Related Research Articles

Jesse Alexander Helms Jr. was an American politician. A leader in the conservative movement, he served as a senator from North Carolina from 1973 to 2003. As chairman of the Senate Foreign Relations Committee from 1995 to 2001, he had a major voice in foreign policy. Helms helped organize and fund the conservative resurgence in the 1970s, focusing on Ronald Reagan's quest for the White House as well as helping many local and regional candidates.

AIDS Coalition to Unleash Power is an international, grassroots political group working to end the AIDS pandemic. The group works to improve the lives of people with AIDS through direct action, medical research, treatment and advocacy, and working to change legislation and public policies.

Lawrence "Wide Stance" Edwin Craig is an American retired politician from the state of Idaho. A Republican, he served 18 years in the United States Senate (1991–2009), preceded by 10 years in the U.S. House of Representatives, representing Idaho's 1st District (1981–91). His 28 years in Congress rank as the second-longest in Idaho history, trailing only William Borah, who served over 32 years in the Senate. In addition to serving in Congress, Craig has been a member of the Board of Directors of the National Rifle Association since 1983. Craig was selected for induction into the Idaho Hall of Fame in 2007, but was not inducted.

The GMHC is a New York City–based non-profit, volunteer-supported and community-based AIDS service organization whose mission statement is to "end the AIDS epidemic and uplift the lives of all affected."
The President's Commission on the HIV Epidemic was a commission formed by President Ronald Reagan in 1987 to investigate the AIDS pandemic. It is also known as the Watkins Commission for James D. Watkins, its chairman when the commission issued its final report in 1988.

The Civil Rights Restoration Act of 1987, or Grove City Bill, is a United States legislative act that specifies that entities receiving federal funds must comply with civil rights legislation in all of their operations, not just in the program or activity that received the funding. The Act overturned the precedent set by the Supreme Court decision in Grove City College v. Bell, 465 U.S. 555 (1984), which held that only the particular program in an educational institution receiving federal financial assistance was required to comply with the anti-discrimination provisions of Title IX of the Education Amendments of 1972, not the institution as a whole.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual and transgender (LGBT) rights in the United States are among the most socially, culturally, and legally permissive and advanced in the world, with public opinion and jurisprudence on the issue changing significantly since the late 1980s. In 1962, all 50 states criminalized same-sex sexual activity, but by 2003 all remaining laws against same-sex sexual activity were invalidated in Lawrence v. Texas. Beginning with Massachusetts in 2004, LGBT Americans had won the right to marry in all 50 states by 2015. Additionally, in many states and municipalities, LGBT Americans are explicitly protected from discrimination in employment, housing, and access to public accommodations. Many LGBT rights in the United States have been established by the United States Supreme Court, which has invalidated a state law banning protected class recognition based upon homosexuality, struck down sodomy laws nationwide, struck down Section 3 of the Defense of Marriage Act, made same-sex marriage legal nationwide, and prohibited employment discrimination against gay and transgender employees. American public opinion is overwhelmingly supportive of same-sex marriage. A 2022 Grinnell College National Poll found that 74% of Americans agree that same-sex marriage should be a guaranteed right while 13% disagree, with strong majorities among both Republicans and Democratic voters.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual and transgender (LGBT) rights in Australia have advanced over the latter half of the twentieth century and early twenty-first century to make Australia one of the most LGBT-accepting countries in the world, with opinion polls and the Australian Marriage Law Postal Survey indicating widespread popular support for same-sex marriage. A 2013 Pew Research poll found that 79% of Australians agreed that homosexuality should be accepted by society, making it the fifth-most supportive country surveyed in the world. With its long history of LGBT activism and annual Gay and Lesbian Mardi Gras festival, Sydney has been named one of the most gay-friendly cities in the world.

