
Liptó County was an administrative county (comitatus) of the Kingdom of Hungary. Its territory is now in northern Slovakia.
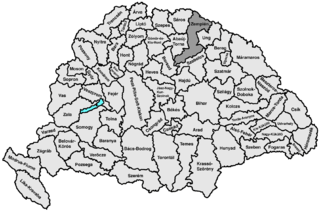
Zemplén was an administrative county (comitatus) of the Kingdom of Hungary. The northern part of its territory is now situated in eastern Slovakia, while a smaller southern portion of the former county belongs to Hungary, as part of Borsod-Abaúj-Zemplén County.

Bars was an administrative county (comitatus) of the Kingdom of Hungary. Its territory is now in central and southern Slovakia. Today in Slovakia, Tekov is the informal designation of the corresponding territory.

Turóc, Slovak: Turiec, Latin: Thurotzium/comitatus Thurociensis, German: Turz) was an administrative county (comitatus) of the Kingdom of Hungary. Its territory is now in north-western Slovakia, where the corresponding Slovak name Turiec is only an informal designation of the corresponding territory.
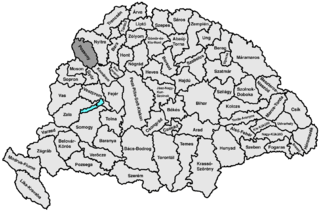
Pozsony county was an administrative county (comitatus) of the Kingdom of Hungary. Its territory is now mostly part of Slovakia, while a small area belongs to Hungary. In 1969, the three villages that remained in Hungary were combined to form Dunasziget.

Nyitra County was an administrative county (comitatus) of the Kingdom of Hungary. Its territory lay in what is now western Slovakia.

Heves was an administrative county in the Kingdom of Hungary. Its territory, which is now in northern Hungary, was slightly larger than that of present Heves county. The capital of the county was Eger.

Trencsén county was an administrative county (comitatus) of the Kingdom of Hungary. Its territory is now in western Slovakia.

Zólyom county was an administrative county (comitatus) of the Kingdom of Hungary. Its territory is now in central Slovakia.

Borsod was an administrative county (comitatus) of the Kingdom of Hungary. The capital of the county was Miskolc. After World War II, the county was merged with the Hungarian parts of Abaúj-Torna County and Zemplén counties to form Borsod-Abaúj-Zemplén county.
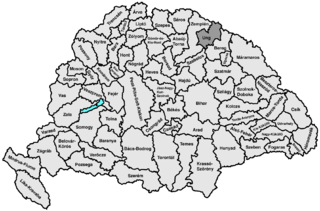
Ung County was an administrative county (comitatus) of the Kingdom of Hungary. Its territory is now mostly in western Ukraine, a smaller part in eastern Slovakia, and a very small area in Hungary.

Máramaros County was an administrative county (comitatus) of the Kingdom of Hungary. Its territory is now in north-western Romania and western Ukraine. The capital of the county was Máramarossziget.
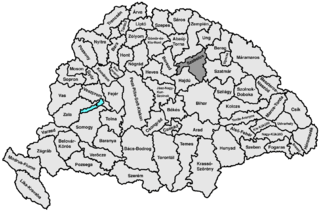
Szabolcs was an administrative county (comitatus) of the Kingdom of Hungary. Its territory is now part of Hungary, except for three villages which are in the Zakarpattia Oblast of Ukraine. The capital of the county was Nyíregyháza.

Ugocsa was an administrative county (comitatus) of the Kingdom of Hungary. Its territory is now in north-western Romania and western Ukraine. The capital of the county was Nagyszőllős. It was the smallest among the counties of historical Hungary.

Fogaras was an administrative county (comitatus) of the Kingdom of Hungary. Its territory is now in central Romania. The county's capital was Fogaras.

Kolozs County was an administrative county (comitatus) of the Kingdom of Hungary, of the Eastern Hungarian Kingdom and of the Principality of Transylvania. Its territory is now in north-western Romania. The capital of the county was Kolozsvár.

Árva County was an administrative county (comitatus) of the Kingdom of Hungary since the 14th century until 1920. Its territory is now in northern Slovakia and southern Poland. Today, the Slovak name is only used as an informal designation of the corresponding territory.

Gömör-Kishont was an administrative county (comitatus) of the Kingdom of Hungary. Its capital was Rimaszombat. Most of its territory is now part of Slovakia, while a smaller part belongs to Hungary.

Nógrád was an administrative county of the Kingdom of Hungary. Its territory is now divided between Hungary and Slovakia. The name Novohrad is still used in Slovakia as an informal designation of the corresponding territory. The name is derived from the former Nógrád castle in Hungary.
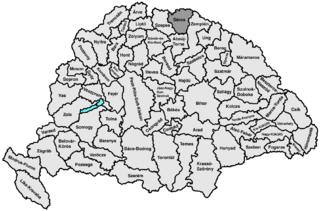
Sáros was an administrative county (comitatus) of the Kingdom of Hungary. Its territory is now in northeastern Slovakia. Today, Šariš is only an informal designation of the corresponding territory.


























