
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the second-most populous country, the seventh-largest country by area, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the south, the Arabian Sea on the southwest, and the Bay of Bengal on the southeast, it shares land borders with Pakistan to the west; China, Nepal, and Bhutan to the north; and Bangladesh and Myanmar to the east. In the Indian Ocean, India is in the vicinity of Sri Lanka and the Maldives; its Andaman and Nicobar Islands share a maritime border with Thailand and Indonesia.

India is the second most populated country in the world with nearly a fifth of the world's population. According to the 2019 revision of the World Population Prospects population stood at 1,352,642,280.

Mumbai is the capital city of the Indian state of Maharashtra. According to United Nations, as of 2018, Mumbai was the second most populous city in India after Delhi and the seventh most populous city in the world with a population of 19.98 million. As per Indian government population census of 2011, Mumbai was the most populous city in India with an estimated city proper population of 12.5 million living under Municipal Corporation of Greater Mumbai. Mumbai is the centre of the Mumbai Metropolitan Region, the sixth most populous metropolitan area in the world with a population of over 23.64 million. Mumbai lies on the Konkan coast on the west coast of India and has a deep natural harbour. In 2008, Mumbai was named an alpha world city. It has the highest number of millionaires and billionaires among all cities in India. Mumbai is home to three UNESCO World Heritage Sites: the Elephanta Caves, Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj Terminus, and the city's distinctive ensemble of Victorian and Art Deco buildings.

Maharashtra is a state in the western peninsular region of India occupying a substantial portion of the Deccan Plateau. It is the second-most populous state and third-largest state by area. Spread over 307,713 km2 (118,809 sq mi), it is bordered by the Arabian Sea to the west, the Indian states of Karnataka and Goa to the south, Telangana to the southeast and Chhattisgarh to the east, Gujarat and Madhya Pradesh to the north, and the Indian union territory of Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu to the north west. It is also the world's second-most populous subnational entity.

The East India Company (EIC), also known as the Honourable East India Company (HEIC), East India Trading Company (EITC), the English East India Company or the British East India Company, and informally known as John Company, Company Bahadur, or simply The Company, was an English and later British joint-stock company. It was formed to trade in the Indian Ocean region, initially with the Moghuls of India and the East Indies, and later with Qing China. The company ended up seizing control of large parts of the Indian subcontinent, colonised parts of Southeast Asia, and colonised Hong Kong after the First Opium War.

The Bharatiya Janata Party is the current ruling political party of the Republic of India. It is one of the two major political parties in India, along with the Indian National Congress. As of 2019, it is the country's largest political party in terms of representation in the national parliament and state assemblies and is the world's largest party in terms of primary membership. BJP is a right-wing party, and its policy has historically reflected Hindu nationalist positions. It has close ideological and organisational links to the much older Rashtriya Swayamsevak Sangh (RSS).

The Indian National Congress is a political party in India with widespread roots. Founded in 1885, it was the first modern nationalist movement to emerge in the British Empire in Asia and Africa. From the late 19th century, and especially after 1920, under the leadership of Mahatma Gandhi, Congress became the principal leader of the Indian independence movement. Congress led India to independence from Great Britain, and powerfully influenced other anti-colonial nationalist movements in the British Empire.

Uttar Pradesh[ˈʊtːəɾ pɾəˈdeːʃ](listen)) is a state in northern India. With roughly 200 million inhabitants, it is the most populous state in India as well as the most populous country subdivision in the world. It was created on 1 April 1937 as the United Provinces of Agra and Oudh during British rule, and was renamed Uttar Pradesh in 1950, giving the acronym UP. The state is divided into 18 divisions and 75 districts with the capital being Lucknow. On 9 November 2000, a new state, Uttarakhand, was carved out from the state's Himalayan hill region. The two major rivers of the state, the Ganges and Yamuna, join at Allahabad and flow further east as Ganges. Hindi is the most widely spoken language and is also the official language of the state, along with Urdu.
India is a federal union comprising 28 states and 8 union territories, for a total of 36 entities. The states and union territories are further subdivided into districts and smaller administrative divisions.

Narendra Damodardas Modi is an Indian politician serving as the 14th and current Prime Minister of India since 2014. He was the Chief Minister of Gujarat from 2001 to 2014 and is the Member of Parliament for Varanasi. Modi is a member of the Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP) and of the Rashtriya Swayamsevak Sangh (RSS), a Hindu nationalist volunteer organisation. He is the first prime minister outside of the Indian National Congress to win two consecutive terms with a full majority and the second to complete five years in office after Atal Bihari Vajpayee.

