Burton, was a Hunt-class destroyer of the Royal Navy in commission from 1941 to 1945. She was a member of the second subgroup of the class, and saw service during much of World War II. She later served in the Royal Danish Navy as HDMS Valdemar Sejr.

HMS Vesper was a V-class destroyer of the British Royal Navy that saw service in World War I and World War II.

HMS Vivacious (D36) was a V-class destroyer of the British Royal Navy that saw service in World War I and World War II.

HMS Vanquisher (D54) was a V-class destroyer of the British Royal Navy that saw service in World War I and World War II.

HMS Versatile (D32) was an Admiralty V-class destroyer of the British Royal Navy that saw service in World War I, the Russian Civil War, and World War II.

HMS Watchman was a W-class destroyer of the British Royal Navy that saw service in the final months of World War I, in the Russian Civil War, and in World War II.

The third HMS Windsor (D42) was a W-class destroyer of the British Royal Navy that saw service in the final months of World War I and in World War II.

HMS Wolsey (D98) was a W-class destroyer of the British Royal Navy that saw service in the final months of World War I, in the Nanking incident of 1927, and in World War II.

The second HMS Wivern, was a Modified W-class destroyer of the British Royal Navy that saw service in World War II.

The eighth HMS Worcester, was a Modified W-class destroyer of the British Royal Navy that saw service in World War II. She later served as an accommodation ship as the second HMS Yeoman.

HMS Berkeley was a Type I Hunt-class destroyer of the Royal Navy. She was a member of the first subgroup of the Hunt class and saw service in World War II before being bombed at Dieppe and then scuttled by HMS Albrighton.
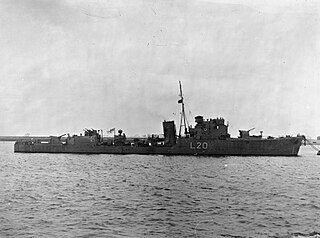
HMS Garth was a Type I Hunt-class destroyer of the Royal Navy built by John Brown & Company on the River Clyde, and launched on 28 December 1939. She was adopted by the Civil Community of Wokingham, Berkshire, as part of the Warship Week campaign in 1942.

HMS Cottesmore was a Hunt-class destroyer of the British Royal Navy. The ship was built by the Scottish shipbuilder Yarrow at their Scotstoun, Glasgow shipyard in 1939–1940, being launched on 5 September 1940 and commissioning on 29 December that year.



















