
Vasco da Gama, 1st Count of Vidigueira, was a Portuguese explorer and the first European to reach India by sea.

The State of India, also referred as the Portuguese State of India or simply Portuguese India, was a state of the Portuguese Empire founded six years after the discovery of a sea route to the Indian subcontinent by Vasco da Gama, a subject of the Kingdom of Portugal. The capital of Portuguese India served as the governing centre of a string of military forts and trade posts scattered all over the Indian Ocean.

The Goa Inquisition was an extension of the Portuguese Inquisition in Portuguese India. Its objective was to enforce Catholic Orthodoxy and allegiance to the Apostolic See of Rome (Pontifex). The inquisition primarily focused on the New Christians accused of secretly practicing their former religions, and Old Christians accused of involvement in the Protestant Revolution of the 16th century. It was established in 1560, briefly suppressed from 1774 to 1778, continued thereafter until it was finally abolished in 1812. Those targeted were predominately accused of crypto-Hinduism. Those accused were imprisoned and depending on the criminal charge, could even be sentenced to death if convicted. The Inquisitors also seized and burnt any books written in Sanskrit, Dutch, English, or Konkani, on the suspicions that they contained deviationist or Protestant material.

Quelimane is a seaport in Mozambique. It is the administrative capital of the Zambezia Province and the province's largest city, and stands 25 km (16 mi) from the mouth of the Rio dos Bons Sinais. The river was named when Vasco da Gama, on his way to India, reached it and saw "good signs" that he was on the right path. The town was the end point of David Livingstone's west-to-east crossing of south-central Africa in 1856. Portuguese is the official language of Mozambique, and many residents of the areas surrounding Quelimane speak Portuguese. The most common local language is Chuabo. Quelimane, along with much of Zambezia Province, is extremely prone to floods during Mozambique's rainy season. The most recent bout of severe flooding took place in January 2007.

Vasco da Gama, often shortened to Vasco, is a city in the state of Goa on the west coast of India. It is named after the Portuguese explorer Vasco da Gama. It is the headquarters of the Mormugão taluka (subdistrict). The city lies on the western tip of the Mormugao peninsula, at the mouth of the Zuari River, about 30 kilometres (19 mi) from Panaji, Goa's capital, 28 kilometres (17 mi) from Margao, the district headquarters and about 5 kilometres (3.1 mi) from Dabolim Airport.
Goans is the demonym used to describe the people native to Goa, India, who form an ethno-linguistic group resulting from the assimilation of Indo-Aryan, Dravidian, Indo-Portuguese, and Austro-Asiatic ethnic and/or linguistic ancestries. They speak different dialects of Konkani language natively, collectively known as Goan Konkani. "Goanese" is an incorrect term for Goans.

There is relatively little history of active practice of Hinduism in Portugal. Presently there is a Hindu community of approximately 9,000 persons, which largely traces its origins to Indians who emigrated from the former Portuguese colonies of Lusophone Africa, particularly from Mozambique, and from the former colony of Diu, Daman and Goa and other possessions in Portuguese India.

The earliest evidence of Hinduism in Tanzania is from the 1st millennium AD when there was trade between East Africa and Indian subcontinent. Most of these traders came from Gujarat, Deccan and the Chola empire. Archaeological evidence of small Hindu settlements have been found in Zanzibar and parts of Swahili coast, Zimbabwe and Madagascar.

Portuguese maritime exploration resulted in the numerous territories and maritime routes recorded by the Portuguese as a result of their intensive maritime journeys during the 15th and 16th centuries. Portuguese sailors were at the vanguard of European exploration, chronicling and mapping the coasts of Africa and Asia, then known as the East Indies, and Canada and Brazil, in what came to be known as the Age of Discovery.
Indian Mozambicans form the sixth-largest Indian diaspora community in Africa, according to the statistics of India's Ministry of External Affairs. Roughly 70,000 people of Indian descent reside in Mozambique, as well as 870 Indian expatriates.

There are currently over 60,000 people of Indian origin in Tanzania. Many of them are traders and they control a sizeable portion of the Tanzanian economy. Indians have a long history in Tanzania starting with the arrival of Gujarati traders. They came to gradually control the trade in Zanzibar. Many of the buildings constructed then still remain in Stone Town, the focal trading point on the island.

