Obstetrics and gynaecology is the medical specialty that encompasses the two subspecialties of obstetrics and gynaecology. The specialization is an important part of care for women's health.

A wet nurse is a woman who breastfeeds and cares for another's child. Wet nurses are employed if the mother dies, or if she is unable or chooses not to nurse the child herself. Wet-nursed children may be known as "milk-siblings", and in some cultures, the families are linked by a special relationship of milk kinship. Wet-nursing existed in cultures around the world until the invention of reliable formula milk in the 20th century. The practice has made a small comeback in the 21st century.

Henry Ford Hospital (HFH) is an 877-bed tertiary care hospital, education and research complex at the western edge of the New Center area in Detroit, Michigan. The flagship facility for the Henry Ford Health System, it was one of the first hospitals in the United States to use a standard fee schedule and favor private or semi-private rooms over large wards. It was the first hospital in the country to form a closed, salaried medical staff. As founder Henry Ford viewed tobacco as being unhealthy, the hospital was one of the first in the United States to institute a total ban on smoking. Henry Ford Hospital is staffed by the Henry Ford Medical Group, one of the nation's largest and oldest group practices with 1,200 physicians in more than 40 specialties.

The Wayne State University School of Medicine (WSUSOM) is the medical school of Wayne State University, a public research university in Detroit, Michigan. It enrolls more than 1,500 students in undergraduate medical education, master's degree, Ph.D., and M.D.-Ph.D. WSUSOM traces its roots through four predecessor institutions since its founding in 1868.
A human milk bank is "a service which collects, screens, processes, and dispenses by prescription human milk donated by nursing mothers who are not biologically related to the recipient infant". As of November 2019, there are 28 milk banks in North America that are members of the Human Milk Banking Association of North America (HMBANA). They are usually housed in hospitals, although some are free standing. Members of HMBANA follow the annually revised "Guidelines for the Establishment and Operation of a Donor Human Milk Bank" which include protocols for soliciting donors and collecting, processing, and distributing the milk. In addition, some states have required standards for donor human milk banks. However, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA), states that "the FDA has not been involved in establishing these voluntary guidelines or state standards." Some of these protocols are described below.

The Detroit Medical Center (DMC) is a for-profit alliance of hospitals that encompasses over 2,000 licensed beds, 3,000 affiliated physicians and over 12,000 employees. Located in Midtown Detroit, the DMC is affiliated with medical schools from Wayne State University and Michigan State University. Detroit Medical Center hospitals are staffed by physicians from the Michigan State University College of Osteopathic Medicine and the Wayne State University School of Medicine, the largest single-campus medical school in the United States and the nation's fourth largest medical school overall. The Detroit Medical Center is fully accredited by the Joint Commission on Accreditation of Healthcare Organizations.

Erotic lactation is sexual arousal by breastfeeding on a woman's breast. Depending on the context, the practice can also be referred to as adult suckling, adult nursing, and adult breastfeeding. Practitioners sometimes refer to themselves as being in an adult nursing relationship (ANR). Two persons in an exclusive relationship can be called a nursing couple.

Harbor–UCLA Medical Center, is a 570-bed public teaching hospital located at 1000 West Carson Street in West Carson, an unincorporated area within Los Angeles County, California. The hospital is owned by Los Angeles County and operated by the Los Angeles County Department of Health Services, while doctors are faculty of the David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA, who oversee the medical residents being trained at the facility.
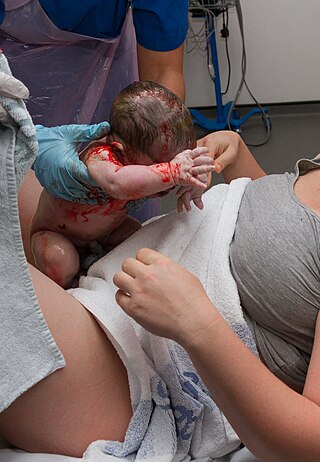
Maternal–fetal medicine (MFM), also known as perinatology, is a branch of medicine that focuses on managing health concerns of the mother and fetus prior to, during, and shortly after pregnancy.

Breastfeeding, or nursing, is the process by which human breast milk is fed to a child. Breast milk may be from the breast, or may be pumped and fed to the infant. The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends that breastfeeding begin within the first hour of a baby's life and continue as often and as much as the baby wants. Health organizations, including the WHO, recommend breastfeeding exclusively for six months. This means that no other foods or drinks, other than vitamin D, are typically given. The WHO recommends exclusive breastfeeding for the first 6 months of life, followed by continued breastfeeding with appropriate complementary foods for up to 2 years and beyond. Of the 135 million babies born every year, only 42% are breastfed within the first hour of life, only 38% of mothers practice exclusive breastfeeding during the first six months, and 58% of mothers continue breastfeeding up to the age of two years and beyond.

