Related Research Articles

A consumer price index (CPI) is a price index, the price of a weighted average market basket of consumer goods and services purchased by households. Changes in measured CPI track changes in prices over time. The CPI is calculated by using a representative basket of goods and services. The basket is updated periodically to reflect changes in consumer spending habits. The prices of the goods and services in the basket are collected monthly from a sample of retail and service establishments. The prices are then adjusted for changes in quality or features. Changes in the CPI can be used to track inflation over time and to compare inflation rates between different countries. The CPI is not a perfect measure of inflation or the cost of living, but it is a useful tool for tracking these economic indicators.
GSS codes are nine-character geocodes maintained by the United Kingdom's Office for National Statistics to represent a wide range of geographical areas of the UK, for use in tabulating census and other statistical data. GSS refers to the Government Statistical Service of which ONS is part.

An air quality index (AQI) is an indicator developed by government agencies to communicate to the public how polluted the air currently is or how polluted it is forecast to become. As air pollution levels rise, so does the AQI, along with the associated public health risk. Children, the elderly, and individuals with respiratory or cardiovascular problems are typically the first groups affected by poor air quality. When the AQI is high, governmental bodies generally encourage people to reduce physical activity outdoors, or even avoid going out altogether. When wildfires result in a high AQI, the use of masks such as N95 respirators outdoors and air purifiers incorporating HEPA filters indoors are also encouraged.
The h-index is an author-level metric that measures both the productivity and citation impact of the publications, initially used for an individual scientist or scholar. The h-index correlates with success indicators such as winning the Nobel Prize, being accepted for research fellowships and holding positions at top universities. The index is based on the set of the scientist's most cited papers and the number of citations that they have received in other publications. The index has more recently been applied to the productivity and impact of a scholarly journal as well as a group of scientists, such as a department or university or country. The index was suggested in 2005 by Jorge E. Hirsch, a physicist at UC San Diego, as a tool for determining theoretical physicists' relative quality and is sometimes called the Hirsch index or Hirsch number.
The Human Poverty Index (HPI) was an indication of the poverty of community in a country, developed by the United Nations to complement the Human Development Index (HDI) and was first reported as part of the Human Development Report in 1997. It is developed by United Nations Development Program which also publishes indexes like HDI It was considered to better reflect the extent of deprivation in deprived countries compared to the HDI. In 2010, it was supplanted by the UN's Multidimensional Poverty Index.
The Carstairs index is an index of deprivation used in spatial epidemiology to identify Socio-economic confounding.
The Indices of deprivation 2004 is a deprivation index at the small area level, created by the British Department for Communities and Local Government(DCLG).

A house price index (HPI) measures the price changes of residential housing as a percentage change from some specific start date. Methodologies commonly used to calculate an HPI are hedonic regression (HR), simple moving average (SMA), and repeat-sales regression (RSR).
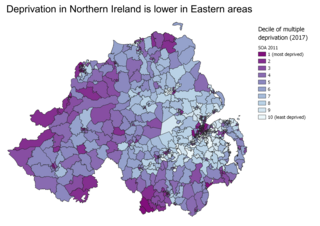
Indices of multiple deprivation (IMD) are widely-used datasets within the UK to classify the relative deprivation of small areas. Multiple components of deprivation are weighted with different strengths and compiled into a single score of deprivation.

Conservation biologists have designed a variety of objective means to empirically measure biodiversity. Each measure of biodiversity relates to a particular use of the data. For practical conservationists, measurements should include a quantification of values that are commonly shared among locally affected organisms, including humans. For others, a more economically defensible definition should allow the ensuring of continued possibilities for both adaptation and future use by humans, assuring environmental sustainability.
The Democracy Ranking is an index compiled by the Association for Development and Advancement of the Democracy Award, an Austria-based non-partisan organization. Democracy Ranking produces an annual global ranking of liberal democracies. The applied conceptual formula, which measures the quality of democracy, integrates democracy and other characteristics of the political system with the performance of non-political dimensions. Democracy Ranking has emphasized a broader understanding of democracy, creating a conceptual link between politics and the output and performance of society. The Democracy Ranking has compared several-year intervals, delivering ranking results, which show how ranking positions and score levels have developed recently. Referring to that information, a Democracy Improvement Ranking has been regularly released.
The income deprivation affecting children index (IDACI) is an index of deprivation used in the United Kingdom.

Multidimensional Poverty Indices use a range of indicators to calculate a summary poverty figure for a given population, in which a larger figure indicates a higher level of poverty. This figure considers both the proportion of the population that is deemed poor, and the 'breadth' of poverty experienced by these 'poor' households, following the Alkire & Foster 'counting method'. The method was developed following increased criticism of monetary and consumption based poverty measures, seeking to capture the deprivations in non-monetary factors that contribute towards well-being. While there is a standard set of indicators, dimensions, cutoffs and thresholds used for a 'Global MPI', the method is flexible and there are many examples of poverty studies that modify it to best suit their environment. The methodology has been mainly, but not exclusively, applied to developing countries.

The Oxford Poverty and Human Development Initiative (OPHI) is an economic research centre within the Oxford Department of International Development at the University of Oxford, England, that was established in 2007.
The OECD Better Life Index, created in May 2011 by the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development, is an initiative pioneering the development of economic indicators which better capture multiple dimensions of economic and social progress.
The Indices of Deprivation 2010 is a deprivation index at the small area level, created by the British Department for Communities and Local Government (DCLG) and released on 24 March 2011. It follows the ID2007 and because much of the datasets are the same or similar between indices allows a comparison of "relative deprivation" of an area between the two indices.

The Gender Inequality Index (GII) is an index for the measurement of gender disparity that was introduced in the 2010 Human Development Report 20th anniversary edition by the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP). According to the UNDP, this index is a composite measure to quantify the loss of achievement within a country due to gender inequality. It uses three dimensions to measure opportunity cost: reproductive health, empowerment, and labor market participation. The new index was introduced as an experimental measure to remedy the shortcomings of the previous indicators, the Gender Development Index (GDI) and the Gender Empowerment Measure (GEM), both of which were introduced in the 1995 Human Development Report.
Trees have a wide variety of sizes and shapes and growth habits. Specimens may grow as individual trunks, multitrunk masses, coppices, clonal colonies, or even more exotic tree complexes. Most champion tree programs focus finding and measuring the largest single-trunk example of each species. There are three basic parameters commonly measured to characterize the size of a single trunk tree: tree height measurement, tree girth measurement, and tree crown measurement. Foresters also perform tree volume measurements. A detailed guideline to these basic measurements is provided in The Tree Measuring Guidelines of the Eastern Native Tree Society by Will Blozan.
The Townsend index is a measure of material deprivation within a population. It was first described by sociologist Peter Townsend in 1988.
Measures of gender equality or inequality are statistical tools employed to quantify the concept of gender equality.
References
- ↑ See "Using the English Indices of Deprivation 2007: Guidance Archived 2008-11-25 at the Wayback Machine "