Related Research Articles

An ecoregion or ecozone is an ecologically and geographically defined area that is smaller than a bioregion, which in turn is smaller than a biogeographic realm. Ecoregions cover relatively large areas of land or water, and contain characteristic, geographically distinct assemblages of natural communities and species. The biodiversity of flora, fauna and ecosystems that characterise an ecoregion tends to be distinct from that of other ecoregions. In theory, biodiversity or conservation ecoregions are relatively large areas of land or water where the probability of encountering different species and communities at any given point remains relatively constant, within an acceptable range of variation.

Soil science is the study of soil as a natural resource on the surface of the Earth including soil formation, classification and mapping; physical, chemical, biological, and fertility properties of soils; and these properties in relation to the use and management of soils.

Silt is granular material of a size between sand and clay, whose mineral origin is quartz and feldspar. Silt may occur as a soil or as sediment mixed in suspension with water and soil in a body of water such as a river. It may also exist as soil deposited at the bottom of a water body, like mudflows from landslides. Silt has a moderate specific area with a typically non-sticky, plastic feel. Silt usually has a floury feel when dry, and a slippery feel when wet. Silt can be visually observed with a hand lens, exhibiting a sparkly appearance. It also can be felt by the tongue as granular when placed on the front teeth.

A biogeographic realm or ecozone is the broadest biogeographic division of Earth's land surface, based on distributional patterns of terrestrial organisms. They are subdivided into ecoregions, which are classified based on their biomes or habitat types.

Soil classification deals with the systematic categorization of soils based on distinguishing characteristics as well as criteria that dictate choices in use.
A soil horizon is a layer parallel to the soil surface whose physical, chemical and biological characteristics differ from the layers above and beneath. Horizons are defined in many cases by obvious physical features, mainly colour and texture. These may be described both in absolute terms and in terms relative to the surrounding material, i.e. ‘coarser’ or ‘sandier’ than the horizons above and below.

In the geosciences, paleosol can have two meanings. The first meaning, common in geology and paleontology, refers to a former soil preserved by burial underneath either sediments or volcanic deposits, which in the case of older deposits have lithified into rock. In Quaternary geology, sedimentology, paleoclimatology, and geology in general, it is the typical and accepted practice to use the term "paleosol" to designate such "fossil soils" found buried within sedimentary and volcanic deposits exposed in all continents as illustrated by Retallack (2001), Kraus (1999), and other published papers and books.
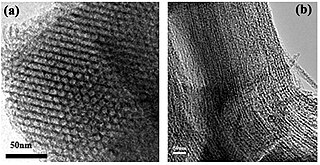
A mesoporous material is a material containing pores with diameters between 2 and 50 nm, according to IUPAC nomenclature. For comparison, IUPAC defines microporous material as a material having pores smaller than 2 nm in diameter and macroporous material as a material having pores larger than 50 nm in diameter.

Nathan Mortimore Newmark was an American structural engineer and academic, who is widely considered as one of the founding fathers of Earthquake Engineering. He was awarded the National Medal of Science for engineering.
Soil texture is a classification instrument used both in the field and laboratory to determine soil classes based on their physical texture. Soil texture can be determined using qualitative methods such as texture by feel, and quantitative methods such as the hydrometer method. Soil texture has agricultural applications such as determining crop suitability and to predict the response of the soil to environmental and management conditions such as drought or calcium (lime) requirements. Soil texture focuses on the particles that are less than two millimeters in diameter which include sand, silt, and clay. The USDA soil taxonomy and WRB soil classification systems use 12 textural classes whereas the UK-ADAS system uses 11. These classifications are based on the percentages of sand, silt, and clay in the soil.

Soil series as established by the National Cooperative Soil Survey of the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) Natural Resources Conservation Service are a level of classification in the USDA Soil Taxonomy classification system hierarchy. The actual object of classification is the so-called soil individual, or pedon. Soil series consist of pedons that are grouped together because of their similar pedogenesis, soil chemistry, and physical properties. More specifically, each series consists of pedons having soil horizons that are similar in soil color, soil texture, soil structure, soil pH, consistence, mineral and chemical composition, and arrangement in the soil profile. These result in soils which perform similarly for land use purposes.
The history of phycology is the history of the scientific study of algae. Human interest in plants as food goes back into the origins of the species and knowledge of algae can be traced back more than two thousand years. However, only in the last three hundred years has that knowledge evolved into a rapidly developing science.
The early concepts of soil were based on ideas developed by a German chemist, Justus von Liebig (1803–1873), and modified and refined by agricultural scientists who worked on samples of soil in laboratories, greenhouses, and on small field plots. The soils were rarely examined below the depth of normal tillage. These chemists held the "balance-sheet" theory of plant nutrition. Soil was considered a more or less static storage bin for plant nutrients—the soils could be used and replaced. This concept still has value when applied within the framework of modern soil science, although a useful understanding of soils goes beyond the removal of nutrients from soil by harvested crops and their return in manure, lime, and fertilizer.
The Australian Soil Classification is the classification system currently used to describe and classify soils in Australia. It is a general-purpose, hierarchical classification system, and consists of five categorical levels from the most general to the most specific: order, suborder, great group, subgroup, and family. An interactive, online key is available. The Australian Soil Classification supersedes other classification systems previously developed for Australian soils, including the Factual Key (1960) and the Handbook of Australian Soils (1968).

Terra rossa is a well-drained, reddish, clayey to silty clayey soil with neutral pH conditions and is typical of the Mediterranean region. The reddish color of terra rossa is the result of the preferential formation of hematite over goethite. This soil type typically occurs as a discontinuous layer that ranges from a few centimeters to several meters in thickness that covers limestone and dolomite bedrock in karst regions. The high internal drainage and neutral pH conditions of terra rossa are a result of the karstic nature of the underlying limestone and dolomite. Terra rossa is also found associated with Mediterranean climates and karst elsewhere in the world.
James Arthur Prescott, CBE, FRS, was an agricultural scientist.

Protozoa is an informal term for a group of single-celled eukaryotes, either free-living or parasitic, which feed on organic matter such as other microorganisms or organic tissues and debris. Historically, protozoans were regarded as "one-celled animals", because they often possess animal-like behaviours, such as motility and predation, and lack a cell wall, as found in plants and many algae. Although the traditional practice of grouping protozoa with animals is no longer considered valid, the term continues to be used in a loose way to describe single-celled protists that feed by heterotrophy. Some examples of protozoa are Amoeba, Paramecium, Euglena and Trypanosoma.
John Robert Victor Prescott FASSA was a British and Australian academic, author, and professor emeritus at the University of Melbourne. A political geographer, most of Prescott's work focused on international boundary issues, particularly maritime boundaries.
The term “duplex” is used in Australia for soils with contrasting texture between soil horizons, although such soils are found in other parts of the world. Duplex soils are also termed “texture contrast soils”.
References
- ↑ Stace, H.C.T.; Hubble, G.D.; Brewer, R.; Northcote, K.H.; Sleeman, J.R.; Mulcahy, M.J.; Hallsworth, E.G. (1968). A Handbook of Australian Soils. Glenside, South Australia: Rellim Technical Publications.
- ↑ Prescott, James A. (1931). The soils of Australia in relation to vegetation and climate. Bulletin No. 52. Australian Council of Scientific and Industrial Research.
| | This soil science–related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |