
The Battle of Amberg, fought on 24 August 1796, resulted in an Habsburg victory by Archduke Charles over a French army led by Jean-Baptiste Jourdan. This French Revolutionary Wars engagement marked a turning point in the campaign, which had previously seen French successes.
The Battle of Rastatt saw part of a Republican French army under Jean Victor Marie Moreau clash with elements of the Habsburg army under Maximilian Anton Karl, Count Baillet de Latour which were defending the line of the Murg River. Leading a wing of Moreau's army, Louis Desaix attacked the Austrians and drove them back to the Alb River in the War of the First Coalition action. Rastatt is a city in the state of Baden-Württemberg in Germany, located 89 kilometers (55 mi) south of Mannheim and 94 kilometres (58 mi) west of Stuttgart.

Louis Lazare Hoche was a French soldier who rose to be general of the Revolutionary army. He won a victory over Royalist forces in Brittany. His surname is one of the names inscribed under the Arc de Triomphe, on Column 3. Richard Holmes says he was "quick-thinking, stern, and ruthless...a general of real talent whose early death was a loss to France." A famous statement of general Hoche: "Facta, non verba"

Henri de La Tour d'Auvergne, vicomte de Turenne, often called simply Turenne, was a French Marshal General and the most illustrious member of the La Tour d'Auvergne family. His military exploits over his five-decade career earned him a reputation as one of the greatest generals in modern history.

The French Revolutionary Wars were a series of sweeping military conflicts lasting from 1792 until 1802 and resulting from the French Revolution. They pitted France against Great Britain, Austria, Prussia, Russia and several other monarchies. They are divided in two periods: the War of the First Coalition (1792–97) and the War of the Second Coalition (1798–1802). Initially confined to Europe, the fighting gradually assumed a global dimension. After a decade of constant warfare and aggressive diplomacy, France had conquered a wide array of territories, from the Italian Peninsula and the Low Countries in Europe to the Louisiana Territory in North America. French success in these conflicts ensured the spread of revolutionary principles over much of Europe.

The Franco-Dutch War, often just the Dutch War, was a conflict that lasted from 1672 to 1678 between the Dutch Republic and France, each supported by allies. France had the support of England and Sweden, while the Dutch were supported by Spain, the Holy Roman Empire and Denmark.

The Army of Sambre and Meuse was one of the armies of the French Revolution. It was formed on 29 June 1794 by combining the Army of the Ardennes, the left wing of the Army of the Moselle and the right wing of the Army of the North. Its maximum paper strength was approximately 83,000.

The Battle of Salzbach or Sasbach was fought July 27, 1675, between the armies of France and the Holy Roman Empire, during the Franco-Dutch War. The term "battle" is something of a misnomer because the encounter consisted primarily of an artillery duel. However, it was costly for the French: the great French marshal, the Vicomte de Turenne, was killed by a cannonball. The Imperial army was commanded by the Italian Field Marshal Raimondo Montecuccoli.

48°7′17″N7°50′57″E
Crossing of the Rhine or Rhine crossing may refer to:

The Battle of Sinsheim took place on 16 June 1674 during the 1672-1678 Franco-Dutch War. An Imperial force commanded by Aeneas de Caprara was marching towards Heidelberg, in order to join their main army under Alexander von Bournonville. It was intercepted just outside Sinsheim by the French commanded by Turenne; the Imperialists repulsed the first two French assaults but were eventually forced to retreat.
The Battle of Mulhouse occurred on December 29, 1674, during the Franco-Dutch War between the French army and troops of the Holy Roman Empire and its allies, as part of Turenne's Winter Campaign. The French army was commanded by the Vicomte de Turenne and the imperial army was led by Prince Alexandre-Hippolyte de Bournonville.
At the Battle of Höchst, the Habsburg Austrian army commanded by François Sébastien Charles Joseph de Croix, Count of Clerfayt outmaneuvered the French Republican Army of Sambre-et-Meuse commanded by Jean-Baptiste Jourdan. Although the French attacked first, they were unable to dislodge an Austrian flanking column. Afterward Jourdan's army retreated to the north. The clash happened during the War of the First Coalition, part of a wider conflict known as the French Revolutionary Wars. Modern-day Höchst is a suburb and administrative district of Frankfurt am Main in the state of Hesse in Germany. Höchst is about 12 kilometers (7 mi) west of the Frankfurt city center.

