
Bandra ([bæːɳɖɾa]) is a coastal suburb located in Mumbai, the largest city of the Konkan division in Maharashtra, India. The area is located to the immediate north of the River Mithi, which separates Bandra from the Mumbai City district. It is the third-largest commercial hub in Maharashtra, after the Bombay city district and Pune, primarily aided by the Bandra-Kurla Complex.

Portuguese creoles are creole languages which have Portuguese as their substantial lexifier. The most widely-spoken creoles influenced by Portuguese are Cape Verdean Creole, Guinea-Bissau Creole and Papiamento.

The Daman and Diu Portuguese Creole, Portuguese: Língua Crioula de Damãon e Dio & by its speakers as Língua da Casa meaning "home language", refers to the variety of Indo-Portuguese creole spoken in the Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu, in the northern Konkan region of India. Before the Indian annexation of the territory, the creole spoken by the Damanese natives underwent a profound decreolisation in the erstwhile Portuguese Goa and Damaon colony, a phenomenon whereby the Indo-Portuguese creole reconverged with European Portuguese.

Salsette Island is an island in Konkan division of the state of Maharashtra, on India's west coast. Administratively known as Greater Mumbai, the city district of Mumbai, Mumbai Suburban district, Mira Bhayander, and a portion of Thane lie within it, making it very populous and one of the most densely populated islands in the world. It has a population of more than 20 million inhabitants living on an area of about 619 square kilometres (239 sq mi).

Vasai is a historical place and city located in Palghar district; which was partitioned out of the Thana district in 2014. It also forms a part of Vasai-Virar twin cities in the Konkan division, Maharashtra, India and comes under Police Jurisdiction of Mira-Bhayander, Vasai-Virar Police Commissionerate.

The East Indians, also called East Indian Catholics or Bombay East Indians, are an ethno-religious Indian Christian community native to the Seven Islands of Bombay and the neighbouring Mumbai Metropolitan Area of the Konkan division.

Fort Vasai is a ruined fort of the town of Vasai (Bassein), Palghar, Maharashtra, India. The structure was formally christened as the Fort of St. Sebastian in the Indo-Portuguese era. The fort is a monument of national importance and is protected by the Archaeological Survey of India.
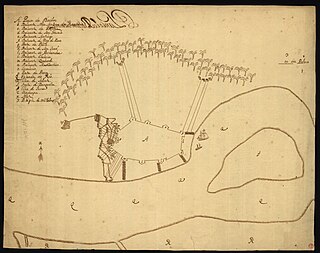
The Battle of Vasai or the Battle of Bassein was fought between the Marathas and the Portuguese rulers of Vasai, a town near Mumbai (Bombay) in the Konkan region of the present-day state of Maharashtra, India. The Marathas were led by Chimaji Appa, a brother of Peshwa Baji Rao I.
Norteiros were a historical people who lived in the former Portuguese exclaves in the western littoral parts of the northern Konkan region, in the present-day Greater Bombay Metropolitan Area and the union territory of Damaon, Diu & Silvassa.

Castella de Aguada, also known as the Bandra Fort, is a fort located in Bandra, Mumbai. "Castella" is a misspelling for Portuguese "Castelo" (castle), although it seems its Portuguese builders actually called it Forte de Bandorá. It is located at Land's End in Bandra. It was built by the Portuguese in 1640 as a watchtower overlooking Mahim Bay, the Arabian Sea and the southern island of Mahim. The strategic value of the fort was enhanced in 1661 after the Portuguese ceded the seven islands of Bombay that lay to the immediate south of Bandra to the English. The name indicates its origin as a place where fresh water was available in the form of a fountain ("Aguada") for Portuguese ships cruising the coasts in the initial period of Portuguese presence. The fort lies over several levels, from sea level to an altitude of 24 metres (79 ft). Castella de Aguada has been featured in several Hindi films, such as Dil Chahta Hai and Buddha Mil Gaya.
Indo-Portuguese creoles are the several Portuguese creoles spoken in the erstwhile Portuguese Indian settlements, Cochin Portuguese Creole, Fort Bassein, Goa and Damaon, Portuguese Ceylon etc; in present-day India and Sri Lanka. These creoles are now mostly extinct or endangered, the creoles have substantial European Portuguese words in their grammars or lexicons:

