
Dressage is a form of horse riding performed in exhibition and competition, as well as an art sometimes pursued solely for the sake of mastery. As an equestrian sport defined by the International Equestrian Federation, dressage is described as "the highest expression of horse training" where "horse and rider are expected to perform from memory a series of predetermined movements."

Horses can use various gaits during locomotion across solid ground, either naturally or as a result of specialized training by humans.
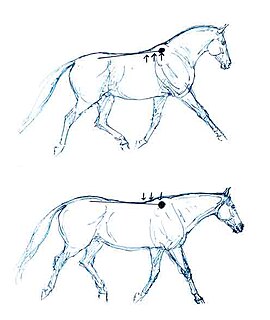
Collection occurs when a horse's center of gravity is shifted backwards. Energy is directed in a more horizontal trajectory with less forward movement. Biomechanical markers include: increased flexion in the lumbo-sacral joint, stifle, and hocks of the horse; increased engagement of the thoracic sling muscles resulting in the withers rising relative to the horse's scapula; and reduced ranges of limb protraction–retraction.

Equitation is the art or practice of horse riding or horsemanship.

The piaffe is a dressage movement where the horse is in a highly collected and cadenced trot, in place or nearly in place. The center of gravity of the horse should be more towards the hind end, with the hindquarters slightly lowered and great bending of the joints in the hind legs. The front end of the horse is highly mobile, free, and light, with great flexion in the joints of the front legs, and the horse remains light in the hand. The horse should retain a clear and even rhythm, show great impulsion, and ideally should have a moment of suspension between the foot falls. As in all dressage, the horse should perform in a calm manner and remain on the bit with a round back.

The trot is a two-beat diagonal horse gait where the diagonal pairs of legs move forward at the same time with a moment of suspension between each beat. It has a wide variation in possible speeds, but averages about 13 kilometres per hour (8.1 mph). A very slow trot is sometimes referred to as a jog. An extremely fast trot has no special name, but in harness racing, the trot of a Standardbred is faster than the gallop of the average non-racehorse, and has been clocked at over 30 miles per hour (48 km/h).

The Spanish Riding School is an Austrian institution dedicated to the preservation of classical dressage and the training of Lipizzaner horses, based in Vienna, Austria, whose performances in the Hofburg are also a tourist attraction. The leading horses and riders of the school also periodically tour and perform worldwide. It is one of the "Big Four", the most prestigious classical riding academies in the world, alongside the Cadre Noir, the Portuguese School of Equestrian Art, and the Royal Andalusian School.

The canter and gallop are variations on the fastest gait that can be performed by a horse or other equine. The canter is a controlled three-beat gait, while the gallop is a faster, four-beat variation of the same gait. It is a natural gait possessed by all horses, faster than most horses' trot, or ambling gaits. The gallop is the fastest gait of the horse, averaging about 40 to 48 kilometres per hour. The speed of the canter varies between 16 to 27 kilometres per hour depending on the length of the horse's stride. A variation of the canter, seen in western riding, is called a lope, and is generally quite slow, no more than 13–19 kilometres per hour (8–12 mph).

A Pirouette is a French word for the Ballet reference, "to whirl about."

An ambling gait or amble is any of several four-beat intermediate horse gaits, all of which are faster than a walk but usually slower than a canter and always slower than a gallop. Horses that amble are sometimes referred to as "gaited", particularly in the United States. Ambling gaits are smoother for a rider than either the two-beat trot or pace and most can be sustained for relatively long periods, making them particularly desirable for trail riding and other tasks where a rider must spend long periods in the saddle. Historically, horses able to amble were highly desired for riding long distances on poor roads. Once roads improved and carriage travel became popular, their use declined in Europe but continued in popularity in the Americas, particularly in areas where plantation agriculture was practiced and the inspection of fields and crops necessitated long daily rides.

Saddle seat is a style of horse riding within the category of English riding that is designed to show off the high action of certain horse breeds. The style developed into its modern form in the United States, and is also seen in Canada and South Africa. To a much lesser extent, it is ridden with American horse breeds in Europe and Australia. The breeds used for this flashy style are typically the showy Morgan Horse, and the high stepping American Saddlebred.

Equestrianism made its Summer Olympics debut at the 1900 Summer Olympics in Paris, France. It disappeared until 1912, but has appeared at every Summer Olympic Games since. The current Olympic equestrian disciplines are Dressage, Eventing, and Jumping. In each discipline, both individual and team medals are awarded. Women and men compete together on equal terms.

A "baucher" is also a type of bit, named after the man.

Riding aids are the cues a rider gives to a horse to communicate what they want the animal to do. Riding aids are broken into the natural aids and the artificial aids.

In equestrianism, throughness is an absence of resistance in the horse to the rider's commands.

The phrases "on the bit", "behind the bit" and "above the bit" are equestrian terms used to describe a horse's posture relative to the reins and the bridle bit. A position on the bit is submissive to the rider's rein aids, given through the bit. When a horse is behind the bit, the head is tucked too far down and rearward. If above the bit, then the head is too high.

The show hack is a type of ridden show horse, exhibited to a standard first established in England.
Studbook selection is a process used in certain breeds of horses to select breeding stock. It allows a breed registry to direct the evolution of the breed towards the ideal by eliminating unhealthy or undesirable animals from the population. The removal of individuals from a population is called culling, and does not suggest killing the animal in question. Typically, culls are castrated or they and their offspring are unable to be registered.

Lead refers to which set of legs, left or right, leads or advances forward to a greater extent when a quadruped animal is cantering, galloping, or leaping. The feet on the leading side touch the ground forward of its partner. On the "left lead", the animal's left legs lead. The choice of lead is of special interest in horse riding.

Five-gaited horses are notable for their ability to perform five distinct horse gaits instead of simply the three gaits, walk, trot and canter or gallop common to most horses. Individual animals with this ability are often seen in the American Saddlebred horse breed, though the Icelandic horse also has five-gaited individuals, though with a different set of gaits than the Saddlebred.



