In the Rhine campaign of 1796, two First Coalition armies under the overall command of Archduke Charles outmaneuvered and defeated two French Republican armies. This was the last campaign of the War of the First Coalition, part of the French Revolutionary Wars.

Sometimes called the Battle of Limburg or Second Battle of Altenkirchen or Battle of the Lahn, this was actually a single-day battle followed by a lengthy rear-guard action. The action occurred during the War of the First Coalition, part of a wider conflict known as the French Revolutionary Wars. Limburg an der Lahn is located in the state of Hesse in Germany about 31 miles (50 km) east of Koblenz. On 16 September, the Habsburg Austrian army commanded by Archduke Charles, Duke of Teschen attacked a Republican French army led by Jean-Baptiste Jourdan in its positions behind the Lahn River. The unexpected collapse and withdrawal of their right flank on the evening of the 16th compelled the French to make a fighting withdrawal that began in the evening of the 16th and continued until late on 19 September.
In the Rhine campaign of 1795, two Habsburg Austrian armies under the command of François Sébastien Charles Joseph de Croix, Count of Clerfayt, defeated two Republican French armies attempting to invade the south German states of the Holy Roman Empire. At the start of the campaign, the French Army of the Sambre and Meuse, led by Jean-Baptiste Jourdan, confronted Clerfayt's Army of the Lower Rhine in the north, while the French Army of the Rhine and Moselle, under Jean-Charles Pichegru, lay opposite Dagobert Sigmund von Wurmser's Army of the Upper Rhine in the south. A French offensive failed in early summer but in August, Jourdan crossed the Rhine and quickly seized Düsseldorf. The Army of the Sambre and Meuse advanced south to the Main River, isolating Mainz. Pichegru's army made a surprise capture of Mannheim and both French armies held significant footholds on the east bank of the Rhine.

During the Battle of Kehl, a Republican French force under the direction of Jean Charles Abbatucci mounted an amphibious crossing of the Rhine River against a defending force of soldiers from the Swabian Circle. In this action of the War of the First Coalition, the French drove the Swabians from their positions in Kehl and subsequently controlled the bridgehead on both sides of the Rhine.
The Battle of Maudach occurred on 15 June 1796 between the French Revolutionary Army and the Army of the First Coalition. This was the opening action of the Rhine Campaign of 1796 on the Upper Rhine, slightly north of the town of Kehl. The Coalition, commanded by Franz Petrasch, lost 10 percent of its manpower missing, killed or wounded. It was fought at the village of Maudach, southwest of Ludwigshafen on the Rhine river opposite Mannheim. Maudach lies 10 km (6 mi) northwest of Speyer and today is a southwest suburb of Ludwigshafen; a principal town on the Rhine river in 1796.
The Battle of Ortenbach, also known as the Battle of Gengenbach, took place on 23 July 1678 during the closing stages of the 1672-1678 Franco-Dutch War, in the modern German state of Baden-Württemberg. It featured a French army commanded by François de Créquy and an Imperial force under Charles V, Duke of Lorraine.
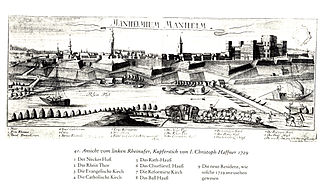
The Action at Mannheim 1795 began in April 1795 when two French armies crossed the Rhine and converged on the confluence of the Main and the Rhine. Initial action at Mannheim resulted in a minor skirmish, but the Bavarian commander negotiated a quick truce with the French and withdrew. On 17 October 1795, 17,000 Habsburg Austrian troops under the command of Dagobert Sigmund von Wurmser engaged 12,000 soldiers, led by Jean-Charles Pichegru in the grounds outside the city of Mannheim. In a combination of maneuvers, the Habsburg army forced 10,000 of the French forces to withdraw into the city itself; other French troops fled to join neighboring Republican armies. First Coalition forces then laid siege to Mannheim. Subsequent action at neighboring cities forced the French to withdraw further westward toward France; after a month's siege, the 10,000-strong Republican French garrison now commanded by Anne Charles Basset Montaigu surrendered to 25,000 Austrians commanded by Wurmser. This surrender brought the 1795 campaign in Germany to an end. The battle and siege occurred during the War of the First Coalition, part of the French Revolutionary Wars. Situated on the Rhine River at its confluence with the Neckar River, Mannheim lies in the federal state of Baden-Württemberg in modern-day Germany.














