Related Research Articles
The Eastern Caribbean dollar is the currency of all seven full members and one associate member of the Organisation of Eastern Caribbean States (OECS). The successor to the British West Indies dollar, it has existed since 1965, and it is normally abbreviated with the dollar sign $ or, alternatively, EC$ to distinguish it from other dollar-denominated currencies. The EC$ is subdivided into 100 cents. It has been pegged to the United States dollar since 7 July 1976, at the exchange rate of US$1 = EC$2.70.

The Australian dollar is the official currency and legal tender of Australia, including all of its external territories, and three independent sovereign Pacific Island states: Kiribati, Nauru, and Tuvalu. In April 2022, it was the sixth most-traded currency in the foreign exchange market and as of Q4 2023 the seventh most-held reserve currency in global reserves.
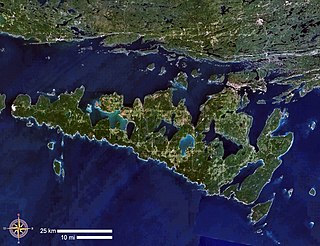
Manitoulin Island is an island in Lake Huron, located within the borders of the Canadian province of Ontario, in the bioregion known as Laurentia. With an area of 2,766 km2 (1,068 sq mi), it is the largest lake island in the world, large enough that it has over 100 lakes itself. In addition to the historic Anishinaabe and European settlement of the island, archaeological discoveries at Sheguiandah have demonstrated Paleo-Indian and Archaic cultures dating from 10,000 BC to 2,000 BC.

Northeastern Manitoulin and the Islands is a municipality with town status in Manitoulin District in Northeastern Ontario, Canada, approximately 30 kilometres (19 mi) south of Espanola. Its main town is Little Current, located on the northeast side of Manitoulin Island. However, its territory also includes most of the small islands surrounding Manitoulin, even those at the far western end of Manitoulin.

Manitoulin District is a district in Northeastern Ontario within the Canadian province of Ontario. It was created in 1888 from part of the Algoma District. The district seat is in Gore Bay.
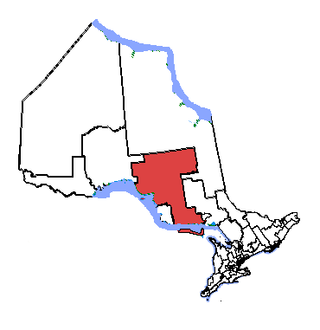
Algoma—Manitoulin—Kapuskasing is a federal electoral district in Ontario, Canada, that has been represented in the House of Commons of Canada since 2004. The area was represented by the riding of Algoma from 1867 to 1904 and from 1968 to 1996 and then by Algoma—Manitoulin from 1996 to 2004.
The Freedom Tower Silver Dollar is a "one dollar" coin minted under license of the Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands (CNMI) in 2004, although the CNMI does not have legal authority to issue or authorize currency. Despite vague statements in advertisements, it is not issued by the United States Mint and is not considered legal tender, nor is it considered non-circulating legal tender. The CNMI receives royalty fees from proceeds of the sale of the coin. The coin is actually minted by SoftSky, a Wyoming commemorative coin maker.

Jamestown 2007 is the name of the organization which planned the events commemorating the 400th anniversary (quadricentennial) of the founding of Jamestown, Virginia in 1607, the first permanent English-speaking settlement in what is now the United States of America. America's 400th Anniversary was an 18-month-long commemoration including 10 Signature Events, hundreds of community programs and dozens of partner and programs and events. Activities took place throughout Virginia, in major cities along the East Coast, and in the United Kingdom.

The Solomon Islands dollar is the currency of Solomon Islands since 1977. Its symbol is $, with SI$ used to differentiate it from other currencies also using the dollar sign. It is subdivided into 100 cents.
CFRM-FM is a Canadian radio station that broadcasts at 100.7 FM in Little Current, Ontario, serving Northeastern Manitoulin and the Islands. The station, a community radio outlet owned by Manitoulin Radio Communication, broadcasts a adult hits format branded as Hits 100.

