Nestorius was the Archbishop of Constantinople from 10 April 428 to August 431. A Christian theologian, several of his teachings in the fields of Christology and Mariology were seen as controversial and caused major disputes. He was condemned and deposed from his see by the Council of Ephesus, the third Ecumenical Council, in 431.

Divine Liturgy or Holy Liturgy is the Eucharistic service of the Byzantine Rite, developed from the Antiochene Rite of Christian liturgy which is that of the Ecumenical Patriarchate of Constantinople. As such, it is used in the Eastern Orthodox, the Byzantine Catholic Churches, and the Ukrainian Lutheran Church. Although the same term is sometimes applied in English to the Eucharistic service of Armenian Christians, both of the Armenian Apostolic Church and of the Armenian Catholic Church, they use in their own language a term meaning "holy offering" or "holy sacrifice". Other churches also treat "Divine Liturgy" simply as one of many names that can be used, but it is not their normal term.

The Assyrian Church of the East, sometimes called Church of the East, officially the Apostolic Catholic Assyrian Church of the East, is an Eastern Christian church that follows the traditional Christology and ecclesiology of the historical Church of the East. It belongs to the eastern branch of Syriac Christianity, and employs the Divine Liturgy of Saints Addai and Mari belonging to the East Syriac Rite. Its main liturgical language is Classical Syriac, a dialect of Eastern Aramaic, and the majority of its adherents are ethnic Assyrians.

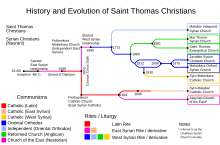
The Syro-Malabar Church is an Eastern Catholic church based in Kerala, India. The Syro-Malabar Church is an autonomous particular church in full communion with the pope and the worldwide Catholic Church, including the Latin Church and the 22 other Eastern Catholic Churches, with self-governance under the Code of Canons of the Eastern Churches (CCEO). The Church is headed by the Metropolitan and Gate of all India Major Archbishop Mar George Cardinal Alencherry. The Syro-Malabar Synod of Bishops canonically convoked and presided over by the Major Archbishop constitutes the supreme authority of the Church. The Major Archiepiscopal Curia of the Church is based in Kakkanad, Kochi. Syro-Malabar is a prefix coined from the words Syriac as the church employs the East Syriac Rite liturgy, and Malabar which is the historical name for modern Kerala. The name has been in usage in official Vatican documents since the nineteenth century. It is the second largest Eastern Catholic Church in the Catholic communion, after the Ukrainian Greek Catholic Church. The Syro-Malabar Church is primarily based in India; with 5 metropolitan archeparchies (archdioceses) and 10 suffragan eparchies in Kerala, there are 17 eparchies in other parts of India, and 4 eparchies outside India.

Theodore of Mopsuestia was a Christian theologian, and Bishop of Mopsuestia from 392 to 428 AD. He is also known as Theodore of Antioch, from the place of his birth and presbyterate. He is the best known representative of the middle School of Antioch of hermeneutics.

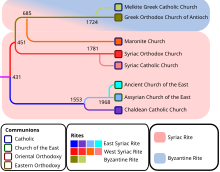
Syriac Christianity is a distinctive branch of Eastern Christianity, whose formative theological writings and traditional liturgies are expressed in Classical Syriac language, a variation of Aramaic language. In a wider sense, the term can also refer to Aramaic Christianity in general, thus encompassing all Christian traditions that are based on liturgical uses of Aramaic language and its variations, both historical and modern.

According to Eastern Christian tradition, Addai of Edessa or Thaddeus of Edessa was one of the seventy disciples of Jesus. He is possibly identical with Thaddaeus, one of the Twelve Apostles. From an early date his hagiography is filled with legends and fabrications. The saint himself may be entirely fictitious.

The Holy Qurbana, refers to the Eucharist as celebrated in East Syriac Christianity. This includes various descendants of the Church of the East. East Syriac Christianity consists of an Edessan liturgical rite, the East Syriac Rite. The major anaphora of the East Syriac tradition is the Holy Qurbana of Saints Addai and Mari; Addai being a disciple of Thomas the Apostle and Mari being Addai's disciple. The churches are primarily based in the Middle East and India, along with the diaspora communities settled in the western world.

The Anaphora is the most solemn part of the Divine Liturgy, or the Holy Sacrifice of the Mass, during which the offerings of bread and wine are consecrated as the body and blood of Christ. This is the usual name for this part of the Liturgy in Greek-speaking Eastern Christianity. In the Eastern Syriac tradition Qudaša is its equalent. In western Christian traditions which have a comparable rite, the Anaphora is more often called the Eucharistic Prayer for the four modern anaphoras in the Latin liturgy, with the first anaphora having the additional name of the Roman Canon. When the Roman Rite had a single Eucharistic Prayer, it was called the Canon of the Mass.

Alphabetical list of Eastern Christianity-related articles on English Wikipedia

The Chaldean Syrian Church of India is an Eastern Christian denomination, based in Thrissur, in India. It is organized as a metropolitan province of the Assyrian Church of the East, and represents traditional Christian communities of the East Syriac Rite along the Malabar Coast of India. It is headed by Mar Aprem Mooken, Metropolitan of India, who is in full communion with Patriarch Mar Awa III, head of the Assyrian Church of the East. Metropolitan is assisted by two Bishops, Mar Yohannan Yoseph, and Mar Awgin Kuriakose.