Manmohan Singh is an Indian economist, academic, and politician who served as the 13th Prime Minister of India from 2004 to 2014. The first Sikh in office, Singh was also the first prime minister since Jawaharlal Nehru to be re-elected after completing a full five-year term.

The economy of India is characterised as a developing market economy. It is the world's fifth-largest economy by nominal GDP and the third-largest by purchasing power parity (PPP). According to the IMF, on a per capita income basis, India ranked 139th by GDP (nominal) and 118th by GDP (PPP) in 2018. From independence in 1947 until 1991, successive governments promoted protectionist economic policies with extensive state intervention and regulation; the end of the Cold War and an acute balance of payments crisis in 1991 led to the adoption of a broad program of economic liberalisation. Since the start of the 21st century, annual average GDP growth has been 6% to 7%, and from 2014 to 2018, India was the world's fastest growing major economy, surpassing China. Historically, India was the largest economy in the world for most of the two millennia from the 1st until 19th century.

The British Raj was the rule by the British Crown on the Indian subcontinent from 1858 to 1947. The rule is also called Crown rule in India, or direct rule in India. The region under British control was commonly called India in contemporaneous usage, and included areas directly administered by the United Kingdom, which were collectively called British India, and areas ruled by indigenous rulers, but under British tutelage or paramountcy, called the princely states. The region as a whole was never officially referred to as the Indian Empire.

Kerala is a state on the southwestern Malabar Coast of India. It was formed on 1 November 1956, following the passage of the States Reorganisation Act, by combining Malayalam-speaking regions of the erstwhile states of Travancore-Cochin and Madras. Spread over 38,863 km2 (15,005 sq mi), Kerala is the twenty-third largest Indian state by area. It is bordered by Karnataka to the north and northeast, Tamil Nadu to the east and south, and the Lakshadweep Sea to the west. With 33,387,677 inhabitants as per the 2011 Census, Kerala is the thirteenth-largest Indian state by population. It is divided into 14 districts with the capital being Thiruvananthapuram. Malayalam is the most widely spoken language and is also the official language of the state.

The Mughal Empire or Mogul Empire, self-designated as Gurkani, was an early-modern empire that controlled much of South Asia between the 16th and 19th centuries. For some two centuries, the empire stretched from the outer fringes of the Indus basin in the west, northern Afghanistan in the northwest, and Kashmir in the north, to the highlands of present-day Assam and Bangladesh in the east, and the uplands of the Deccan plateau in south India.
A Union territory is a type of administrative division in the Republic of India. Unlike the states of India, which have their own governments, union territories are federal territories governed directly by the Central Government of India.
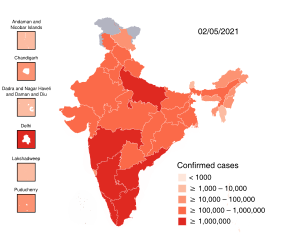
The first case of the COVID-19 pandemic in India was reported on 30 January 2020, originating from China. As of 22 May 2020, the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare have confirmed a total of 118,447 cases, 48,534 recoveries and 3,583 deaths in the country. India currently has the fourth largest number of confirmed cases in Asia with number of cases breaching the 100,000 mark on 19 May 2020. The highest single day surge in new cases was recorded on 22 May 2020, when 6,088 cases were reported. India's case fatality rate is relatively lower at 3.09%, against the global 6.63% as of 20 May 2020. Five cities account for around half of all reported cases in the country – Mumbai, Delhi, Ahmedabad, Chennai and Pune. As of 20 May 2020, two regions, Sikkim and Lakshadweep have not reported a case.
On 24 March 2020, the Government of India under Prime Minister Narendra Modi ordered a nationwide lockdown for 21 days, limiting movement of the entire 1.3 billion population of India as a preventive measure against the COVID-19 pandemic in India. It was ordered after a 14-hour voluntary public curfew on 22 March, followed by enforcement of a series of regulations in the country's COVID-19 affected regions. The lockdown was placed when the number of confirmed positive coronavirus cases in India was approximately 500. Observers stated that the lockdown had slowed the growth rate of the pandemic by 6 April to a rate of doubling every six days, and by 18 April, to a rate of doubling every eight days.















