Related Research Articles
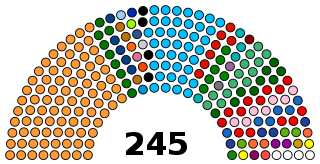
The Rajya Sabha or Council of States is the upper house of the bicameral Parliament of India. It currently has a maximum membership of 245, of which 233 are elected by the legislatures of the states and union territories using single transferable votes through Open Ballot while the President can appoint 12 members for their contributions to art, literature, science, and social services. The potential seating capacity of the Rajya Sabha is 250, according to article 80 of the Indian Constitution. Members sit for staggered terms lasting six years, with elections every year but almost a third of the 233 designates up for election every two years, specifically in even-numbered years. The Rajya Sabha meets in continuous sessions, and unlike the Lok Sabha, being the lower house of the Parliament, the Rajya Sabha, which is the upper house of Parliament, is not subjected to dissolution. However, the Rajya Sabha, like the Lok Sabha can be prorogued by the President.
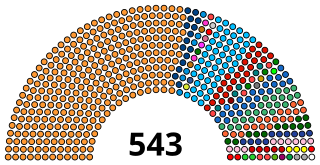
The Lok Sabha, or House of the People, is the lower house of India's bicameral Parliament, with the upper house being the Rajya Sabha. Members of the Lok Sabha are elected by adult universal suffrage and a first-past-the-post system to represent their respective constituencies, and they hold their seats for five years or until the body is dissolved by the President on the advice of the council of ministers. The house meets in the Lok Sabha Chambers of the Sansad Bhavan, New Delhi.

Purno Agitok Sangma was an Indian politician who served as the Speaker of the Lok Sabha from 1996 to 1998 and Chief Minister of Meghalaya from 1988 to 1990. He was the candidate for the 2012 Indian presidential election, however he lost to Shri Pranab Mukherjee, who became the 13th President of India

The Parliament of India is the supreme legislative body of the Republic of India. It is a bicameral legislature composed of the President of India and the two houses: the Rajya Sabha and the Lok Sabha. The President in his role as head of legislature has full powers to summon and prorogue either house of Parliament or to dissolve Lok Sabha. The president can exercise these powers only upon the advice of the Prime Minister and his Union Council of Ministers.

The Government of India, often abbreviated as GoI, is the union government created by the constitution of India as the legislative, executive and judicial authority of the union of twenty eight states and eight union territories of a constitutionally democratic republic. The seat of the Government is located in New Delhi, the capital of India.
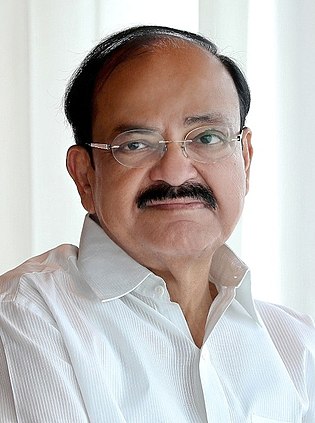
The Vice President of India is the second-highest constitutional office in India after the President. Article 63 of Indian Constitution states that "There shall be a Vice President of India." The Vice President acts as President in the absence of the president due to death, resignation, impeachment, or other situations.
India is a country, divided into states and union territories, with a parliamentary system governed under the Constitution of India, which defines the power distribution among the federal government and the states.

The Speaker of the Lok Sabha is the presiding officer and the highest authority of the Lok Sabha, the lower house of the Parliament of India. The speaker is elected generally in the first meeting of the Lok Sabha following general elections. Serving for a term of five years, the speaker chosen from sitting members of the Lok Sabha, and is by convention a member of the ruling party or alliance.

Kamal Nath is an Indian politician who served as the 18th Chief Minister of Madhya Pradesh for approximately 15 months and resigned after a political crisis. He is the Leader of the Opposition in the Madhya Pradesh Legislative Assembly since March 2020.

