Carnivora is an order of placental mammals that have specialized in primarily eating flesh, whose members are formally referred to as carnivorans. The order Carnivora is the sixth largest order of mammals, comprising at least 279 species on every major landmass and in a variety of habitats, ranging from the cold polar regions of Earth to the hyper-arid region of the Sahara Desert and the open seas. These mammals have a large array of diverse body plans with a wide diversity of shapes and sizes.

The walrus is a large pinniped marine mammal with discontinuous distribution about the North Pole in the Arctic Ocean and subarctic seas of the Northern Hemisphere. It is the only extant species in the family Odobenidae and genus Odobenus. This species is subdivided into two subspecies: the Atlantic walrus, which lives in the Atlantic Ocean, and the Pacific walrus, which lives in the Pacific Ocean.

An eared seal, otariid, or otary is any member of the marine mammal family Otariidae, one of three groupings of pinnipeds. They comprise 15 extant species in seven genera and are commonly known either as sea lions or fur seals, distinct from true seals (phocids) and the walrus (odobenids). Otariids are adapted to a semiaquatic lifestyle, feeding and migrating in the water, but breeding and resting on land or ice. They reside in subpolar, temperate, and equatorial waters throughout the Pacific and Southern Oceans, the southern Indian, and Atlantic Oceans. They are conspicuously absent in the north Atlantic.

Pinnipeds, commonly known as seals, are a widely distributed and diverse clade of carnivorous, fin-footed, semiaquatic, mostly marine mammals. They comprise the extant families Odobenidae, Otariidae, and Phocidae, with 34 extant species and more than 50 extinct species described from fossils. While seals were historically thought to have descended from two ancestral lines, molecular evidence supports them as a monophyletic group. Pinnipeds belong to the suborder Caniformia of the order Carnivora; their closest living relatives are musteloids, having diverged about 50 million years ago.

Caniformia is a suborder within the order Carnivora consisting of "dog-like" carnivorans. They include dogs, bears, raccoons, and mustelids. The Pinnipedia are also assigned to this group. The center of diversification for the Caniformia is North America and northern Eurasia. Caniformia stands in contrast to the other suborder of Carnivora, the Feliformia, the center of diversification of which was in Africa and southern Asia.
Potamotherium an extinct genus of caniform carnivoran from the Miocene epoch of France and Germany. It has historically been assigned to the family Mustelidae, but more recent studies suggest that it represents a primitive relative of pinnipeds

Acrophoca longirostris, also known as the swan-necked seal, is an extinct genus of Late Miocene pinniped. It was thought to have been the ancestor of the modern leopard seal; however, it is now thought to be a species of monk seal.

Enaliarctos is an extinct genus of pinnipedimorph, and may represent the ancestor to all pinnipeds. The five species in the genus Enaliarctos have been recovered from late Oligocene and early Miocene strata of California and Oregon.

Odobenocetops is an extinct genus of small toothed whale known from Chile and Peru. Its fossils are found in Miocene-aged marine strata of the Bahía Inglesa Formation and Pisco Formation. Two species of Odobenocetops are currently recognized, O. peruvianus and the slightly younger O. leptodon.
A molluscivore is a carnivorous animal that specialises in feeding on molluscs such as gastropods, bivalves, brachiopods and cephalopods. Known molluscivores include numerous predatory molluscs,, arthropods such as crabs and firefly larvae, and, vertebrates such as fish, birds and mammals. Molluscivory is performed in a variety ways with some animals highly adapted to this method of feeding behaviour. A similar behaviour, durophagy, describes the feeding of animals that consume hard-shelled or exoskeleton bearing organisms, such as corals, shelled molluscs, or crabs.

Gomphotaria is a genus of very large shellfish-eating dusignathine walrus found along the coast of what is now California, during the late Miocene.

Kolponomos is an extinct genus of carnivoran mammal that existed in the Late Arikareean North American Land Mammal Age, early Miocene epoch, about 20 million years ago. It was likely a marine mammal. The genus was erected in 1960 by Ruben A. Stirton, a paleontologist at the University of California Museum of Paleontology, Berkeley, for the species K. clallamensis, on the basis of a partial skull and jaw found on the Olympic Peninsula. At the time, Stirton questionably assigned it to Procyonidae, its systematic position remained problematic until the discovery of more fossils including a nearly complete cranium from the original locality of K. clallamensis which helped identify it as part of the group from which pinnipeds evolved.

Allodesmus is an extinct genus of pinniped from the middle to late Miocene of California and Japan that belongs to the extinct pinniped family Desmatophocidae.

Desmatophocidae is an extinct family of pinnipeds closely related to either the eared seals and walruses or to the earless seals. These animals were the first group of large-bodied pinnipeds to evolve, first appearing in the Early Miocene, with no direct modern descendants. Desmatophocids have only been found to live in the North Pacific, with fossils being found in Baja California, California, Oregon, Washington, and Japan.

Pontolis is an extinct genus of large walrus. It contained three species, P. magnus, P. barroni, and P. kohnoi. Like all pinnipeds, Pontolis was a heavily built amphibious carnivore. Pontolis lived along the Pacific coast of North America along what is now the western coasts of California and Oregon between 11.608 and 5.332 million years ago, during the Miocene and Pliocene.
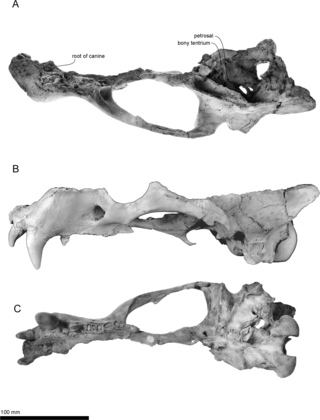
Archaeodobenus is an extinct genus of pinniped that lived during the Late Miocene of what is now Japan. It belonged to the Odobenidae family, which is today only represented by the walrus, but was much more diverse in the past, containing at least 16 genera.
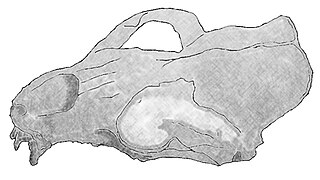
Prototaria is an extinct genus of pinniped that lived approximately 15.97 to 13.65 mya during the Middle Miocene in what is now Japan. It belonged to the family Odobenidae, the only extant species of which is the walrus. Members of the genus Prototaria are believed to be the most basal imagotariine pinnipeds.

Proneotherium is an extinct genus of pinniped that lived approximately 20.43 to 15.97 mya during the Early Miocene in what is now Oregon, U.S. It belonged to the family Odobenidae, the only extant species of which is the walrus.

Nanodobenus is an extinct genus of pinniped that lived approximately 15.97 to 7.246 mya during the Miocene in what is now Baja California Sur, Mexico. It belonged to the family Odobenidae, the only extant species of which is the walrus.
Osodobenus is an extinct genus of walrus from the Miocene to Pliocene of California. Osodobenus may have been the first tusked walrus and shows several adaptations that suggest it was a suction feeder, possibly even a benthic feeder like modern species. Three skulls are known showing pronounced sexual dimorphism, with the female lacking the same tusks as the male. Only a single species, Osodobenus eodon, is currently recognized.





















