Related Research Articles
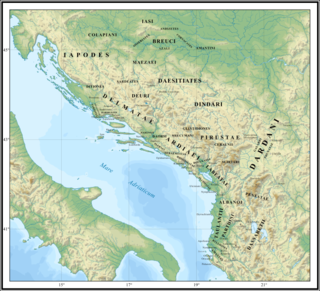
In classical antiquity, Illyria was a region in the western part of the Balkan Peninsula inhabited by numerous tribes of people collectively known as the Illyrians.

The Illyrians were a group of Indo-European-speaking people who inhabited the western Balkan Peninsula in ancient times. They constituted one of the three main Paleo-Balkan populations, along with the Thracians and Greeks.

Lezhë is a city in the Republic of Albania and seat of Lezhë County and Lezhë Municipality. It is one of Albania's continuously inhabited cities, with roughly 2,400 years of recorded history.
Taulantii or Taulantians were an Illyrian people that lived on the Adriatic coast of southern Illyria. They dominated at various times much of the plain between the rivers Drin (Drilon) and Vjosa (Aoös). Their central area was the hinterland of Epidamnos-Dyrrhachion, corresponding to present-day Tirana and the region between the valleys of Mat and Shkumbin (Genusus). The Taulantii are among the oldest attested Illyrian peoples, who established a powerful kingdom in southern Illyria. They are among the peoples who most marked Illyrian history, and thus found their place in the numerous works of historians in classical antiquity.

Illyrius is the son of Cadmus and Harmonia, who eventually ruled Illyria and became the eponymous ancestor of the Illyrians. Illyrius/Illyriós/Illyri is a name known in different stories found in ancient Greek mythology.
The Ardiaei were an Illyrian people who resided in the territory of present-day Albania, Kosovo, Montenegro, Bosnia and Herzegovina, and Croatia between the Adriatic coast on the south, Konjic on the north, along the Neretva river and its right bank on the west, and extending to Lake Shkodra to the southeast. From the 3rd century BC to 168 BC the capital cities of the Ardiaean State were Rhizon and Scodra.
The Dexaroi were an ancient Chaonian tribe living under Mount Amyron. In ancient literature the Dexari are mentioned only by the ancient Greek writer Hecataeus of Miletus, cited by Stephanus of Byzantium. The Dexaroi were the northernmost tribe that belonged to the Chaonian group, one of the three major North-Western Greek-speaking tribes of Epirus.
The Parthini, Partini or Partheni were an Illyrian tribe that lived in the inlands of southern Illyria. They likely were located in the Shkumbin valley controlling the important route between the Adriatic Sea and Macedonia, which corresponded to the Via Egnatia of Roman times. Consequently, their neighbours to the west were the Taulantii and to the east the Dassaretii in the region of Lychnidus.
Illyrian religion refers to the religious beliefs and practices of the Illyrian peoples, a group of tribes who spoke the Illyrian languages and inhabited part of the western Balkan Peninsula from at least the 8th century BC until the 7th century AD. The available written sources are very tenuous. They consist largely of personal and place names, and a few glosses from Classical sources.

Monounios or Monunius was an Illyrian king who reigned in southern Illyria, in the territory of the Taulantii, around the hinterland of Dyrrhachion and Apollonia. He is the first known Illyrian king to have struck his own silver coins, which were minted in Dyrrhachion. The fact that Monounios' coins were struck in the city mint of Dyrrhachion stresses that he exercised to some extent his authority over the city, as did his successor and probably son Mytilos later.
Mytilos or Mytilus was an Illyrian king who reigned in southern Illyria, around the hinterland of Dyrrhachion and Apollonia. He was the successor of Monunios, and probably his son. Mytilus is mentioned by Pompeius Trogus and Frontinus reporting the events of the military conflict between the Illyrians and the Epirotes under Alexander II, son of Pyrrhus. From around 270 BC Mytilus minted in Dyrrhachion his own bronze coins bearing the king's name and the symbol of the city.
The Grabaei were a minor Illyrian tribe who lived near Lake Skadar. They were mentioned by Pliny the Elder.

The Illyrian Kingdom was an Illyrian political entity that existed on the western part of the Balkan Peninsula in ancient times. Regardless of the number of the alternately ruling dynasties, of their tribal affiliation, and of the actual extension of their kingdom, it represented an alliance of Illyrian tribes that united under the rulership of a single leader, expressly referred to as "King of the Illyrians" in ancient historical records.

The Illyrian language was an Indo-European language or group of languages spoken by the Illyrians in Southeast Europe during antiquity. The language is unattested with the exception of personal names and placenames. Just enough information can be drawn from these to allow the conclusion that it belonged to the Indo-European language family.
Epidaurus or Epidauros was an ancient Greek colony founded sometime in the 6th century BC and renamed to Epidaurum during Roman rule in 228 BC, when it was part of the province of Illyricum and later of Dalmatia. It is located at present-day Cavtat in Croatia, 15 km (9 mi) south of Dubrovnik.

