
Rheidae is a family of flightless ratite birds which first appeared in the Paleocene. It is today represented by the sole living genus Rhea, but also contains several extinct genera.

Phorusrhacids, colloquially known as terror birds, are an extinct family of large carnivorous, mostly flightless birds that were among the largest apex predators in South America during the Cenozoic era. Their definitive fossil records range from the Middle Eocene to the Late Pleistocene around 43 to 0.1 million years ago, though some specimens suggest that they were present since the Early Eocene.

Phorusrhacos is an extinct genus of giant flightless terror birds that inhabited South America during the Miocene epoch. Phorusrhacos was one of the dominant land predators in South America at the time it existed. It is thought to have lived in woodlands and grasslands.
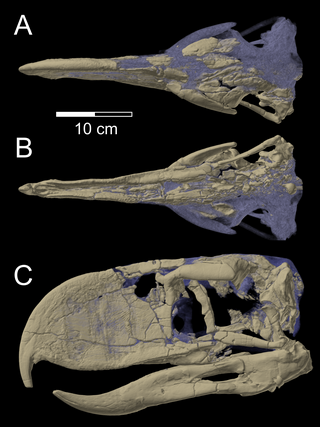
Andalgalornis is a genus of flightless predatory birds of the extinct family Phorusrhacidae that lived in Argentina. The type and only species is A. steulleti.

Brontornis is an extinct genus of giant bird that inhabited Argentina during the Early to Middle Miocene. Its taxonomic position is highly controversial, with authors alternatively considering it to be a cariamiform, typically a phorusrhacid or an anserimorph.

Mesembriornis is a genus of intermediate-sized phorusrhacids that grew up to 1.5 metres (4.9 ft) in height. They represent a well-distinct lineage of terror birds, differing from the massive large groups and the smaller Psilopterinae. In general proportions, they most resembled the Patagornithinae which flourished somewhat earlier, mainly to the south of the range of Mesembriornis. Fossils of the terror bird have been found in Montehermosan deposits of the Monte Hermoso Formation, as well as the Andalgala Formation and Chapadmalal Formation in Argentina.

Kelenken is a genus of phorusrhacid, an extinct group of large, predatory birds, which lived in what is now Argentina in the middle Miocene about 15 million years ago. The only known specimen was discovered by high school student Guillermo Aguirre-Zabala in Comallo, in the region of Patagonia, and was made the holotype of the new genus and species Kelenken guillermoi in 2007. The genus name references a spirit in Tehuelche mythology, and the specific name honors the discoverer. The holotype consists of one of the most complete skulls known of a large phorusrhacid, as well as a tarsometatarsus lower leg bone and a phalanx toe bone. The discovery of Kelenken clarified the anatomy of large phorusrhacids, as these were previously much less well known. The closest living relatives of the phorusrhacids are the seriemas. Kelenken was found to belong in the subfamily Phorusrhacinae, along with for example Devincenzia.
Physornis is an extinct genus of giant flightless predatory birds of the family Phorusrhacidae or "terror birds", most closely related to Paraphysornis, that lived in Argentina. The type species is P. fortis. It lived during the Middle to Late Oligocene (Deseadan). Few fossils are known, but the available material suggests that Physornis was one of the largest phorusrhacids.

Devincenzia is an extinct genus of giant flightless predatory birds in the family Phorusrhacidae or "terror birds" that lived during the Early Miocene (Deseadan) Fray Bentos Formation of Uruguay, Late Miocene (Huayquerian) Ituzaingó Formation, Early Pliocene (Montehermosan) of Argentina, and possibly the Early Pleistocene Raigón Formation of Uruguay. The type species D. pozzi was formerly known as Onactornis pozzi. The largest possible specimen weighed up to 350 kilograms (770 lb), making it one of the largest phorusrhacids and carnivorous birds known.

Patagornis is a genus of extinct flightless predatory birds of the family Phorusrhacidae. Known as "terror birds", these lived in what is now Argentina during the Early and Middle Miocene; the Santa Cruz Formation in Patagonia contains numerous specimens. Patagornis was an agile, medium sized Patagornithine and was likely a pursuit predator.

Andrewsornis is an extinct genus of giant flightless predatory birds of the family Phorusrhacidae or "terror birds" that lived in Oligocene Argentina. Fossils have been found in the Sarmiento Formation, and possibly the Agua de la Piedra Formation.

Psilopterus is an extinct genus of phorusrhacid from the Middle Oligocene to possibly the Late Pleistocene of Argentina and Uruguay. Compared to other phorusrhacids, members of the genus are both relatively gracile and diminutive, and include the smallest known species of terror bird: with the head raised P. bachmanni was 70–80 centimeters (2.3–2.6 ft) in height and weighed about 5 kilograms (11 lb), while the largest members of the genus were only about 8 kilograms (18 lb). The birds resemble the modern cariama, except with a heavier build and considerably smaller wings. Fossil finds in Uruguay indicate the genus may have survived until 96,040 ± 6,300 years ago, millions of years after the larger phorusrhacids became extinct.

Llallawavis scagliai is a large, extinct predatory bird from Pliocene Argentina. Its fossil is the most complete fossil of a phorusrhacid yet found.

Conflicto antarcticus is a species of stem waterfowl whose fossils were found in the early Paleocene López de Bertodano Formation of Antarctica, the only species of its genus and the family Conflictonidae. It is characterized by it slender body and long legs, yet possesses a duck-like bill which indicates the form of beak evolved early in Anseriformes.
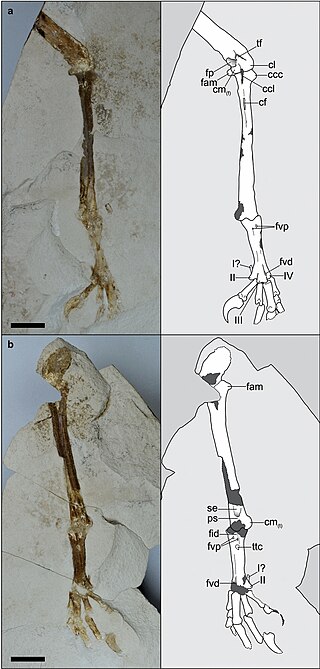
Ueekenkcoracias is an extinct genus of primobucconid bird in the order Coraciiformes from the Huitrera Formation of Patagonia. A relatively large member of the stem-Coracii, Ueekenkcoracias possessed a robust femur and stout tibiotarsus, with a strongly projected facies articularis medialis.
Dryornis, also called the Argentinian vulture, is an extinct genus of cathartid, known from Argentina. The genus contains two species, D. pampeanus and D. hatcheri.
Rhea mesopotamica is an extinct species of bird in the genus Rhea, whose living species are known as suris, rhea, or choiques. It lived in the Southern Cone of South America.
Yarquen is an extinct genus of owls which lived in what is now Argentina in the middle Miocene. It contains a single species, Yarquen dolgopolae. It is the oldest owl to have been formally described from South America.
Wunketru is an extinct genus of waterfowl from the Eocene Las Flores Formation of Chubut Province, Argentina. The genus contains a single species, W. howardae, known from a partial skeleton previously classified as a species of Telmabates.
Telmabates is an extinct genus of presbyornithid bird from the Eocene Bird Clay Locality of the Sarmiento Formation of Chubut Province, Argentina. The genus contains a single species, T. antiquus.
















