
In naval terminology, a destroyer is a fast, maneuverable, long-endurance warship intended to escort larger vessels in a fleet, convoy, or carrier battle group and defend them against a wide range of general threats. They were originally conceived in 1885 by Fernando Villaamil for the Spanish Navy as a defense against torpedo boats, and by the time of the Russo-Japanese War in 1904, these "torpedo boat destroyers" (TBDs) were "large, swift, and powerfully armed torpedo boats designed to destroy other torpedo boats". Although the term "destroyer" had been used interchangeably with "TBD" and "torpedo boat destroyer" by navies since 1892, the term "torpedo boat destroyer" had been generally shortened to simply "destroyer" by nearly all navies by the First World War.

A torpedo boat is a relatively small and fast naval ship designed to carry torpedoes into battle. The first designs were steam-powered craft dedicated to ramming enemy ships with explosive spar torpedoes. Later evolutions launched variants of self-propelled Whitehead torpedoes.
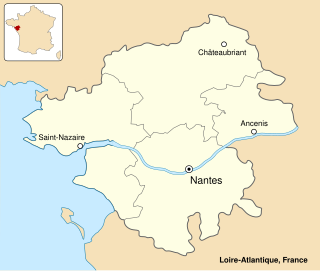
The St Nazaire Raid or Operation Chariot was a British amphibious attack on the heavily defended Normandie dry dock at St Nazaire in German-occupied France during the Second World War. The operation was undertaken by the Royal Navy (RN) and British Commandos under the auspices of Combined Operations Headquarters on 28 March 1942. St Nazaire was targeted because the loss of its dry dock would force any large German warship in need of repairs, such as Tirpitz, sister ship of Bismarck, to return to home waters by running the gauntlet of the Home Fleet of the Royal Navy and other British forces, via the English Channel or the North Sea.

A warship or combatant ship is a ship that is built and primarily intended for naval warfare. Usually they belong to the armed forces of a nation. As well as being armed, warships are designed to withstand damage and are typically faster and more maneuverable than merchant ships. Unlike a merchant ship, which carries cargo, a warship typically carries only weapons, ammunition and supplies for its crew. Warships usually belong to a navy, though they have also been operated by individuals, cooperatives and corporations.

HMS Kingston was a K-class destroyer of the Royal Navy.

Portland Harbour is located beside the Isle of Portland, Dorset, on the south coast of England. Construction of the harbour began in 1849; when completed in 1872, its 520-hectare (1,300-acre) surface area made it the largest human-made harbour in the world, and it remains one of the largest in the world today. It is naturally sheltered by Portland to the south, Chesil Beach to the west and mainland Dorset to the north. It consists of four breakwaters: two southern and two northern. These have a total length of 4.57 km (2.84 mi) and enclose approximately 1,000 ha of water.

HMS Sceptre (P215) was a third-batch S-class submarine built for the Royal Navy during World War II. Completed in April 1943, she spent the majority of her career in the North Sea, off Norway. After an uneventful patrol, the submarine participated in Operation Source, an attack on German battleships in Norway using small midget submarines to penetrate their anchorages and place explosive charges. However, the midget submarine that she was assigned to tow experienced technical difficulties and the mission was aborted. During her next four patrols, Sceptre attacked several ships, but only succeeded in severely damaging one. She was then ordered to tow the submarine X24, which was to attack a floating dry dock in Bergen. The operation, codenamed Guidance, encountered difficulties with the attacking submarine's charts, and the explosives were laid on a merchant ship close to the dock instead. The dock was damaged and the ship sunk, and X24 was towed back to England. Sceptre then conducted a patrol in the Bay of Biscay, sinking two German merchant ships, before being reassigned to tow X24 to Bergen again. The operation was a success, and the dry dock was sunk.
Seven commissioned ships of the British Royal Navy have been named Bermuda and given the prefix HMS, after the British Overseas Territory and former Imperial fortress of Bermuda. Two other vessels operated by the Royal Navy that were not commissioned warships were also named Bermuda.

A motor torpedo boat is a fast torpedo boat, especially of the mid 20th century. The motor in the designation originally referred to their use of petrol engines, typically marinised aircraft engines or their derivatives, which distinguished them from other naval craft of the era, including other torpedo boats, that used steam turbines or reciprocating steam engines. Later, diesel-powered torpedo boats appeared, in turn or retroactively referred to as "motor torpedo boats" for their internal combustion engines, as distinct from steam powered reciprocating or turbine propulsion.