Colva is a seaside village situated in Salcete subdistrict, South Goa district, Goa state on the west coast of India. Colva Beach spans about 2.5 km (1.6 mi) along a sandy coastline of approximately 25 km (16 mi) extending from Bogmalo in the north to Cabo de Rama in the south.
The captain of a steam ship naturally chooses the shortest route to nearby destinations. Since a sailing ship is usually pushed by winds and currents, its captain must find a route where the wind will probably blow in the right direction. Tacking, i.e. using contrary wind to pull (sic) the sails, was always possible but wasted time because of the zigzagging required, and this would significantly delay long voyages. The early European explorers were not only looking for new lands. They also had to discover the pattern of winds and currents that would carry them where they wanted to go. During the age of sail winds and currents determined trade routes and therefore influenced European imperialism and modern political geography. For an outline to the main wind systems see Global wind patterns.
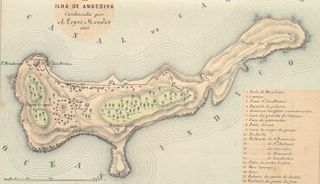
Fort Anjediva, built on the Anjadip Island, off the coast of the Indian state of Karnataka but under the administrative jurisdiction of the Indian state of Goa, was once under Portuguese rule. The island of Anjadip has an area of 1.5 square kilometres (0.58 sq mi).
Gaspar da Gama also known as Gaspar da India and Gaspar de Almeida was an interpreter and guide to several fleets of the Portuguese maritime explorations. He was of Jewish origin and was probably born in Poznań in the Kingdom of Poland. In 1498 he was taken captive aboard Vasco da Gama's fleet on its return voyage to Portugal from India. He was known to speak multiple languages including Hebrew and Chaldean, as well as a mixture of Italian and Spanish.

The Portuguese Indian Armadas were the fleets of ships funded by the Crown of Portugal, and dispatched on an annual basis from Portugal to India. The principal destination was Goa, and previously Cochin. These armadas undertook the Carreira da Índia from Portugal, following the maritime discovery of the Cape route, to the Indian Subcontinent by Vasco da Gama in 1497–99. During the Dutch occupation of Cochin and the Dutch siege of Goa, the harbour of Bom Bahia, now known as Mumbai (Bombay), off the coast of the northern Konkan region, served as the standard diversion for the armadas.

Luso-Indians or Portuguese-Indian, is a subgroup of the larger multiracial ethnic creole people of Luso-Asians. Luso-Indians are people who have mixed varied Indian subcontinent and European Portuguese ancestry or people of Portuguese descent born or living or originating in former Portuguese Indian colonies, the most important of which were Goa and Damaon of the Konkan region in the present-day Republic of India, and their descendants/ diaspora around the world, the Anglosphere, Lusosphere, Portuguese East Indies etc. Luso-Asians of the Indian subcontinent are primarily from Velha Goa, Damaon, Dio district, St Mary's islands of Mangalore, Bombay (Mumbai), Korlai (Chaul), Vasai (Bassein), Silvassa, Cape Comorin, Fort Cochin etc. There are also a number of New Christian Brahmins and Christian Cxatrias with Portuguese surnames, but do not necessarily possess European ancestry, being named as such in the process of their religious conversion to Western Christianity by Portuguese missionaries in the sixteenth century. This was done to prevent Hindu caste based discrimination among the native converts. Nevertheless, they are in many cases indistinguishable from the wider Luso-Indian population.

The Goan Muslims are a minority community who follow Islam in the Indian coastal state of Goa, some are also present in the union territory of Damaon, Diu& Silvassa. They are native to Goa, unlike recent Muslim migrants from mainland India and are commonly referred to as Moir by Goans in Goan Konkani. Moir is derived from the Portuguese word mour. The Portuguese called them Mouros because they were in contact with the Moors, people of predominantly Muslim Maghreb country, who had conquered and colonised the Iberian peninsula for centuries.

Goa is a state on the southwestern coast of India within the Konkan region, geographically separated from the Deccan highlands by the Western Ghats. It is located between the Indian states of Maharashtra to the north and Karnataka to the east and south, with the Arabian Sea forming its western coast. It is India's smallest state by area and its fourth-smallest by population. Goa has the highest GDP per capita among all Indian states, two and a half times as high as the GDP per capita of the country as a whole. The Eleventh Finance Commission of India named Goa the best-placed state because of its infrastructure, and India's National Commission on Population rated it as having the best quality of life in India. It is the third-highest ranking among Indian states in the human development index.
Luso-Asians are people whose ethnicity is partially or wholly Portuguese and ancestrally are based in or hail primarily from Portugal, South Asia, Southeast Asia, and East Asia. They historically came under the cultural and multi-ethnic sway of the Portuguese Empire in the East and retain certain aspects of the Portuguese language, Roman Catholic faith, and Latin cultural practices, including internal and external architecture, art, and cuisine that reflect this contact. The term Luso comes from the Roman empire's province of Lusitania, it roughly corresponds to modern Portugal.

