The Sansad Bhavan is the seat of the Parliament of India. At a distance of 750 meters from Rashtrapati Bhavan, it is located along Sansad Marg which crosses the Central Vista; this is surrounded by the India Gate, war memorial, prime minister's office and residence, ministerial buildings and other administrative units of Indian government. It houses the Lok Sabha and the Rajya Sabha which represent lower and upper houses respectively in India's bicameral parliament.
This is a brief description of the lawmaking procedure in India.
An ex officio member is a member of a body who is part of it by virtue of holding another office. The term ex officio is Latin, meaning literally 'from the office', and the sense intended is 'by right of office'; its use dates back to the Roman Republic.

Sudip Bandyopadhyay is an Indian politician and a Member of Parliament from Kolkata Uttar Constituency of West Bengal,India. Sudip Bandyopadhyay has been a member of the Lok Sabha for five terms, serving in the 13th, 14th, 15th, 16th, 17th Lok Sabhas. He represents the Kolkata Uttar constituency of West Bengal and is a member of the Trinamool Congress political party.He is the Leader of the Lok Sabha of the All India Trinamool Congress Party. He has also represented India at the United Nations two times, first in Geneva and second in New York where he delivered his speech in the Central Hall of the General Assembly.
Subhash C. Kashyap is a former Secretary-General of 7th Lok Sabha, 8th Lok Sabha and 9th Lok Sabha and Lok Sabha Secretariat from 1984 to 1990. He is well known Political Scientist, expert in Indian Constitution, Constitutional Law, Parliamentary Experts and distinguished scholar. He also headed an International Centre for Parliamentary Documentation,IPU at Geneva till 1983. He was Honorary Constitutional Advisor to the Government of India on Panchayati Raj Laws and Institutions. He is also Recipient of several prestigious awards for the Best Books in Constitution, Law and Political Science. At present Dr. Kashyap is an Honorary Research Professor at the Centre for Policy Research (CPR), New Delhi. He was also a Member of the National Commission to Review the Working of Constitution and Chairman of its Drafting and Editorial Committee.
Peter Garnett Marbaniang was an Indian parliamentarian, legislator and academician from the state of Meghalaya. He served as a Member of the Lok Sabha from 1989 to 1996, as Speaker of the Meghalaya Legislative Assembly and as a Minister in the Government of Meghalaya. He was the President of the All India Catholic Union from 1994 to 1996.
Hirendranath Mukhopadhyay, also known as Hiren Mukerjee, was an Indian politician, lawyer and academic. He was a member of the Communist Party of India having joined in 1936 when it was still illegal. He was elected to the Lok Sabha the lower house of the Indian Parliament from the Calcutta North East constituency in 1951, 1957, 1962, 1967 and 1971. He suffered an electoral reverse when he lost to Pratap Chandra Chunder in 1977 after the CPI supported Emergency.

Meenakshi Lekhi is an Indian politician and a member of Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP). She is a Member of Parliament from New Delhi Parliamentary constituency in the 16th and 17th Lok Sabha. She is the national spokesperson of Bharatiya Janata Party and a Supreme Court of India lawyer. She won the high-profile New Delhi parliamentary constituency as a BJP candidate in the 2014 elections and was re-elected in 2019. In July 2016, she was appointed as chairperson of the Committee on Privileges of the Lok Sabha in Parliament. On 26 July 2019, Lok Sabha speaker Om Birla appointed Lekhi as a chairperson of parliamentary committee on Public Undertakings and is continuing since then in that position.
The Parliamentary Standing Committee on Defence (SCOD) is a department related standing committee (DRSC) of selected members of parliament, constituted by the Parliament of India, for the purpose of legislative oversight of the defence policies and decision making of the Ministry of Defence (MOD). It is one of the 24 DRSCs that have been mandated with the onerous task of ministry specific oversight.
The Parliamentary Standing Committee on Finance (SCOF) is a department related standing committee (DRSC) constituted by the Parliament of India comprising selected members of parliament for the purpose of legislative oversight on the policies and decision making of the following four ministries:
- Ministry of Finance (MoF)
- Ministry of Corporate Affairs
- Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation
- NITI Aayog
References
- 1 2 "Indian Parliamentary Group". NIC, Government of India. Retrieved 18 April 2012.
- ↑ "Parliament of India: Handbook" (PDF). Government of India. Retrieved 18 April 2012.