Mains electricity or utility power, power grid, domestic power, and wall power, or, in some parts of Canada, hydro, is a general-purpose alternating-current (AC) electric power supply. It is the form of electrical power that is delivered to homes and businesses through the electrical grid in many parts of the world. People use this electricity to power everyday items by plugging them into a wall outlet.

The Westinghouse Electric Corporation was an American manufacturing company founded in 1886 by George Westinghouse. It was originally named "Westinghouse Electric & Manufacturing Company" and was renamed "Westinghouse Electric Corporation" in 1945. The company acquired the CBS television network in 1995 and was renamed "CBS Corporation" until being acquired by Viacom in 1999, a merger completed in April 2000. The CBS Corporation name was later reused for one of the two companies resulting from the split of Viacom in 2005.

A phone connector, also known as phone jack, audio jack, headphone jack or jack plug, is a family of electrical connectors typically used for analog audio signals. A plug, the "male" connector, is inserted into the jack, the "female" connector.

A power strip is a block of electrical sockets that attaches to the end of a flexible cable, allowing multiple electrical devices to be powered from a single electrical socket. Power strips are often used when many electrical devices are in proximity, such as for audio, video, computer systems, appliances, power tools, and lighting. Power strips often include a circuit breaker to interrupt the electric current in case of an overload or a short circuit. Some power strips provide protection against electrical power surges. Typical housing styles include strip, rack-mount, under-monitor and direct plug-in.
AC power plugs and sockets connect electric equipment to the alternating current (AC) mains electricity power supply in buildings and at other sites. Electrical plugs and sockets differ from one another in voltage and current rating, shape, size, and connector type. Different standard systems of plugs and sockets are used around the world.

A banana connector is a single-wire electrical connector used for joining wires to equipment. The term 4 mm connector is also used, especially in Europe, although not all banana connectors will mate with 4 mm parts, and 2 mm banana connectors exist. Various styles of banana plug contacts exist, all based on the concept of spring metal applying outward force into the unsprung cylindrical jack to produce a snug fit with good electrical conductivity. Common types include: a solid pin split lengthwise and splayed slightly, a tip of four leaf springs, a cylinder with a single leaf spring on one side, a bundle of stiff wire, a central pin surrounded by a multiple-slit cylinder with a central bulge, or simple sheet spring metal rolled into a nearly complete cylinder. The plugs are frequently used to terminate patch cords for electronic test equipment such as laboratory power supply units, while sheathed banana plugs are common on multimeter probe leads.

Industrial and multiphase plugs and sockets provide a connection to the electrical mains rated at higher voltages and currents than household plugs and sockets. They are generally used in polyphase systems, with high currents, or when protection from environmental hazards is required. Industrial outlets may have weatherproof covers, waterproofing sleeves, or may be interlocked with a switch to prevent accidental disconnection of an energized plug. Some types of connectors are approved for hazardous areas such as coal mines or petrochemical plants, where flammable gas may be present.
MK Electric is a company that makes electrical accessories. The company's headquarters are in Basildon, Essex, England, from where it sells goods worldwide.
A pull switch, also known as pull-cord switch, or light pull, or pull chain is a switch that is actuated by means of a chain or string.

Graybar Electric Company, Inc. is an American wholesale electrical, communications and data networking products distribution business, which also supplies related supply-chain management and logistics services. Based in Clayton, Missouri, the employee-owned corporation is included on the Fortune 500 list of the largest United States corporations.

AS/NZS 3112 is the harmonised Australian and New Zealand standard for AC power plugs (male) and sockets (female). The standard is used in Australia, Argentina, New Zealand, Fiji, Tonga, Solomon Islands, Papua New Guinea and several other Pacific island countries. The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) "world plugs" Web site calls this plug Type I.

NEMA connectors are power plugs and receptacles used for AC mains electricity in North America and other countries that use the standards set by the US National Electrical Manufacturers Association. NEMA wiring devices are made in current ratings from 15 to 60 amperes (A), with voltage ratings from 125 to 600 volts (V). Different combinations of contact blade widths, shapes, orientations, and dimensions create non-interchangeable connectors that are unique for each combination of voltage, electric current carrying capacity, and grounding system.

Edison screw (ES) is a standard lightbulb socket for electric light bulbs. It was developed by Thomas Edison (1847–1931), patented in 1881, and was licensed in 1909 under General Electric's Mazda trademark. The bulbs have right-hand threaded metal bases (caps) which screw into matching threaded sockets. For bulbs powered by AC current, the thread is generally connected to neutral and the contact on the bottom tip of the base is connected to the "live" phase.
The Bryant Electric Company was a manufacturer of wiring devices, electrical components, and switches founded in 1888 in Bridgeport, Connecticut. It grew to become for a time both the world's largest plant devoted to the manufacture of wiring devices and Bridgeport's largest employer and was involved in a number of notable strikes, before being closed in 1988 and having its remaining interests sold to Hubbell in 1991.

An automobile auxiliary power outlet in an automobile was initially designed to power an electrically heated cigarette lighter, but became a de facto standard DC connector to supply electrical power for portable accessories used in or near an automobile directly from the vehicle's electrical system. Such include mobile phone chargers, cooling fans, portable fridges, electric air pumps, and power inverters.
Benjamin Electric Manufacturing Company was a Des Plaines, Illinois electrical company founded in the late 19th century.

The Anderson Powerpole is a family of electrical connectors by Anderson Power Products (APP), although plug compatible connectors are now available from alternate sources. Specific variants of this series of connectors have become de facto standards for conveying "higher power" direct current (DC) electrical power, although these standards are inconsistent and sometimes ignored.

Plugs and sockets for electrical appliances not hardwired to mains electricity originated in the United Kingdom in the 1870s and were initially two-pin designs. These were usually sold as a mating pair, but gradually de facto and then official standards arose to enable the interchange of compatible devices. British standards have proliferated throughout large parts of the former British Empire.

Hubbell Incorporated, headquartered in Shelton, Connecticut, is an American company that designs, manufactures, and sells electrical and electronic products for non-residential and residential construction, industrial, and utility applications. Hubbell was founded by Harvey Hubbell as a proprietorship in 1888, and was incorporated in Connecticut in 1905.
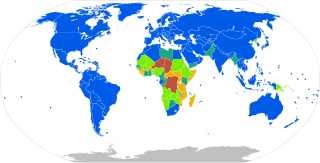
There are approximately 20 types in common use around the world, such as AC power plugs and sockets, and many obsolete socket types which are still found in older buildings.














