In music theory, a diatonic scale is any heptatonic scale that includes five whole steps and two half steps (semitones) in each octave, in which the two half steps are separated from each other by either two or three whole steps, depending on their position in the scale. This pattern ensures that, in a diatonic scale spanning more than one octave, all the half steps are maximally separated from each other.
In music, a glissando is a glide from one pitch to another. It is an Italianized musical term derived from the French glisser, "to glide". In some contexts, it is distinguished from the continuous portamento. Some colloquial equivalents are slide, sweep, bend, smear, rip, lip, plop, or falling hail.
The harmonica, also known as a French harp or mouth organ, is a free reed wind instrument used worldwide in many musical genres, notably in blues, American folk music, classical music, jazz, country, and rock. The many types of harmonica include diatonic, chromatic, tremolo, octave, orchestral, and bass versions. A harmonica is played by using the mouth to direct air into or out of one holes along a mouthpiece. Behind each hole is a chamber containing at least one reed. The most common is the diatonic Richter-tuned with ten air passages and twenty reeds, often called the blues harp. A harmonica reed is a flat, elongated spring typically made of brass, stainless steel, or bronze, which is secured at one end over a slot that serves as an airway. When the free end is made to vibrate by the player's air, it alternately blocks and unblocks the airway to produce sound.
In music theory, the key of a piece is the group of pitches, or scale, that forms the basis of a musical composition in classical, Western art, and Western pop music.
Tonality or key: Music which uses the notes of a particular scale is said to be "in the key of" that scale or in the tonality of that scale.

A pitch pipe is a small device used to provide a pitch reference for musicians. Although it may be described as a musical instrument, it is not typically used to play music as such. Technically, it is a harmonica; however, it lacks many characteristics of harmonicas.
A jazz scale is any musical scale used in jazz. Many "jazz scales" are common scales drawn from Western European classical music, including the diatonic, whole-tone, octatonic, and the modes of the ascending melodic minor. All of these scales were commonly used by late nineteenth and early twentieth-century composers such as Rimsky-Korsakov, Debussy, Ravel and Stravinsky, often in ways that directly anticipate jazz practice. Some jazz scales, such as the bebop scales, add additional chromatic passing tones to the familiar diatonic scales.
Chris "Buddha" Michalek was an American harmonica player.
Overblowing is the manipulation of supplied air through a wind instrument that causes the sounded pitch to jump to a higher one without a fingering change or the operation of a slide. Overblowing may involve a change in the air pressure, in the point at which the air is directed, or in the resonance characteristics of the chamber formed by the mouth and throat of the player.

A mouth organ is any free reed aerophone with one or more air chambers fitted with a free reed. Though it spans many traditions, it is played universally the same way by the musician placing their lips over a chamber or holes in the instrument, and blowing or sucking air to create a sound. Many of the chambers can be played together or each individually.
Chromaticism is a compositional technique interspersing the primary diatonic pitches and chords with other pitches of the chromatic scale. Chromaticism is in contrast or addition to tonality or diatonicism and modality. Chromatic elements are considered, "elaborations of or substitutions for diatonic scale members".
Not only at the beginning of a composition but also in the midst of it, each scale-step [degree] manifests an irresistible urge to attain the value of the tonic for itself as that of the strongest scale-step. If the composer yields to this urge of the scale-step within the diatonic system of which this scale-step forms part, I call this process tonicalization and the phenomenon itself chromatic.
Chromaticism is almost by definition an alteration of, an interpolation in or deviation from this basic diatonic organization.
Throughout the nineteenth century, composers felt free to alter any or all chord members of a given tertian structure [chord built from thirds] according to their compositional needs and dictates. Pronounced or continuous chordal alteration [and 'extension'] resulted in chromaticism. Chromaticism, together with frequent modulations and an abundance of non-harmonicism [non-chord tones], initially effected an expansion of the tertian system; the overuse of the procedures late in the century forewarned the decline and near collapse [atonality] of the system [tonality].
Chromaticism is the name given to the use of tones outside the major or minor scales. Chromatic tones began to appear in music long before the common-practice period, and by the beginning of that period were an important part of its melodic and harmonic resources. Chromatic tones arise in music partly from inflection [alteration] of scale degrees in the major and minor modes, partly from secondary dominant harmony, from a special vocabulary of altered chords, and from certain nonharmonic tones... Notes outside the scale do not necessarily affect the tonality...tonality is established by the progression of roots and the tonal functions of the chords, even though the details of the music may contain all the tones of the chromatic scale.
Sometimes...a melody based on a regular diatonic scale is laced with many accidentals, and although all 12 tones of the chromatic scale may appear, the tonal characteristics of the diatonic scale are maintained. ... Chromaticism [is t]he introduction of some pitches of the chromatic scale into music that is basically diatonic in orientation, or music that is based on the chromatic scale instead of the diatonic scales.
Mixolydian mode may refer to one of three things: the name applied to one of the ancient Greek harmoniai or tonoi, based on a particular octave species or scale; one of the medieval church modes; or a modern musical mode or diatonic scale, related to the medieval mode.

