Inositol trisphosphate or inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate abbreviated InsP3 or Ins3P or IP3 is an inositol phosphate signaling molecule. It is made by hydrolysis of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2), a phospholipid that is located in the plasma membrane, by phospholipase C (PLC). Together with diacylglycerol (DAG), IP3 is a second messenger molecule used in signal transduction in biological cells. While DAG stays inside the membrane, IP3 is soluble and diffuses through the cell, where it binds to its receptor, which is a calcium channel located in the endoplasmic reticulum. When IP3 binds its receptor, calcium is released into the cytosol, thereby activating various calcium regulated intracellular signals.

Jasmonate (JA) and its derivatives are lipid-based plant hormones that regulate a wide range of processes in plants, ranging from growth and photosynthesis to reproductive development. In particular, JAs are critical for plant defense against herbivory and plant responses to poor environmental conditions and other kinds of abiotic and biotic challenges. Some JAs can also be released as volatile organic compounds (VOCs) to permit communication between plants in anticipation of mutual dangers.

Inositol, or more precisely myo-inositol, is a carbocyclic sugar that is abundant in the brain and other mammalian tissues; it mediates cell signal transduction in response to a variety of hormones, neurotransmitters, and growth factors and participates in osmoregulation.

Inositol trisphosphate receptor (InsP3R) is a membrane glycoprotein complex acting as a Ca2+ channel activated by inositol trisphosphate (InsP3). InsP3R is very diverse among organisms, and is necessary for the control of cellular and physiological processes including cell division, cell proliferation, apoptosis, fertilization, development, behavior, learning and memory. Inositol triphosphate receptor represents a dominant second messenger leading to the release of Ca2+ from intracellular store sites. There is strong evidence suggesting that the InsP3R plays an important role in the conversion of external stimuli to intracellular Ca2+ signals characterized by complex patterns relative to both space and time, such as Ca2+ waves and oscillations.

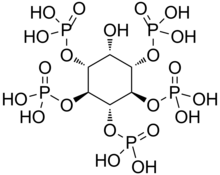
Phytic acid is a six-fold dihydrogenphosphate ester of inositol, also called inositol hexakisphosphate (IP6) or inositol polyphosphate. At physiological pH, the phosphates are partially ionized, resulting in the phytate anion.

Inositol phosphates are a group of mono- to hexaphosphorylated inositols. Each form of inositol phosphate is distinguished by the number and position of the phosphate group on the inositol ring.

Inositol-trisphosphate 3-kinase B is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ITPKB gene.

The enzyme Inositol phosphate-phosphatase is of the phosphodiesterase family of enzymes. It is involved in the phosphophatidylinositol signaling pathway, which affects a wide array of cell functions, including but not limited to, cell growth, apoptosis, secretion, and information processing. Inhibition of inositol monophosphatase may be key in the action of lithium in treating bipolar disorder, specifically manic depression.
In enzymology, a diphosphoinositol-pentakisphosphate kinase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an inositol-pentakisphosphate 2-kinase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Inositol (1,4,5) trisphosphate 3-kinase (EC 2.7.1.127), abbreviated here as ITP3K, is an enzyme that facilitates a phospho-group transfer from adenosine triphosphate to 1D-myo-inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate. This enzyme belongs to the family of transferases, specifically those transferring phosphorus-containing groups (phosphotransferases) with an alcohol group as acceptor. The systematic name of this enzyme class is ATP:1D-myo-inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate 3-phosphotransferase. ITP3K catalyzes the transfer of the gamma-phosphate from ATP to the 3-position of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate to form inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate. ITP3K is highly specific for the 1,4,5-isomer of IP3, and it exclusively phosphorylates the 3-OH position, producing Ins(1,3,4,5)P4, also known as inositol tetrakisphosphate or IP4.

Type I inositol-3,4-bisphosphate 4-phosphatase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the INPP4A gene.

Inositol hexakisphosphate kinase 2 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the IP6K2 gene.

Type II inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate 5-phosphatase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the INPP5B gene.

Multiple inositol polyphosphate phosphatase 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the MINPP1 gene.

Inositol polyphosphate 1-phosphatase is an enzyme that, in humans, is encoded by the INPP1 gene. INPP1 encodes the enzyme inositol polyphosphate-1-phosphatase, one of the enzymes involved in phosphatidylinositol signaling pathways. This enzyme removes the phosphate group at position 1 of the inositol ring from the polyphosphates inositol 1,4-bisphosphate and inositol 1,3,4-trisphophosphate.

Inositol hexakisphosphate kinase 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the IP6K1 gene.

A diglyceride, or diacylglycerol (DAG), is a glyceride consisting of two fatty acid chains covalently bonded to a glycerol molecule through ester linkages. Two possible forms exist, 1,2-diacylglycerols and 1,3-diacylglycerols. DAGs can act as surfactants and are commonly used as emulsifiers in processed foods. DAG-enriched oil has been investigated extensively as a fat substitute due to its ability to suppress the accumulation of body fat; with total annual sales of approximately USD 200 million in Japan since its introduction in the late 1990s till 2009.
Inositol-polyphosphate multikinase is an enzyme with systematic name ATP:1D-myo-inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate 6-phosphotransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction

Inositol polyphosphate kinase (IPK) is a family of enzymes that have a similar 3-dimensional structure. All members of the family catalyze the transfer of phosphate groups from ATP to various inositol phosphates. Members of the family include inositol-polyphosphate multikinases, inositol-hexakisphosphate kinases, inositol-trisphosphate 3-kinases, and inositol-pentakisphosphate 2-kinase, which is more distantly related to the others