
Within Christianity, there are a variety of views on sexual orientation and homosexuality. Even within a denomination, individuals and groups may hold different views, and not all members of a denomination necessarily support their church's views on homosexuality. Various mainline protestant denominations have taken a supportive stance towards blessing homosexual clergy and same sex marriage while others such as the Catholic church have not.

Anti-LGBT rhetoric comprises themes, catchphrases, and slogans that have been used against homosexuality or other non-heterosexual sexual orientations in order to demean lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people. They range from the demeaning and the pejorative to expressions of hostility towards homosexuality which are based on religious, medical, or moral grounds. It is a form of hate speech which is illegal in countries such as the Netherlands, Norway, and Sweden.

The Family Research Council (FRC) is an American evangelical activist group and think-tank with an affiliated lobbying organization. FRC promotes what it considers to be family values. It opposes and lobbies against: access to pornography, embryonic stem-cell research, abortion, divorce, and LGBT rights. The FRC has been criticized by media sources and professional organizations such as the American Sociological Association for using "anti-gay pseudoscience" to falsely conflate homosexuality and pedophilia, and falsely to claim that the children of same-sex parents suffer from more mental health problems.

"Gay agenda" is a term introduced by sectors of the Christian religious right as a disparaging way to describe the advocacy of cultural acceptance and normalization of non-heterosexual sexual orientations and relationships. The term originated among social conservatives in the United States and has been adopted in other nations with active anti-LGBT movements such as Hungary and Uganda.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual and transgender (LGBT) people in Ukraine face legal challenges not experienced by non-LGBT people. Same-sex sexual activity between consenting adults is legal in Ukraine, but prevailing social attitudes are often intolerant of LGBT people, and households headed by same-sex couples are not eligible for any of the same legal protections and recognition available to opposite-sex couples.
Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) persons in Ghana face legal and societal challenges not experienced by non-LGBT citizens.
Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) persons in Jamaica face legal and social issues not experienced by non-LGBT people. Sexual intercourse between same-sex partners is legally punishable by imprisonment, torture, vigilante executions, and vigilante beatings.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in Moldova face legal and social challenges and discrimination not experienced by non-LGBT residents. Households headed by same-sex couples are not eligible for the same rights and benefits as households headed by opposite-sex couples. Same-sex unions are not recognized in the country, so consequently same-sex couples have little to no legal protection. Nevertheless, Moldova bans discrimination based on sexual orientation in the workplace, and same-sex sexual activity has been legal since 1995.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people living in Rwanda face legal challenges not experienced by non-LGBT residents. While neither homosexuality nor homosexual acts are illegal, homosexuality is considered a taboo topic, and there is no significant public discussion of this issue in any region of the country. No special legislative protections are afforded to LGBT citizens, and same-sex marriages are not recognized by the state, as the Constitution of Rwanda provides that "[o]nly civil monogamous marriage between a man and a woman is recognized". LGBT Rwandans have reported being harassed, blackmailed, and even arrested by the police under various laws dealing with public order and morality.

Both male and female homosexual activity is illegal in Uganda. Under the Penal Code, "carnal knowledge against the order of nature" between two males carries a potential penalty of life imprisonment.
Seventh-day Adventist Kinship International is a support organization that provides a spiritual and social community to current and former Seventh-day Adventists who are lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender, asexual and/or intersex (LGBTI), and have felt hurt or rejected because of their sexual orientation and/or gender identity. SDA Kinship offers them the compassion and support perceived to not be available within the organized Adventist Church.
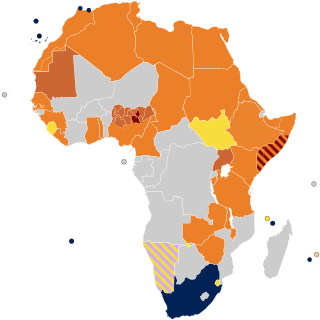
With the exception of South Africa and Cape Verde, lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) rights in Africa are limited in comparison to the United States, Canada, Western Europe, Australia, and New Zealand. Out of the 54 states recognised by the United Nations or African Union or both, the International Gay and Lesbian Association stated in 2015 that homosexuality is outlawed in 34 African countries. Human Rights Watch notes that another two countries, Benin and the Central African Republic, do not outlaw homosexuality, but have certain laws which discriminate against homosexual individuals.
Many views are held or have been expressed by religious organizations in relation to same-sex marriage. Arguments both in favor of and in opposition to same-sex marriage are often made on religious grounds and/or formulated in terms of religious doctrine. Although many of the world's religions are opposed to same-sex marriage, the number of religious denominations that are conducting same-sex marriages have been increasing since 2010. Religious views on same-sex marriage are closely related to religious views on homosexuality.

The Anti-Homosexuality Act, 2014 was an act passed by the Parliament of Uganda on 20 December 2013, which prohibited sexual relations between persons of the same sex. The act was previously called the "Kill the Gays bill" in the western mainstream media due to death penalty clauses proposed in the original version, but the penalty was later amended to life in prison. The bill was signed into law by the President of Uganda Yoweri Museveni on 24 February 2014. On 1 August 2014, however, the Constitutional Court of Uganda ruled the act invalid on procedural grounds.

Christopher Senyonjo is a clergyman and campaigner for LGBT rights in Uganda. He was elevated to bishop in the Church of Uganda in 1974 and retired in 1998. In 2001, he was barred from performing services. Whilst it is widely claimed that this is because of his stance on gay rights, the church claims that it was because of his participation in the consecration of a man to be a bishop of a church with which the Church of Uganda is not in communion. He has since worked with the Charismatic Church of Uganda and the progressive Episcopal Church of the United States, and founded Integrity Uganda and the Saint Paul's Reconciliation and Equality Centre in Kampala. In 2006 the Church of Uganda declared him "no longer a bishop" and revoked all remaining privileges for his involvement with the Charismatic denomination. For his stance Senyonjo has received several honours including the Clinton Global Citizen Award, and has been invited to participate in documentaries and international speaking tours.

David Kato Kisule was a Ugandan teacher and LGBT rights activist, considered a father of Uganda's gay rights movement and described as "Uganda's first openly gay man". He served as advocacy officer for Sexual Minorities Uganda (SMUG).

The majority of the countries of the Commonwealth of Nations, formerly known as the British Commonwealth, still criminalise sexual acts between consenting adults of the same sex and other forms of sexual orientation, gender identity and expression. Homosexual activity remains a criminal offence in 35 of the 54 sovereign states of the Commonwealth; and legal in only 19.
This is a timeline of notable events in the history of non-heterosexual conforming people of African ancestry, who may identify as LGBTIQGNC, men who have sex with men, or related culturally specific identities. This timeline includes events both in Africa, the Americas and Europe and in the global African diaspora, as the histories are very deeply linked.

The political activity of the Catholic Church on LGBT issues mainly consists of efforts made by the Catholic Church to support or oppose civil government legislation on issues of importance to LGBT people. The Church generally condemns all forms of violence against gay and lesbian people. However, the Church in certain countries has occasionally resisted efforts to decriminalize homosexuality or to introduce measures to tackle discrimination. The Catholic Church also supports legally defining marriage in civil legislation as the union of one man and one woman, therefore generally opposing efforts to introduce gay civil unions and gay marriage – although some clergymen have expressed support for same-sex unions. The Church teaches that not all discrimination is "unjust," and that discrimination against gay people in some spheres of life serves the common good.
