Hohner Musikinstrumente GmbH & Co. KG is a German manufacturer of musical instruments, founded in 1857 by Matthias Hohner (1833–1902). The roots of the Hohner firm are in Trossingen, Baden-Württemberg. Since its foundation, and though known for its harmonicas, Hohner has manufactured a wide range of instruments, such as kazoos, accordions, recorder flutes, melodicas, banjos, electric, acoustic, resonator and classical guitars, basses, mandolins and ukuleles

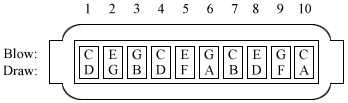
The Richter-tuned harmonica, or 10-hole harmonica or blues harp, is the most widely known type of harmonica. It is a variety of diatonic harmonica, with ten holes which offer the player 19 notes in a three-octave range.

A melodeon or diatonic button accordion is a member of the free-reed aerophone family of musical instruments. It is a type of button accordion on which the melody-side keyboard contains one or more rows of buttons, with each row producing the notes of a single diatonic scale. The buttons on the bass-side keyboard are most commonly arranged in pairs, with one button of a pair sounding the fundamental of a chord and the other the corresponding major triad.
The chromatic harmonica is a type of harmonica that uses a button-activated sliding bar to redirect air from the hole in the mouthpiece to the selected reed-plate desired. When the button is not pressed, an altered diatonic major scale of the key of the harmonica is available, while depressing the button accesses the same scale a semitone higher in each hole. Thus, the instrument is capable of playing the 12 notes of the Western chromatic scale. The chromatic harmonica can thus be contrasted with a standard harmonica, which can play only the notes in a given musical key.

Tremolo harmonicas are a type of Diatonic harmonica, distinct by having two reeds per note. In a tremolo harmonica the two reeds are tuned slightly off a reference pitch, one slightly sharp and the other slightly flat. This gives a unique wavering or warbling sound created by the two reeds being not exactly in tune with each other and difference in their subsequent waveforms acting against one another. The degree of beating can be varied depending on the desired effect. Instruments where the beating is faster due to the reeds being farther apart from the reference pitch are called "wet", whereas those where the beating is slower and less noticeable due to the reeds being more closely in tune are called "dry".

Diatonic and chromatic are terms in music theory that are most often used to characterize scales, and are also applied to musical instruments, intervals, chords, notes, musical styles, and kinds of harmony. They are very often used as a pair, especially when applied to contrasting features of the common practice music of the period 1600–1900.

Tablature is a form of musical notation indicating instrument fingering rather than musical pitches.
Richter tuning is a system of choosing the reeds for a diatonic wind instrument. It is named after Joseph Richter, a Bohemian instrument maker who adopted the tuning for his harmonicas in the early 19th century and is credited with inventing the blow/draw mechanism that allows the harmonica to play different notes when the air is drawn instead of blown.

The Anglo or Anglo-German concertina is a member of the concertina family of free-reed instruments.