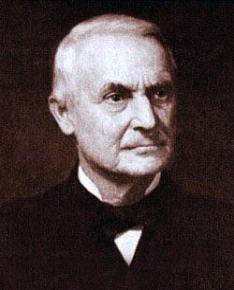John Moses Browning was an American firearm designer who developed many varieties of military and civilian firearms, cartridges, and gun mechanisms, many of which are still in use around the world. He made his first firearm at age 13 in his father's gun shop and was awarded the first of his 128 firearm patents on October 7, 1879, at the age of 24. He is regarded as one of the most successful firearms designers of the 19th and 20th centuries and a pioneer of modern repeating, semi-automatic, and automatic firearms.

Samuel Colt was an American inventor, industrialist, and businessman who established Colt's Patent Fire-Arms Manufacturing Company and made the mass production of revolvers commercially viable.

Sharps Rifle Manufacturing Company was the manufacturer of the Sharps Rifle. The company was organized by Samuel Robbins and Richard S. Lawrence as a holding company in Hartford, Connecticut, on October 9, 1851 with $100,000 in capital. Despite Sharps departing from the company bearing his name, Sharps Rifle Manufacturing Company produced over 100,000 rifles, but it dissolved in 1881 with the widespread use of repeating rifles.

Colt's Manufacturing Company, LLC is an American firearms manufacturer, founded in 1855 by Samuel Colt and now a subsidiary of Czech holding company Colt CZ Group. It is the successor corporation to Colt's earlier firearms-making efforts, which started in 1836. Colt is known for the engineering, production, and marketing of firearms, most especially between the 1850s and World War I, when it was a dominating force in its industry and a seminal influence on manufacturing technology. Colt's earliest designs played a major role in the popularization of the revolver and the shift away from single-shot pistols. Although Samuel Colt did not invent the revolver concept, his designs resulted in the first very successful model.
The Winchester Repeating Arms Company was a prominent American manufacturer of repeating firearms and ammunition. The firm was established in 1866 by Oliver Winchester and was located in New Haven, Connecticut. The firm went into receivership in 1931 and was bought by the Western Cartridge Company, a forerunner of the Olin Corporation. The Winchester brand name is still owned by the Olin Corporation, which makes ammunition under that name. The Winchester name is also used under license for firearms produced by two subsidiaries of the Herstal Group – FN Herstal of Belgium and the Browning Arms Company of Ogden, Utah.
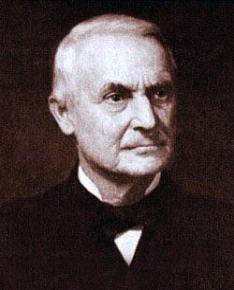
Horace Smith was an American gunsmith, inventor, and businessman. He and his business partner Daniel B. Wesson formed two companies named "Smith & Wesson", the first of which was eventually reorganized into the Winchester Repeating Arms Company and the latter of which became the modern Smith & Wesson.

William Mason was a patternmaker, engineer and inventor who worked for Remington Arms, Colt's Patent Fire Arms Manufacturing Company, and Winchester Repeating Arms Company in the 19th century.

Charles Ethan Billings (1834–1920) was an American mechanical engineer, inventor, superintendent, and businessman. He held various U.S. patents on hand tools, either assigned or licensed to the firm that he and Christopher M. Spencer cofounded, the Billings & Spencer Company. His name as patent holder is stamped on countless forged hand tools, many of which survive. Billings was an expert in drop forging and was an influential leader in the American system of manufacturing and its successor systems of mass production for firearms, sewing machines, hand tools, bicycles, and other goods. He served as president of the American Society of Mechanical Engineers in 1895 and 1896. The Billings & Spencer Company was both a machine tool builder and a manufacturer of hand tools made with its machine tools.

The Eli Whitney Museum, in Hamden, Connecticut, is an experimental learning workshop for students, teachers, and families. The museum's main building is located on a portion of the Eli Whitney Gun Factory site, a gun factory erected by Eli Whitney in 1798. The museum focuses on teaching experiments that are the roots of design and invention, featuring hands-on building projects and exhibits on Whitney and A. C. Gilbert.