Detroit Receiving Hospital in Detroit, Michigan, is the state's first Level I Trauma Center. Receiving's emergency department treats more than 105,000 patients annually, and nearly 60% of Michigan's emergency physicians are trained at Receiving. Receiving also features the state's largest burn center, Michigan's first hospital-based 24/7 hyperbaric oxygen therapy program, and Metro Detroit's first certified primary stroke center. In addition, the hospital has a comprehensive neurosurgical unit. It is one of the eight hospitals and institutions that comprise the Detroit Medical Center.

Children's Hospital of Michigan (CHM) is a for-profit, pediatric acute care hospital located in Detroit, Michigan. The hospital has 227 beds and is affiliated with both the Wayne State University School of Medicine and the Michigan State University Medical School. The hospital provides comprehensive pediatric specialties and subspecialties to pediatric patients aged 0–21 throughout eastern Michigan and the Detroit area and is a part of the Detroit Medical Center. The hospital features the only freestanding pediatric Level 1 Pediatric Trauma Center in the Detroit region, 1 of 3 in the state. It is an international provider of pediatric neurology, neurosurgery, cardiology, oncology and diagnostic services including Positron Emission Tomography and MRI.

Harper University Hospital is one of eight hospitals and institutes that compose the Detroit Medical Center. Harper offers services in a broad range of clinical areas, including cardiology, neurology, neurosurgery, organ transplant, plastic surgery, general surgery, bariatric endocrinology and sleep disorders.
DMC Sinai-Grace Hospital is the largest of the eight hospitals that comprise the Detroit Medical Center. Located in northwest Detroit, Sinai-Grace provides health care services in over 40 specialties and has 334 inpatient beds, is a full-service hospital including comprehensive cardiac care, stroke, surgical intensive care, medical intensive care, trauma and emergency medicine, cancer treatment, general and robotic surgeries, women's health, urology, gastrointestinal, gerontology, obstetrics/gynecology and cosmetic/plastic surgery.

Lactation describes the secretion of milk from the mammary glands and the period of time that a mother lactates to feed her young. The process naturally occurs with all sexually mature female mammals, although it may predate mammals. The process of feeding milk in all female creatures is called nursing, and in humans it is also called breastfeeding. Newborn infants often produce some milk from their own breast tissue, known colloquially as witch's milk.
Charles Howard Wright was a Detroit physician and founder of the Charles H. Wright Museum of African American History.

A human milk bank, breast milk bank or lactarium is a service that collects, screens, processes, pasteurizes, and dispenses by prescription human milk donated by nursing mothers who are not biologically related to the recipient infant. The optimum nutrition for newborn infants is breast milk for at least the first 6 months of life. For women who are unable to breast feed or produce enough milk, pasteurized donor breast milk may be an effective approach to feeding. Breast milk supplied by a woman other than the baby's mother that is not pasteurized and informal breast milk sharing is associated with a risk of transmitting bacteria and viruses from the donor mother to the baby and is not considered a safe alternative. If pasteurized donor breast milk is not available, commercial formula is suggested as a second alternative.

Monroe Carell Jr. Children's Hospital at Vanderbilt, also known as Children's Hospital at Vanderbilt, is a nationally ranked pediatric acute care children's teaching hospital and entity of Vanderbilt University Medical Center in Nashville, Tennessee. The hospital is affiliated with Vanderbilt University School of Medicine's Department of Pediatrics.

Thomas Benton Cooley was an American pediatrician and hematologist and professor of hygiene and medicine at the University of Michigan and Wayne State University. He was the director of the Pasteur Institute at the University of Michigan from 1903 to 1904. He worked in private practice in Detroit as the city's first pediatrician starting in 1905. He worked with the Babies' Milk Fund and helped to reduce Detroit's high infant mortality rate in the 1900s and 1910s. During World War I, Cooley went to France as the assistant chief of the Children's Bureau of the American Red Cross. He was decorated in 1924 with the cross of the Legion of Honor for his work in France. From 1921 to 1941, Cooley was the head of pediatric service at Children's Hospital of Michigan. Cooley gained acclaim for his scientific work in the field of pediatric hematology and is principally remembered for his discovery of, and research into, a form of childhood anemia that became known as Cooley's anemia. Cooley was also a professor at the Wayne University College of Medicine from 1936 to 1941.
Eleonore Hutzel was a nurse and social worker in Detroit, Michigan, who was known for her efforts on behalf of women's health and welfare. The Hutzel Women's Hospital and the Eleonore Hutzel Recovery Center, both in Detroit, are named in her honor. She was inducted into the Michigan Women's Hall of Fame in 1999.
