Chimaji Balaji Bhat (1707–1740), commonly referred to as Appa or Bhau, was the son of Balaji Vishwanath Bhat and the younger brother of Bajirao Peshwa of Maratha Empire. He was an able military commander who liberated the western coast of India from Portuguese rule. The high watermark of his career was the capture of Vasai fort from the Portuguese.
The Treaty of Baçaim was signed by Sultan Bahadur of Gujarat and the Kingdom of Portugal on 23 December 1534 while on board the galleon São Mateus. Based on the terms of the agreement, the Portuguese Empire gained control of the city of Baçaim, as well as its territories, islands, and seas. The Ilhas de Bombaim which were ruled from Portuguese Goa included Colabá Grande, Colabá Pequeno, Bombaim, Mazagão, Vorlim, Matungá, and Mahim. Salsette, Damão é Div, Thane, Kalyan, and Chaul were other territories controlled and settled by the Portuguese.
The Kupari consist of Kadodi Christians and Samvedi Christians, which are a Roman Catholic Brahmin sub-group in the Christian Bombay East Indian community, of the people of Konkan division. They are concentrated mostly in Bassein (Vasai), India, which is about 60 kilometres (37 mi) north of Mumbai (Bombay) city. Kadodi ancestors were a mixture of Samvedi Brahmins, Goan Konkani Brahmins& Portuguese New Christians; because of intermarriages between them. The population is about 40,000 to 45,000. The two Konkani dialects spoken by the Kuparis are Samvedi Boli Bhasha and Kadodi, which are a mixture of Gujrati, Marathi & Indo-Portuguese. 97% of the population is Roman Catholic and the remaining minority is a mixed population of various Protestant Revolutionary denominations.
Manickpur is a small village in the Vasai (Bassein) township of the Palghar district in the Maharashtra, India.

Bombay, also called Bom Bahia or Bom Baim in Indo-Portuguese creole, Mumbai in the local language; is the financial and commercial capital of India and one of the most populous cities in the world. It's also the cosmopolitan city centre of the Greater Bombay Metropolitan Area, and the cultural base of the Bollywood film industry. At the time of arrival of the Portuguese Armadas, Bombay was an archipelago of seven islands. Between the third century BCE and 1348, the islands came under the control of successive Hindu dynasties. The Delhi Sultanate had been ruling the area along with Chaul, New Bombay (Thana) & Damaon, with the administrative centre in Bassein (Vasai) since the raids of Malik Kafur in the Konkan region and across the Indian subcontinent. This territory in North Konkan along with the Bombay islands were later taken over by the Sultan of Guzerat from 1391 to 1534, when he had declared the end of the suzerainty to Delhi, after the Timurid invasion of it. Growing apprehensive of the power of the Moghal emperor Humayun, Sultan Bahadur Shah of Gujarat was obliged to sign the Treaty of Bassein on 23 December 1534; according to which, the seven islands of Bombay, Fort San Sebastian of Bassein in strategic town of Bassein (Vasai), and its dependencies were offered to the Portuguese East Indies. The places were only later officially surrendered on 25 October 1535, by the Sultan of Guzerat.

Vasai-Virar is an agglomeration of four previously governed municipal councils: Vasai (Bassein), Virar, Nallasopara and Navghar-Manikpur, as well as a few towns to the east and west of the urban area. It lies in the Konkan division of Maharashtra, India.
Panchkalshi is a Hindu community. They are one of the original native communities of Bombay (Mumbai) metropolitan area in the Konkan division of India. Since the 19th century the community has called itself Somvanshi Kshatriya Pathare.

Bandra is a railway station on the Western Line and Harbour Line of the Mumbai Suburban Railway network. It serves the Bandra suburban area and the commercial area of Bandra-Kurla Complex (BKC). Bandra Terminus is near to Bandra railway station and serves interstate traffic on the Western Railway.
Bombay Backbay railway station was a railway station of the erstwhile BB&CI Railway(today's Western Railway), located in Bombay Backbay in Mumbai. It was the starting point of the first regular local train service of the BB&CI Railway. It started on 12 April 1867, between the Station and Viraur (Virar).