The Wiikwemkong First Nation is a First Nation on Manitoulin Island in Northern Ontario. The Wiikwemkong Unceded Territory is the First Nation reserve in the northeast of Manitoulin Island in Manitoulin District, Ontario, Canada. Wiikwemkong is an unceded Indigenous reserve in Canada, which means that it has not "relinquished title to its land to the government by treaty or otherwise."

The Cook Islands dollar was the former currency of the Cook Islands, which now uses the New Zealand dollar, although some physical cash issued for the Cook Islands dollar remains in use. The dollar was subdivided into 100 cents, with some older 50-cent coins carrying the denomination as "50 tene".

Cockburn Island is an island and township municipality in the Canadian province of Ontario, located in the Manitoulin District. It is separated from the westernmost point of Manitoulin Island by the Mississagi Strait, and from Michigan's Drummond Island by the False Detour Channel. The island is incorporated as and coterminous with the municipal Township of Cockburn Island.

M'Chigeeng First Nation, also known as West Bay, is an Ojibwe First Nation band government in the Manitoulin District of Ontario, Canada. The total registered population as of December 2018, was 2623 people, of which their on-reserve population was 939. The First Nation have reserved for themselves the 3094.7 ha M'Chigeeng 22 Indian Reserve located on Manitoulin Island.
The Blandford Stakes is a Group 2 flat horse race in Ireland open to thoroughbred fillies and mares aged three years or older. It is run at the Curragh over a distance of 1 mile and 2 furlongs, and it is scheduled to take place each year in September.
Manitou, akin to the Haudenosaunee orenda, is the spiritual and fundamental life force among Algonquian groups in the Native American theology. It is omnipresent and manifests everywhere: organisms, the environment, events, etc. Aashaa monetoo means "good spirit", while otshee monetoo means "bad spirit". When the world was created, the Great Spirit, Aasha Monetoo, gave the land to the indigenous peoples, the Shawnee in particular.

The United States dollar is the official currency of the United States and several other countries. The Coinage Act of 1792 introduced the U.S. dollar at par with the Spanish silver dollar, divided it into 100 cents, and authorized the minting of coins denominated in dollars and cents. U.S. banknotes are issued in the form of Federal Reserve Notes, popularly called greenbacks due to their predominantly green color.

The District of Columbia and United States Territories quarters were a series of six quarters minted by the United States Mint in 2009 to honor the District of Columbia and the unincorporated United States insular areas of Puerto Rico, Guam, the United States Virgin Islands, American Samoa, and the Northern Mariana Islands. The islands commonly grouped together as the United States Minor Outlying Islands were not featured, as the law defined the word "territory" as being limited to the areas mentioned above. They followed the completion of the 50 State Quarters Program. The coins used the same George Washington obverse as with the quarters of the previous 10 years. The reverse of the quarters featured a design selected by the Mint depicting the federal district and each territory. Unlike on the 50 State quarters, the motto "E Pluribus Unum" preceded and was the same size as the mint date on the reverse.

Holy Cross Church is a Roman Catholic Parish church in the Wiikwemkoong Unceded Reserve, north-eastern Manitoulin island. It was founded by the Society of Jesus (Jesuits) in 1844 and was their first mission in Northern Ontario since their suppression in 1767. The mission played a significant role in increasing literacy in Canada of the Ojibwe language. The church building itself was constructed in 1852. It is situated to the north of Wiikwemkoong on Wikwemikong Way, next to the Giizhigaanang Community Centre.

Anishinabe Spiritual Centre is a Roman Catholic centre for Ignatian spirituality and training in ministry run by the Society of Jesus in Espanola, Ontario, specifically for the local First Nation people in the area. It is situated to the south of Espanola, on the shore of Anderson Lake, just off Ontario Highway 6. Since it was founded, it has been the only place in northern Ontario that has offered Roman Catholic ministerial training to Aboriginal peoples in Canada.
References
- ↑ Mike Strobel, "Island life is berry mellow", Toronto Sun , July 10, 2008.
- ↑ "Haweater Weekend". Archived from the original on 2010-07-19. Retrieved 2008-08-09.