
Flounders are a group of flatfish species. They are demersal fish, found at the bottom of oceans around the world; some species will also enter estuaries.
Sea bass is a common name for a variety of different species of marine fish. Many fish species of various families have been called sea bass.

Halibut is the common name for three species of flatfish in the family of right-eye flounders.In some regions, and less commonly, other species of large flatfish are also referred to as halibut.

The chum salmon, also known as dog salmon or keta salmon, is a species of anadromous salmonid fish from the genus Oncorhynchus native to the coastal rivers of the North Pacific and the Beringian Arctic, and is often marketed under the trade name silverbrite salmon in North America. The English name "chum salmon" comes from the Chinook Jargon term tsəm, meaning "spotted" or "marked"; while keta in the scientific name comes from Russian, which in turn comes from the Evenki language of Eastern Siberia. The term 'Dog Salmon' is most commonly used in Alaska and refers to the Salmon whose flesh Alaskans use to feed their dogs.

Pleuronectidae, also known as righteye flounders, are a family of flounders. They are called "righteye flounders" because most species lie on the sea bottom on their left sides, with both eyes on their right sides. The Paralichthyidae are the opposite, with their eyes on the left side. A small number of species in Pleuronectidae can also have their eyes on the left side, notably the members of the genus Platichthys.

The Antarctic silverfish, or Antarctic herring, is a species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Nototheniidae, the notothens or cod icefishes. It is native to the Southern Ocean and the only truly pelagic fish in the waters near Antarctica. It is a keystone species in the ecosystem of the Southern Ocean.

Hippoglossus stenolepis, the Pacific halibut, is a species of righteye flounder. This very large species of flatfish is native to the North Pacific and is fished by commercial fisheries, sport fishers, and subsistence fishers.

The Atlantic halibut is a flatfish of the family Pleuronectidae. They are demersal fish living on or near sand, gravel or clay bottoms at depths of between 50 and 2,000 m. The halibut is among the largest teleost (bony) fish in the world, and is a threatened species owing to a slow rate of growth and overfishing. Halibut are strong swimmers and are able to migrate long distances. Halibut size is not age-specific, but rather tends to follow a cycle related to halibut abundance.

Paralichthys adspersus, the fine flounder, is a species of large-tooth flounder native to the eastern Pacific Ocean, along the continental shelf from the coast of Ecuador in the north to the coast of Peru in the south.

Sebastolobus, the thornyheads, is a genus of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the subfamily Sebastinae, the rockfishes, part of the family Scorpaenidae. These fishes are native to the northern and eastern Pacific Ocean. They are generally found in deep waters.

Microstomus is a genus of righteye flounders native to the northern Pacific and north-eastern Atlantic oceans.

The Pacific sand sole, also known as simply sand sole, is a species of flatfish found in the north-eastern Pacific waters where it lives on sandy bottoms. It is the only species in the genus Psettichthys, and ranges from the Bering Sea to northern California.

Dissostichus, the toothfish, is a genus of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Nototheniidae, the notothens or cod icefish. These fish are found in the Southern Hemisphere. Toothfish are marketed in the United States as Chilean sea bass or less frequently as white cod. "Chilean sea bass" is a marketing name coined in 1977 by Lee Lantz, a fish wholesaler who wanted a more attractive name for selling the Patagonian toothfish to Americans. In 1994, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) accepted "Chilean sea bass" as an "alternative market name" for Patagonian toothfish. The toothfish was remarkably successful in the United States, Europe and Asia, and earned the nickname "white gold" within the market. Toothfish are vital to the ecological structure of Southern Ocean ecosystems. For this reason, on 4 September a national day is dedicated to the toothfish in South Georgia.

The Atka mackerel is a mackerel in the family Hexagrammidae. Atka mackerel are common in the northern Pacific Ocean, and are one of only two members of the genus Pleurogrammus - the other being the Arabesque greenling. The Atka mackerel was named for Atka Island, the largest island of the Andreanof islands, a branch of the Aleutians.

Eumicrotremus is a genus of lumpfishes native to the northern oceans. The name for this genus comes from the Greek roots eu meaning "good", mikros meaning "small" or "little", and trema meaning "hole".

The redbanded rockfish, also known as the bandit, barber pole, flag rockfish, Spanish flag, Hollywood, convict, and canary, is a species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the subfamily Sebastinae, the rockfishes, part of the family Scorpaenidae. It is found in the northern Pacific Ocean.
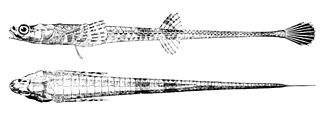
The alligatorfish, also known commonly as the Aleutian alligatorfish and the Atlantic alligatorfish, is a fish in the family Agonidae. It was described by Marcus Elieser Bloch in 1786. It is a marine, temperate water-dwelling fish which is known from the northwestern Atlantic Ocean, including western Greenland; Labrador, Canada; and Cape Cod, Massachusetts, USA. It dwells at a depth range of 0–695 metres, most often around 60–150 m, and inhabits sand and mud bottoms mostly on the lower continental shelf all year. It prefers a temperature range of -1.07 to 2.52 °C. Males can reach a maximum total length of 22 centimetres, but more commonly reach a TL of 14.2 cm.

Sebastes melanostictus, the blackspotted rockfish, is a species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the subfamily Sebastinae, the rockfishes, part of the family Scorpaenidae. It is found in the northern Pacific Ocean.



















