
A supercomputer is a type of computer with a high level of performance as compared to a general-purpose computer. The performance of a supercomputer is commonly measured in floating-point operations per second (FLOPS) instead of million instructions per second (MIPS). Since 2022, supercomputers have existed which can perform over 1018 FLOPS, so called exascale supercomputers. For comparison, a desktop computer has performance in the range of hundreds of gigaFLOPS (1011) to tens of teraFLOPS (1013). Since November 2017, all of the world's fastest 500 supercomputers run on Linux-based operating systems. Additional research is being conducted in the United States, the European Union, Taiwan, Japan, and China to build faster, more powerful and technologically superior exascale supercomputers.
Floating point operations per second is a measure of computer performance in computing, useful in fields of scientific computations that require floating-point calculations.
The Earth Simulator (ES) is a series of supercomputers deployed at Japan Agency for Marine-Earth Science and Technology Yokohama Institute of Earth Sciences.

Blue Gene was an IBM project aimed at designing supercomputers that can reach operating speeds in the petaFLOPS (PFLOPS) range, with relatively low power consumption.
Cray Inc., a subsidiary of Hewlett Packard Enterprise, is an American supercomputer manufacturer headquartered in Seattle, Washington. It also manufactures systems for data storage and analytics. Several Cray supercomputer systems are listed in the TOP500, which ranks the most powerful supercomputers in the world.

NEC SX describes a series of vector supercomputers designed, manufactured, and marketed by NEC. This computer series is notable for providing the first computer to exceed 1 gigaflop, as well as the fastest supercomputer in the world between 1992–1993, and 2002–2004. The current model, as of 2018, is the SX-Aurora TSUBASA.

EPCC, formerly the Edinburgh Parallel Computing Centre, is a supercomputing centre based at the University of Edinburgh. Since its foundation in 1990, its stated mission has been to accelerate the effective exploitation of novel computing throughout industry, academia and commerce.

The National Energy Research Scientific Computing Center (NERSC), is a high-performance computing (supercomputer) research facility that was founded in 1974. The National User Facility is operated by Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory for the United States Department of Energy Office of Science.
The Oak Ridge Leadership Computing Facility (OLCF), formerly the National Leadership Computing Facility, is a designated user facility operated by Oak Ridge National Laboratory and the Department of Energy. It contains several supercomputers, the largest of which is an HPE OLCF-5 named Frontier, which was ranked 1st on the TOP500 list of world's fastest supercomputers as of June 2023. It is located in Oak Ridge, Tennessee.

The TOP500 project ranks and details the 500 most powerful non-distributed computer systems in the world. The project was started in 1993 and publishes an updated list of the supercomputers twice a year. The first of these updates always coincides with the International Supercomputing Conference in June, and the second is presented at the ACM/IEEE Supercomputing Conference in November. The project aims to provide a reliable basis for tracking and detecting trends in high-performance computing and bases rankings on HPL benchmarks, a portable implementation of the high-performance LINPACK benchmark written in Fortran for distributed-memory computers.
The National Center for Computational Sciences (NCCS) is a United States Department of Energy (DOE) Leadership Computing Facility that houses the Oak Ridge Leadership Computing Facility (OLCF), a DOE Office of Science User Facility charged with helping researchers solve challenging scientific problems of global interest with a combination of leading high-performance computing (HPC) resources and international expertise in scientific computing.
Shaheen is the name of a series of supercomputers owned and operated by King Abdullah University of Science and Technology (KAUST), Saudi Arabia. Shaheen is named after the Peregrine Falcon. The most recent model, Shaheen III, is the largest and most powerful supercomputer in the Middle East.
The Swiss National Supercomputing Centre is the national high-performance computing centre of Switzerland. It was founded in Manno, canton Ticino, in 1991. In March 2012, the CSCS moved to its new location in Lugano-Cornaredo.

Japan operates a number of centers for supercomputing which hold world records in speed, with the K computer being the world's fastest from June 2011 to June 2012, and Fugaku holding the lead from June 2020 until June 2022.

Several centers for supercomputing exist across Europe, and distributed access to them is coordinated by European initiatives to facilitate high-performance computing. One such initiative, the HPC Europa project, fits within the Distributed European Infrastructure for Supercomputing Applications (DEISA), which was formed in 2002 as a consortium of eleven supercomputing centers from seven European countries. Operating within the CORDIS framework, HPC Europa aims to provide access to supercomputers across Europe.

Trinity is a United States supercomputer built by the National Nuclear Security Administration (NNSA) for the Advanced Simulation and Computing Program (ASC). The aim of the ASC program is to simulate, test, and maintain the United States nuclear stockpile.

The Cray XC40 is a massively parallel multiprocessor supercomputer manufactured by Cray. It consists of Intel Haswell Xeon processors, with optional Nvidia Tesla or Intel Xeon Phi accelerators, connected together by Cray's proprietary "Aries" interconnect, stored in air-cooled or liquid-cooled cabinets. The XC series supercomputers are available with the Cray DataWarp applications I/O accelerator technology.

The Hewlett Packard Enterprise Company (HPE) is an American multinational information technology company based in Spring, Texas.
The Cray XC50 is a massively parallel multiprocessor supercomputer manufactured by Cray. The machine can support Intel Xeon processors, as well as Cavium ThunderX2 processors, Xeon Phi processors and NVIDIA Tesla P100 GPUs. The processors are connected by Cray's proprietary "Aries" interconnect, in a dragonfly network topology. The XC50 is an evolution of the XC40, with the main difference being the support of Tesla P100 processors and the use of Cray software release CLE 6 or 7.
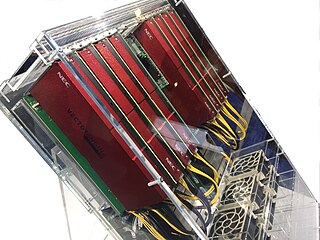
The NEC SX-Aurora TSUBASA is a vector processor of the NEC SX architecture family. Unlike previous SX supercomputers, the SX-Aurora TSUBASA is provided as a PCIe card, termed by NEC as a "Vector Engine" (VE). Eight VE cards can be inserted into a vector host (VH) which is typically a x86-64 server running the Linux operating system. The product has been announced in a press release on 25 October 2017 and NEC has started selling it in February 2018. The product succeeds the SX-ACE.












