
HMS Mercury was one of two Iris-class despatch vessels, later redesignated as second class cruiser built for the Royal Navy during the 1870s. The two ships were the first all-steel warships in the Royal Navy.
The Amazon class was a class of six screw sloops of wooden construction built for the Royal Navy between 1865 and 1866.

The Satellite class was a class of 12-gun composite sloops built for the Royal Navy between 1883 and 1888, and reclassified as corvettes in 1884.
HMS Arabis was a Flower-class corvette of the Royal Navy. The ship was commissioned into the Royal Navy as HMS Arabis. She was transferred to the United States Navy in 1942, serving as USS Saucy. Returned to the United Kingdom in 1945, she was recommissioned into the Royal Navy as HMS Snapdragon.

HMS Sapphire was an Amethyst-class corvette built for the Royal Navy at Devonport Dockyard and launched on 24 September 1874.

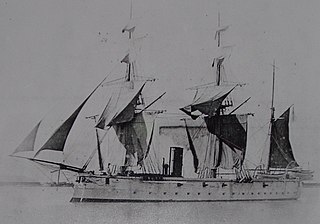
HMS Diamond was an Amethyst-class corvette in service 1874–89.

HMS Encounter was an Amethyst-class corvette built for the Royal Navy in the early 1870s.

The Amethyst-class corvettes were a class of the last wooden warships to be built for the British Royal Navy; each was built at a Royal Dockyard. Three were ordered under the 1871–72 Programme and two under the 1872–73 Programme. Built in the early and middle 1870s, they mostly served overseas and were retired early as they were regarded as hopelessly obsolete by the late 1880s. She served alongside HMS Shah in the action against the Peruvian warship Huascar on 29th May 1877.

The Plover-class gunvessels were a class of wooden gunboats built for the Royal Navy in the late 1860s. They mostly served overseas and were retired early as they were regarded as hopelessly obsolete by the late 1880s.
HMS Osprey was an Osprey-class sloop built for the Royal Navy in the mid-1870s.

HMS Albatross was a 4-gun Fantome-class sloop built for the Royal Navy in the mid-1870s.

HMS Fantome was the lead ship of the Fantome-class sloops built for the Royal Navy in the mid-1870s.

The Emerald-class corvettes were a class of six composite screw corvettes built for the Royal Navy in the mid-1870s. The Opal was built by contract under the 1873-74 Programme, and Turquoise, Ruby, Tourmaline and Emerald under the 1874-75 Programme - the first three also by contract, while Emerald was dockyard-built at Pembroke. The final ship (Garnet) was also dockyard-built at Chatham under the 1875-76 Programme.

HMCS Mimico was a modified Flower-class corvette that served with the Royal Canadian Navy during the Second World War. She served primarily as a convoy escort in the Battle of the Atlantic. She was originally laid down by the Royal Navy as HMS Bullrush but was never commissioned into the RN, being transferred to the RCN before completion. She is named for Mimico, Ontario, a town that was eventually amalgamated into the larger city Toronto, Ontario.
HMS Oxlip was a Flower-class corvette that served in the Royal Navy during World War II.

HMS Borage was a Flower-class corvette that served in the Royal Navy during World War II.
HMS Daphne was a Nymphe-class composite screw sloop and the fifth ship of the Royal Navy to bear the name. Developed and constructed for the Royal Navy on a design by William Henry White, Director of Naval Construction, she was launched at Sheerness Dockyard on 29 May 1888. It was the first command of Admiral Sir William Christopher Pakenham, KCB, KCMG, KCVO.
HMS Snapdragon was a Flower-class corvette that served in the Royal Navy and was built by Smith's Dock Company in 1940. She was named after Snapdragon. Commissioned in 1940 and sunk by Luftwaffe on 19 December 1942.
HMS Auricula was a Flower-class corvette that served in the Royal Navy and was built by George Brown and Company in 1940. She was named after Auricula. Commissioned in 1941 and sunk by a mine on 6 May 1942.

HMS Gardenia was a Flower-class corvette that served in the Royal Navy and was built by William Simons and Company in 1940. She was named after Gardenia. Commissioned in 1940, rammed and sunk by HMS Fluellen on 9 November 1942.














