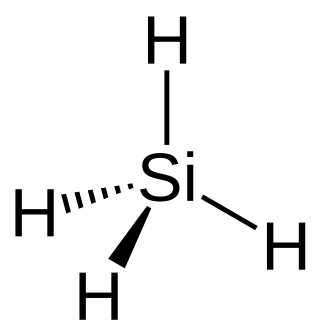
Silane (Silicane) is an inorganic compound with chemical formula SiH4. It is a colorless, pyrophoric, toxic gas with a sharp, repulsive, pungent smell, somewhat similar to that of acetic acid. Silane is of practical interest as a precursor to elemental silicon. Silane with alkyl groups are effective water repellents for mineral surfaces such as concrete and masonry. Silanes with both organic and inorganic attachments are used as coupling agents. They are commonly used to apply coatings to surfaces or as an adhesion promoter.

Trichlorosilane is an inorganic compound with the formula HCl3Si. It is a colourless, volatile liquid. Purified trichlorosilane is the principal precursor to ultrapure silicon in the semiconductor industry. In water, it rapidly decomposes to produce a siloxane polymer while giving off hydrochloric acid. Because of its reactivity and wide availability, it is frequently used in the synthesis of silicon-containing organic compounds.

Silicon tetrachloride or tetrachlorosilane is the inorganic compound with the formula SiCl4. It is a colorless volatile liquid that fumes in air. It is used to produce high purity silicon and silica for commercial applications. It is a part of the chlorosilane family.
Iron(III) chloride describes the inorganic compounds with the formula FeCl3(H2O)x. Also called ferric chloride, these compounds are some of the most important and commonplace compounds of iron. They are available both in anhydrous and in hydrated forms which are both hygroscopic. They feature iron in its +3 oxidation state. The anhydrous derivative is a Lewis acid, while all forms are mild oxidizing agents. It is used as a water cleaner and as an etchant for metals.

Tungsten(VI) fluoride, also known as tungsten hexafluoride, is an inorganic compound with the formula WF6. It is a toxic, corrosive, colorless gas, with a density of about 13 kg/m3 (22 lb/cu yd). It is the only known gaseous transition metal compound and the densest known gas under standard ambient temperature and pressure. WF6 is commonly used by the semiconductor industry to form tungsten films, through the process of chemical vapor deposition. This layer is used in a low-resistivity metallic "interconnect". It is one of seventeen known binary hexafluorides.

Titanium tetrachloride is the inorganic compound with the formula TiCl4. It is an important intermediate in the production of titanium metal and the pigment titanium dioxide. TiCl4 is a volatile liquid. Upon contact with humid air, it forms thick clouds of titanium dioxide and hydrochloric acid, a reaction that was formerly exploited for use in smoke machines. It is sometimes referred to as "tickle" or "tickle 4", as a phonetic representation of the symbols of its molecular formula.
Tin(IV) chloride, also known as tin tetrachloride or stannic chloride, is an inorganic compound of tin and chlorine with the formula SnCl4. It is a colorless hygroscopic liquid, which fumes on contact with air. It is used as a precursor to other tin compounds. It was first discovered by Andreas Libavius (1550–1616) and was known as spiritus fumans libavii.
In inorganic chemistry, chlorosilanes are a group of reactive, chlorine-containing chemical compounds, related to silane and used in many chemical processes. Each such chemical has at least one silicon-chlorine bond. Trichlorosilane is produced on the largest scale. The parent chlorosilane is silicon tetrachloride.

Hafnium(IV) chloride is the inorganic compound with the formula HfCl4. This colourless solid is the precursor to most hafnium organometallic compounds. It has a variety of highly specialized applications, mainly in materials science and as a catalyst.
Calcium hypochlorite is an inorganic compound with chemical formula Ca(ClO)2, also written as Ca(OCl)2. It is a white solid, although commercial samples appear yellow. It strongly smells of chlorine, owing to its slow decomposition in moist air. This compound is relatively stable as a solid and solution and has greater available chlorine than sodium hypochlorite. "Pure" samples have 99.2% active chlorine. Given common industrial purity, an active chlorine content of 65-70% is typical. It is the main active ingredient of commercial products called bleaching powder, used for water treatment and as a bleaching agent.
Boron trichloride is the inorganic compound with the formula BCl3. This colorless gas is a reagent in organic synthesis. It is highly reactive towards water.

Vanadium oxytrichloride is the inorganic compound with the formula VOCl3. This yellow distillable liquid hydrolyzes readily in air. It is an oxidizing agent. It is used as a reagent in organic synthesis. Samples often appear red or orange owing to an impurity of vanadium tetrachloride.

Zirconium(IV) chloride, also known as zirconium tetrachloride, is an inorganic compound frequently used as a precursor to other compounds of zirconium. This white high-melting solid hydrolyzes rapidly in humid air.

Hexafluorosilicic acid is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula H
2SiF
6. Aqueous solutions of hexafluorosilicic acid consist of salts of the cation and hexafluorosilicate anion. These salts and their aqueous solutions are colorless.
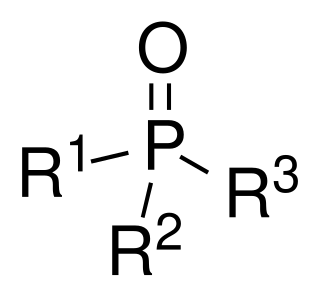
Phosphine oxides are phosphorus compounds with the formula OPX3. When X = alkyl or aryl, these are organophosphine oxides. Triphenylphosphine oxide is an example. An inorganic phosphine oxide is phosphoryl chloride (POCl3). The parent phosphine oxide (H3PO) remains rare and obscure.
Silicon compounds are compounds containing the element silicon (Si). As a carbon group element, silicon often forms compounds in the +4 oxidation state, though many unusual compounds have been discovered that differ from expectations based on its valence electrons, including the silicides and some silanes. Metal silicides, silicon halides, and similar inorganic compounds can be prepared by directly reacting elemental silicon or silicon dioxide with stable metals or with halogens. Silanes, compounds of silicon and hydrogen, are often used as strong reducing agents, and can be prepared from aluminum–silicon alloys and hydrochloric acid.
Deoxygenation is a chemical reaction involving the removal of oxygen atoms from a molecule. The term also refers to the removal of molecular oxygen (O2) from gases and solvents, a step in air-free technique and gas purifiers. As applied to organic compounds, deoxygenation is a component of fuels production as well a type of reaction employed in organic synthesis, e.g. of pharmaceuticals.
Copper silicide can refer to either Cu4Si or pentacopper silicide, Cu5Si.
Dimethyldichlorosilane is a tetrahedral organosilicon compound with the formula Si(CH3)2Cl2. At room temperature it is a colorless liquid that readily reacts with water to form both linear and cyclic Si-O chains. Dimethyldichlorosilane is made on an industrial scale as the principal precursor to dimethylsilicone and polysilane compounds.

Silicon tetraazide is a thermally unstable binary compound of silicon and nitrogen with a nitrogen content of 85.7%. This high-energy compound combusts spontaneously and can only be studied in a solution. A further coordination to a six-fold coordinated structure such as a hexaazidosilicate ion [Si(N3)6]2− or as an adduct with bidentate ligands Si(N3)4·L2 will result in relatively stable, crystalline solids that can be handled at room temperature.