The Labeatae, Labeatai or Labeates were an Illyrian people that lived on the Adriatic coast of southern Illyria, between modern Albania and Montenegro, around Lake Scodra.
The Enchelei were an ancient people that lived around the River Drin and the region of Lake Shkodra and Lake Ohrid, in modern-day Albania, Montenegro, and North Macedonia. They are one of the oldest known peoples of the eastern shore of the Adriatic Sea. In ancient sources they sometimes appear as an ethnic group distinct from the Illyrians, but they are mostly mentioned as one of the Illyrian tribes. They held a central position in the earlier phase of Illyrian history. In ancient Greek literature they are linked with the end of the mythical narrative of Cadmus and Harmonia, a tradition deeply rooted among the Illyrian peoples.
The Penestae were an Illyrian tribe dwelling in southeastern Illyria, in an inland region that was called Penestia, which was located around the Black Drin valley north of Lake Ohrid, between present-day eastern Albania and western North Macedonia. They are firstly mentioned by ancient Roman historian Livy. They appear several times in Livy's accounts of the events concerning the Third Macedonian War, which was fought between the Roman Republic and the Kingdom of Macedonia under Perseus. Their chief city was Uscana, most likely located in the valley of the Black Drin in the region of Dibra.
Illyrology or Illyrian studies is interdisciplinary academic field which focuses on scientific study of Illyria and Illyrians as a regional and thematic branch of the larger disciplines of ancient history and archaeology. A practitioner of the discipline is called Illyrologist. His duty is to investigate the range of ancient Illyrian history, culture, art, language, heraldry, numizmatic, mythology, economics, ethics, etc. from c. 1000 BC up to the end of Roman rule around the 5th century.
References
Notes
- ↑ Mate Suić and Radoslav Katičić question the existence of a separate people of Illyrii. For them, Illyrii proprie dicti are peoples inhabiting the heartland of the Illyrian kingdom; Suić, M. (1976) "Illyrii proprie dicti" ANUBiH 11 gcbi 11, 179–197. Katičić, R. (1964) "Illyrii proprie dicti" ZAnt 13–14, 87–97 Katičić, R. (1965) "Nochmals Illyrii proprie dicti" ZAnt 16, 241–244. This view is also supported in Papazoglu, F. (1989) "L'organisation politique de l'Illyrie meridionale (A propos du livre de P. Cabanes sur "Les Illyriens de Bardylis a Genthios")" ZAnt. 39, 31–53.
Citations
- ↑ Wilkes 1969, p. 161.
- ↑ Katicic 1976, p. 158.
- ↑ Pliny the Elder 1949, p. III-22.
- 1 2 Dzino 2014, pp. 45–65.
- ↑ Matijasić 2011, p. 293.
- ↑ Dzino 2014, p. 46.
- ↑ Garašanin 1982.
- ↑ Wilkes 1992, pp. 92, 216.
- ↑ Fortson 2011, p. 465.
Bibliography
- Ceka, Neritan (2014). Ilirët deri te shqiptarët (in Albanian). Tiranë: Migjeni. pp. 40, 249, 364. ISBN 978-9928-4074-7-4.
- Fortson, Benjamin W. (2011). Indo-European Language and Culture: An Introduction. John Wiley & Sons. p. 465. ISBN 9781444359688.
- Dzino, Danijel (2014). "'Illyrians' in ancient ethnographic discourse". Dialogues d'histoire ancienne. 40 (2): 46. doi:10.3917/dha.402.0045.
- Garašanin, M. (1982). "The Early Iron Age in the Central Balkan Area, c. 1000–750 B.C.". In J. Boardman; I. E. S. Edwards; N. G. L. Hammond; E. Sollberger (eds.). The Cambridge Ancient History: The Prehistory of the Balkans; and the Middle East and the Aegean world, tenth to eighth centuries B.C. Vol. III (part 1) (2 ed.). Cambridge University Press. pp. 585–586. ISBN 0521224969.
- Katicic, Radoslav (1 January 1976). Ancient Languages of the Balkans. Walter de Gruyter. pp. 158–. ISBN 978-3-11-156887-4.
- Matijasić, Ivan (2011). "'Shrieking like Illyrians'. Historical Geography and the Greek Perspective of the Illyrian World in the 5th Cent. BC". Arheološki Vestnik. 62. Research Centre of the Slovenian Academy of Sciences and Arts: 293.
- Pliny the Elder (1949). Natural History. Translated by Rackham, H.; Jones, W.H.S.; Eichholz, D.E.
- Wilkes, J.J. (1969). History of the Provinces of the Roman Empire. Routledge. ISBN 9780710062857.
- Wilkes, J. J. (1992). The Illyrians. ISBN 0-631-19807-5.