The Captain class was the designation given to 78 frigates of the Royal Navy, constructed in the United States, launched in 1942–1943 and delivered to the United Kingdom under the provisions of the Lend-Lease agreement. They were drawn from two classes of the American destroyer escort classification: 32 of the GMT (Evarts) Type and 46 of the TE (Buckley) Type. Upon reaching the UK the ships were substantially modified by the Royal Navy, making them distinct from the US Navy destroyer escort ships.

The British U-class submarines were a class of 49 small submarines built just before and during the Second World War. The class is sometimes known as the Undine class, after the first submarine built. A further development was the British V-class submarine of 1942.

A motor launch (ML) is a small military vessel in Royal Navy service. It was designed for harbour defence and submarine chasing. Similar vessels were used by the Royal Air Force for armed high-speed air-sea rescue. Some vessels for water police service are also known as motor launches. Motor launches were slower than motor torpedo boats and motor gun boats

HMS Vernon was a shore establishment or "stone frigate" of the Royal Navy in Portsmouth. Vernon was established on 26 April 1876, as the Royal Navy's Torpedo Branch also known as the Torpedo School, named after the ship HMS Vernon which served as part of its floating base. After the First World War, HMS Vernon moved ashore, taking over the Gunwharf site, where it continued to operate until 1 April 1996, when the various elements comprising the establishment were split up and moved to different commands.

Two Daring-class destroyers were the very first torpedo boat destroyers ("TBDs") to be ordered for the Royal Navy, the order being placed on 27 June 1892.

Coastal Forces was a division of the Royal Navy initially established during World War I, and then again in World War II under the command of Rear-Admiral, Coastal Forces. It remained active until the last minesweepers to wear the "HM Coastal Forces" cap tally were taken out of reserve in 1968. The division received more gallantry awards than any other branch of the Royal Navy during that period.

The Coastal Forces of the Royal Canadian Navy (RCN) was a specialized naval force of well-armed, small and fast motor launch (ML) and motor torpedo boat (MTB) flotillas, primarily manned by members of the Royal Canadian Naval Volunteer Reserve (RCNVR). Tasked with escort, coastal defence, anti-submarine, minesweeping and search and rescue duties, the Coastal Forces of the RCN contributed to securing Allied sea lines of communication off the coasts of Canada and Britain during the Second World War.

An armed yacht was a yacht that was armed with weapons and was typically in the service of a navy. The word "yacht" was originally applied to small, fast and agile naval vessels suited to piracy and to employment by navies and coast guards against smugglers and pirates. Vessels of this type were adapted to racing by wealthy owners. The origin of civilian yachts as naval vessels, with their speed and maneuverability, made them useful for adaptation to their original function as patrol vessels. In the United States Navy armed yachts were typically private yachts expropriated for government use in times of war. Armed yachts served as patrol vessels during the Spanish–American War and the World Wars. In the latter conflicts, armed yachts were used as patrol vessels, convoy escorts, and in anti-submarine duties. In the United States, yachts were purchased from their owners with the owners given an option to repurchase their yacht at the close of hostilities.

Corpach is a large village north of Fort William, in the Scottish Highlands. The canal lock at Corpach Basin on Loch Linnhe, east of the narrows leading to Loch Eil, is the western sea entrance of the Caledonian Canal. It is a natural harbour, unlike Fort William.

HMS Llewellyn was a Laforey-class destroyer that served with the Royal Navy. Laid down on 14 December 1912 as HMS Picton, the ship was renamed on 30 September 1913 under an Admiralty order to become one of the first alphabetical class destroyers, being launched on 30 October. On commissioning, the vessel joined the Third Destroyer Flotilla and operated as part of the Harwich Force during the First World War. The destroyer took part in the Battle of Heligoland Bight, as well as undertaking anti-submarine patrols and escort duties. It was during one of these patrols on 4 December 1916 that the vessel unsuccessfully attacked the German submarine UB-18. On 17 March 1917, the destroyer was struck in the bow by a torpedo launched by a German torpedo boat while rescuing survivors from the sunk destroyer Paragon, but returned to port safely by steaming backwards. With the cessation of hostilities, the ship was placed in reserve. Although subsequently offered for sale to the Finnish Navy, Llewellyn was instead withdrawn from service and sold to be broken up on 18 March 1922.


