Colt Defense LLC, together with its subsidiaries, is an American designer, developer and manufacturer of small arms weapons systems for individual soldiers and law enforcement personnel. It is headquartered in West Hartford, Connecticut. The company traces its portfolio of products and services back to Colt's Manufacturing Company and prior to that to Colt's Patent Firearms Manufacturing Company.

Eli Terry Sr. was an inventor and clockmaker in Connecticut. He received a United States patent for a shelf clock mechanism. He introduced mass production to the art of clockmaking, which made clocks affordable for the average American citizen. Terry occupies an important place in the beginnings of the development of interchangeable parts manufacturing. Terry is considered the first person in American history to actually accomplish interchangeable parts with no government funding. Terry became one of the most accomplished mechanics in New England during the early part of the nineteenth century. The village of Terryville, Connecticut is named for his son, Eli Terry Jr.
Pope Manufacturing Company was founded by Albert Augustus Pope around 1876 in Boston, Massachusetts, US and incorporated in Hartford, Connecticut in 1877. Manufacturing of bicycles began in 1878 in Hartford at the Weed Sewing Machine Company factory. Pope manufactured bicycles, motorcycles, and automobiles. From 1905 to 1913, Pope gradually consolidated manufacturing to the Westfield Mass plant. The main offices remained in Hartford. It ceased automobile production in 1915 and ceased motorcycle production in 1918. The company subsequently underwent a variety of changes in form, name and product lines through the intervening years. To this day, bicycles continue to be sold under the Columbia brand.

The Colt Armory is a historic factory complex for the manufacture of firearms, created by Samuel Colt. It is located in Hartford, Connecticut along the Connecticut River, and as of 2008 is part of the Coltsville Historic District, named a National Historic Landmark District. It is slated to become part of Coltsville National Historical Park, now undergoing planning by the National Park Service.

The Colt New Model revolving rifles were early repeating rifles produced by the Colt's Manufacturing Company from 1855 until 1864. The design was essentially similar to revolver type pistols, with a rotating cylinder that held five or six rounds in a variety of calibers from .36 to .64 inches. They were mainly based upon the Colt Model 1855 Sidehammer Pocket Revolver developed by Elisha K. Root. Colt revolving pistols and rifles were attractive mainly because of their high rate of fire. They were used to a limited extent on the Pony Express and made a brief appearance in the American Civil War. However, the rifles were generally disliked by soldiers, and were ultimately discontinued due to serious design flaws.

O. F. Mossberg & Sons is an American firearms manufacturer, specializing in shotguns, rifles, scopes, and pistol accessories.
Daniel Leavitt was an early American inventor who, with his partner Edwin Wesson, patented the first revolver after Samuel Colt's, and subsequently manufactured one of the first American revolving pistols. The innovative design was manufactured only briefly before a patent suit by Colt forced the company to stop producing the Leavitt & Wesson Dragoon revolver. But Leavitt's early patents, and those of his partner Wesson, stoked competition and helped drive the technological and manufacturing boom that produced the modern firearms industry.
Robert Hillberg was a firearm designer and the head of Research & Development at the High Standard Manufacturing Company. His designs included the folding shotgun stock, the Whitney Wolverine lightweight pistol, Wildey .45 gas-operated pistol, COP .357 Derringer pistol, and M60 machine gun. Hillberg developed a variety of insurgency weapons, primarily multiple barrel shotguns, which could be covertly distributed to partisan forces fighting in the United States' national interests. Gun Digest editors have described Hillberg as a "national treasure."

Christopher Miner Spencer was an American inventor, from Manchester, Connecticut, who invented the Spencer repeating rifle, one of the earliest models of lever-action rifle, a steam powered "horseless carriage", and several other inventions. He developed the first fully automatic turret lathe, which in its small- to medium-sized form is also known as a screw machine.

Frog Hollow is one of the neighborhoods of Hartford, Connecticut. It is a predominantly working-class residential area, bounded on the north by Capitol Avenue, the east by Lafayette Street, the south by Madison and Hamilton Streets, and on the west by Interstate 84. The neighborhood was developed between about 1850 and 1930, and still contains a remarkable concentration of residential housing from that period. The entire neighborhood, covering more than 150 acres (61 ha) and including more than 900 buildings, is listed on the National Register of Historic Places.