The Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS) is a third generation mobile cellular system for networks based on the GSM standard. Developed and maintained by the 3GPP, UMTS is a component of the International Telecommunication Union IMT-2000 standard set and compares with the CDMA2000 standard set for networks based on the competing cdmaOne technology. UMTS uses wideband code-division multiple access (W-CDMA) radio access technology to offer greater spectral efficiency and bandwidth to mobile network operators.
A SIM lock, simlock, network lock, carrier lock or (master) subsidy lock is a technical restriction built into GSM and CDMA mobile phones by mobile phone manufacturers for use by service providers to restrict the use of these phones to specific countries and/or networks. This is in contrast to a phone that does not impose any SIM restrictions.
DoJa profile is a Java application environment specification for DoCoMo's i-mode mobile phone.

NTT Docomo, Inc. is a Japanese mobile phone operator. The name is officially an abbreviation of the phrase, "do communications over the mobile network", and is also from a compound word dokomo, meaning "everywhere" in Japanese. The company is headquartered in Sanno Park Tower, Nagatachō, Chiyoda, Tokyo. Docomo provides phone, video phone, i-mode (internet), and mail services. It is the largest wireless carrier in Japan, with 82.632 million subscribers as of March 2021.

Freedom of Mobile Multimedia Access (FOMA) is the brand name of the W-CDMA-based 3G telecommunications services being offered by the Japanese telecommunications service provider NTT DoCoMo. It is an implementation of the Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS) and was the world's first 3G mobile data service to commence commercial operations.

In Japan, mobile phones became ubiquitous years before the phenomenon spread worldwide. In Japanese, mobile phones are called keitai denwa (携帯電話), literally "portable telephones," and are often known simply as keitai (携帯).

Vodafone live! was the brand name for the multimedia portal service of mobile phone operator Vodafone, offering news content, picture messaging, instant messaging, email, and downloadable ringtones and games. The service officially launched on 24 October 2002, originally in eight countries. The first compatible phones were the Japanese Sharp GX10 and Panasonic GD87, and the Nokia 7650.
Sha-Mail was a 2G mailing and picture messaging service launched by J-Phone in 2000 that allowed users to take a photo with their mobile phone and send it to another user on the service as an email attachment. A related service introduced in 2002, Video Sha-Mail, let users record and send videos as well. Sha-Mail was widely successful upon its launch, became a household name in Japan, and sparked a boom in camera phone services worldwide. The term derives from sha, the first part of the Japanese word shashin, and mail.
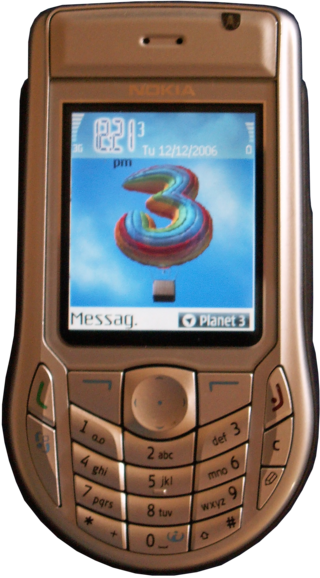
The Nokia 6630 is a 3G mobile phone announced by Nokia on 14 June 2004 and released in November. It runs on Symbian OS 8.0a. Codenamed Charlie during development, it is an evolution of the 6600 and 6620 smartphones, supporting tri-band GSM.
Wi-Fi calling refers to mobile phone voice calls and data that are made over IP networks using Wi-Fi, instead of the cell towers provided by cellular networks. Using this feature, compatible handsets are able to route regular cellular calls through a wireless LAN (Wi-Fi) network with broadband Internet, while seamlessly change connections between the two where necessary. This feature makes use of the Generic Access Network (GAN) protocol, also known as Unlicensed Mobile Access (UMA).
Wireless Application Protocol (WAP) is a technical standard for accessing information over a mobile wireless network. A WAP browser is a web browser for mobile devices such as mobile phones that use the protocol. Introduced in 1999, WAP achieved some popularity in the early 2000s, but by the 2010s it had been largely superseded by more modern standards. Almost all modern handset internet browsers now fully support HTML, so they do not need to use WAP markup for web page compatibility, and therefore, most are no longer able to render and display pages written in WML, WAP's markup language.
Voce was a premium Mobile Virtual Network Operator (MVNO) using the AT&T GSM network sold by Neiman-Marcus and created by Japanese company Faith Communications. During the month of January 2008, ownership was transferred to SunCal Midwest. The service launched November 2005 and subsequently shut down February 1, 2008 with no official announcement, which caught most customers and some company executives completely by surprise.

The Tizen Association, formerly the LiMo Foundation, is a non-profit consortium which develops and maintains the Tizen mobile operating system. Tizen is a Linux-based operating system for smartphones and other mobile devices. The founding members were Motorola, NEC, NTT DoCoMo, Panasonic Mobile Communications, Samsung Electronics, and Vodafone. The consortium's work resulted in the LiMo Platform—which was integrated into mobile phone products from NEC, Panasonic and Samsung—and later became the Tizen platform.
MOAP is the software platform for NTT DoCoMo's Freedom of Mobile Multimedia Access (FOMA) service for mobile phones.

The Symbian Foundation was a non-profit organisation that stewarded the Symbian operating system for mobile phones which previously had been owned and licensed by Symbian Ltd. Symbian Foundation never directly developed the platform, but evangelised, co-ordinated and ensured compatibility. It also provided key services to its members and the community such as collecting, building and distributing Symbian source code. During its time it competed against the Open Handset Alliance and the LiMo Foundation.
In telecommunications, long-term evolution (LTE) is a standard for wireless broadband communication for mobile devices and data terminals, based on the GSM/EDGE and UMTS/HSPA standards. It improves on those standards' capacity and speed by using a different radio interface and core network improvements. LTE is the upgrade path for carriers with both GSM/UMTS networks and CDMA2000 networks. Because LTE frequencies and bands differ from country to country, only multi-band phones can use LTE in all countries where it is supported.
Novarra was a mobile internet software company founded in 2000 and based in Itasca, Illinois, United States. It created web-based services such as web internet access, portals, videos, widgets and advertising for mobile devices. Novarra provided access to the internet and other services through wireless handsets, PDAs and laptops and sold directly to operators, mobile handset manufacturers and internet brand companies. In 2010, Nokia acquired 100% of Novarra's shares.

The Japanese mobile phone industry is one of the most advanced in the world. As of March, 2022 there were 199.99 million mobile contracts in Japan according to the Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications. This is 158 percent of Japan's total population.

ACCESS CO., LTD., founded in April 1979 and incorporated in February 1984 in Tokyo, Japan, by Arakawa Toru and Kamada Tomihisa, is a company providing a variety of software for connected and mobile devices, such as mobile phones, PDAs, video game consoles and set top boxes.
Enhanced Voice Services (EVS) is a superwideband speech audio coding standard that was developed for VoLTE. It offers up to 20 kHz audio bandwidth and has high robustness to delay jitter and packet losses due to its channel aware coding and improved packet loss concealment. It has been developed in 3GPP and is described in 3GPP TS 26.441. The application areas of EVS consist of improved telephony and teleconferencing, audiovisual conferencing services, and streaming audio. Source code of both decoder and encoder in ANSI C is available as 3GPP TS 26.442 and is being updated regularly. Samsung uses the term HD+ when doing a call using EVS.