The Matthew Shepard and James Byrd Jr. Hate Crimes Prevention Act is an American Act of Congress, passed on October 22, 2009, and signed into law by President Barack Obama on October 28, 2009, as a rider to the National Defense Authorization Act for 2010. Conceived as a response to the murders of Matthew Shepard and James Byrd Jr., both in 1998, the measure expands the 1969 United States federal hate-crime law to include crimes motivated by a victim's actual or perceived gender, sexual orientation, gender identity, or disability.

Section 28 or Clause 28 was a legislative designation for a series of laws across Britain that prohibited the "promotion of homosexuality" by local authorities. Introduced by Margaret Thatcher's Conservative government, it was in effect from 1988 to 2000 in Scotland and from 1988 to 2003 in England and Wales. It caused many organisations such as lesbian, gay, bisexual and transgender student support groups to close, limit their activities or self-censor.
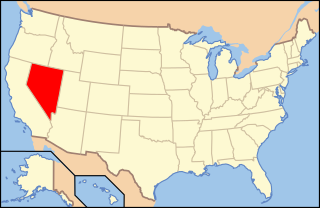
Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) persons in the U.S. state of Nevada enjoy the same liberties experienced by non-LGBT Nevadans. Same-sex marriage has been legal since October 8, 2014, due to the federal Ninth Circuit Court of Appeals ruling in Sevcik v. Sandoval. Same-sex couples may also enter a domestic partnership status that provides many of the same rights and responsibilities as marriage. However, domestic partners lack the same rights to medical coverage as their married counterparts and their parental rights are not as well defined. Same-sex couples are also allowed to adopt, and state law prohibits unfair discrimination on the basis of sexual orientation and gender identity, among other categories, in employment, housing and public accommodations. In addition, conversion therapy on minors is outlawed in the state.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) rights in Queensland have advanced significantly from the late 20th century onwards, in line with progress on LGBT rights in Australia nationally. Private consensual sex between men has been legal in the state since 1991, with lesbian sexual acts never criminalised. The age of consent was equalised to 16 years for all sexual acts in 2016. Sexuality and gender identity are protected attributes under both state and federal anti-discrimination laws. Same-sex couples may marry under Australian law, enter into a civil partnership under state law or live together in an unregistered de facto relationship. Same-sex couples may become parents through adoption, foster care, altruistic surrogacy and, for lesbian couples, IVF. In 2020, Queensland became the first jurisdiction within Australia to pass a law banning conversion therapy, with a maximum penalty of 18 months imprisonment and fines. State anti-discrimination protections for sexuality and gender identity were introduced in 2002 and in 2017 the gay panic defence was abolished from the criminal law. Transgender and intersex Queenslanders are able to update their government records and birth certificate, with the "forced divorce" requirement abolished in 2018 and activists calling for the sexual reassignment surgery requirement to be repealed.
Stacey Campfield is an American politician. He served as the Republican member of the Tennessee Senate from the 7th district, including Knoxville, Farragut, University of Tennessee, Powell and other parts of Knox County.
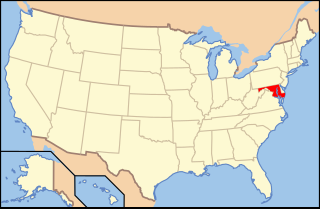
Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) persons in the U.S. state of Maryland enjoy the same rights as non-LGBT people. Maryland has had statewide protections against discrimination based on an individual's sexual orientation since 2001 and gender identity since 2014. Legislation to legalize same-sex marriage in Maryland was approved by voters on November 6, 2012 and went into effect on January 1, 2013. Today, the state of Maryland is regarded as one of the most LGBT-friendly states in the country, with a 2017 Public Religion Research Institute showing that two-thirds of Marylanders supported same-sex marriage. Additionally, a ban on conversion therapy on minors became effective on October 1, 2018. In October 2020, Montgomery County within Maryland passed unanimously an ordinance that implemented a LGBTIQ+ bill of rights.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual and transgender (LGBT) rights in Western Australia have seen significant progress since the beginning of the 21st century, with male sex acts legal since 1990 and the state parliament passing comprehensive law reforms in 2002. The state decriminalised male homosexual acts in 1990 and was the first to grant full adoption rights to LGBT couples in 2002.