The West Syriac Rite, also called Syro-Antiochene Rite, is an Eastern Christian liturgical rite that employs the Divine Liturgy of Saint James in the West Syriac dialect. It is practised in the Maronite Church, the Syriac Orthodox Church, the Syriac Catholic Church and various Malankara Churches of India. It is one of two main liturgical rites of Syriac Christianity, the other being the East Syriac Rite.

Antiochene Rite or Antiochian Rite designates the family of liturgies originally used in the Patriarchate of Antioch.

The East Syriac Rite or East Syrian Rite, also called the Edessan Rite, Assyrian Rite, Persian Rite, Chaldean Rite, Nestorian Rite, Babylonian Rite or Syro-Oriental Rite, is an Eastern Christian liturgical rite that employs the Divine Liturgy of Saints Addai and Mari and the East Syriac dialect as its liturgical language. It is one of two main liturgical rites of Syriac Christianity, the other being the West Syriac Rite.

Aba I or Mar Abba the Great was the Patriarch of the Church of the East at Seleucia-Ctesiphon from 540 to 552. He introduced to the church the anaphoras of Theodore of Mopsuestia and Nestorius beside the more ancient liturgical rite of Addai and Mari. Though his tenure as catholicos saw Christians in the region threatened during the Persian-Roman wars and attempts by both Sassanid Persian and Byzantine rulers to interfere with the governance of the church, his reign is reckoned a period of consolidation, and a synod he held in 544 as instrumental in unifying and strengthening the church. In 544, the Synod of Mar Aba I adopted the ordinances of the Council of Chalcedon. He is thought to have written and translated a number of religious works. After his death in February 552, the faithful carried his casket from his simple home across the Tigris to the monastery of Mar Pithyon.

The Hallowing of Nestorius is one of the Eucharistic liturgies used in the Church of the East. It is currently employed in the Holy Qurbana of the Chaldean Catholic Church, Assyrian Church of the East, Ancient Church of the East, and the Syro-Malabar Church, which are descendants of the Church of the East. It is a part of the East Syriac Rite, formally attributed to Nestorius, Patriarch of Constantinople and is traditionally celebrated for the Feast of the Epiphany, Commemoration of St. John the Baptist, Commemoration of the Greek Teachers: Mar Diodore, Mar Theodore the interpreter and Mar Nestorius, and also for the Wednesday liturgy of the Rogation of the Ninevites, and the Feast of the Passover.

The Liturgy of Addai and Mari is the Eucharistic liturgy belonging to the East Syriac Rite and was historically used in the Church of the East of the Sasanian (Persian) Empire. This liturgy is traditionally attributed to Saint Addai and Saint Mari. It is currently in regular use in the Assyrian Church of the East of Iraq, the Ancient Church of the East of Iraq, the Syro-Malabar Church of India, and the Chaldean Catholic Church of Iraq. The latter two are Eastern Catholic churches in full communion with the Holy See of Rome.

Several historical evidences shed light on a significant Malankara–Persian ecclesiastical relationship that spanned centuries. While an ecclesiastical relationship existed between the Saint Thomas Christians of India and the Church in Sassanid Empire in the earlier centuries, closer ecclesiastical ties developed as early as seventh century, when India became an ecclesiastical province of the Church of the East, albeit restricted to matters of purely ecclesiastical nature such as ordination of priests, and not involved in matters of temporal administration. This relationship endured until the Portuguese protectorate of Cochin of Malabar came to be in 16th century, and the Portuguese discovery of a sea route to India. The Christians who came under the two ancient yet distinct lineages of Malankara and Persia had one factor in common: their Saint Thomas heritage. The Church of the East shared communion with the Great Church until the Council of Ephesus in the 5th century, separating primarily over differences in Christology.
Holy Leaven, also known as Malka, is a powder added to the sacramental bread used in the Eucharist of both the Ancient Church of the East and the Assyrian Church of the East and historically in the Church of the East. Both churches hold the Holy Leaven to be one of their seven sacraments. The Syro-Malabar Church in India, which was historically a part of the Church of the East, also uses Holy Leaven to prepare sacramental bread in several churches whereas unleavened bread is also in use. There are two rituals associated with the Holy Leaven: its addition to sacramental bread before it is baked, and the annual renewal of the Holy Leaven itself.

The Holy Qurobo or Holy Qurbono, also called Qurobo Alohoyo, refers to the Eucharist as celebrated in Syro-Antiochene Rite. Some of the West Syrian Rite Churches in India often refer the Eucharist as Holy Qurbana. West Syriac Rite includes various descendants of the Oriental Orthodox and Eastern Catholic churches. It consists of two distinct liturgical traditions: the Maronite Rite, and the Jacobite Rite. The major Anaphora of both the traditions is the Divine Liturgy of Saint James in Syriac language. The Churches are primarily based in the Middle East, Africa, and India.