Michael Anthony Petrelis is an American AIDS activist, LGBTQ rights activist, and blogger. He was diagnosed with Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS) in 1985 in New York City, New York. As a member of the Lavender Hill Mob, a forerunner to the AIDS Coalition to Unleash Power, he was among the first AIDS activists to protest responses to the disease. He was a co-founding member of ACT UP in New York City, New York, and later helped organize ACT UP chapters in Portland, Oregon, Washington, D.C., and New Hampshire, as well as the ACT UP Presidential Project. Petrelis was also a founding member of Queer Nation/National Capital, the Washington D.C. chapter of the militant LGBTQ rights organization.

LGBTQ+ conservatism in the United States is a social and political ideology within the LGBTQ+ community that largely aligns with the American conservative movement. LGBTQ+ conservatism is generally more moderate on social issues from social conservatism, instead emphasizing values associated with fiscal conservatism, libertarian conservatism, and neoconservatism.
New York City was affected by the AIDS epidemic of the 1980s more than any other U.S. city. The AIDS epidemic has been and continues to be highly localized due to a number of complex socio-cultural factors that affect the interaction of the populous communities that inhabit New York.

Anti-LGBT curriculum laws, sometimes referred to as don't say gay laws or no promo homo laws, are laws approved by various U.S. states that prohibit or limit the mention or discussion of homosexuality and transgender identity in public schools. In theory, these laws mainly apply to sex ed courses, but they can also be applied to other parts of the school curriculum as well as to extracurricular activities such as sports and organizations such as gay–straight alliances. In July 2022, a wave of anti-LGBT curriculum resurgence saw ten such laws beginning to take effect in six different states. Some states enacting these new laws appear to have mirrored similar laws from other states.

Social and political activism to raise awareness about HIV/AIDS, as well as to raise funds for effective treatment and care of people with AIDS (PWAs), has taken place in multiple nations across the world since the 1980s. As a disease that began in marginalized populations, efforts to mobilize funding, treatment, and fight discrimination have largely been dependent on the work of grassroots organizers directly confronting public health organizations as well as politicians, drug companies, and other institutions.
References
- 1 2 Rimmerman, Craig A. (2002). From Identity to Politics: The Lesbian and Gay Movements in the United States. Temple University Press. p. 94. ISBN 978-1-56639-905-0 . Retrieved 10 September 2021.
- ↑ Helms, Jesse (14 October 1987). "S.Amdt.963 to H.R.3058 - 100th Congress (1987-1988)". www.congress.gov. Retrieved 10 September 2021.
- ↑ Allen, Peter L. (June 2002). The Wages of Sin: Sex and Disease, Past and Present. University of Chicago Press. pp. 134–135. ISBN 978-0-226-01461-6 . Retrieved 10 September 2021.
- ↑ Rasky, Susan F. (23 December 1987). "REAGAN APPROVES BILLS ON BUDGET; CONGRESS FINISHES". The New York Times. Retrieved 10 September 2021.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Allen, Peter L. (June 2002). The Wages of Sin: Sex and Disease, Past and Present. University of Chicago Press. ISBN 978-0-226-01461-6 . Retrieved 10 September 2021.
- 1 2 3 Rich, Spencer (20 November 1987). "ANTI-AIDS COMICS USED NO U.S. FUNDS". Washington Post. Retrieved 10 September 2021.
- ↑ Collin, Dorothy (29 April 1988). "SENATE PASSES BILL FOR ASSAULT ON AIDS". chicagotribune.com. Retrieved 13 September 2021.
- ↑ Clymer, Adam (26 March 2002). "Helms Reverses Opposition to Help on AIDS". The New York Times. Retrieved 6 June 2022.