
Desalination is a process that takes away mineral components from saline water. More generally, desalination refers to the removal of salts and minerals from a target substance, as in soil desalination, which is an issue for agriculture. Saltwater is desalinated to produce water suitable for human consumption or irrigation. The by-product of the desalination process is brine. Desalination is used on many seagoing ships and submarines. Most of the modern interest in desalination is focused on cost-effective provision of fresh water for human use. Along with recycled wastewater, it is one of the few rainfall-independent water resources.
Geothermal desalination refers to the process of using geothermal energy to power the process of converting salt water to fresh water. The process is considered economically efficient, and while overall environmental impact is uncertain, it has potential to be more environmentally friendly compared to conventional desalination options. Geothermal desalination plants have already been successful in various regions, and there is potential for further development to allow the process to be used in an increased number of water scarce regions.

Water conservation includes all the policies, strategies and activities to sustainably manage the natural resource of fresh water, to protect the hydrosphere, and to meet the current and future human demand. Population, household size and growth and affluence all affect how much water is used. Factors such as climate change have increased pressures on natural water resources especially in manufacturing and agricultural irrigation. Many countries have already implemented policies aimed at water conservation, with much success. The key activities to conserve water are as follows: any beneficial reduction in water loss, use and waste of resources, avoiding any damage to water quality; and improving water management practices that reduce the use or enhance the beneficial use of water. Technology solutions exist for households, commercial and agricultural applications. Water conservation programs involved in social solutions are typically initiated at the local level, by either municipal water utilities or regional governments.

Water reclamation is the process of converting municipal wastewater (sewage) or industrial wastewater into water that can be reused for a variety of purposes. Types of reuse include: urban reuse, agricultural reuse (irrigation), environmental reuse, industrial reuse, planned potable reuse, de facto wastewater reuse. For example, reuse may include irrigation of gardens and agricultural fields or replenishing surface water and groundwater. Reused water may also be directed toward fulfilling certain needs in residences, businesses, and industry, and could even be treated to reach drinking water standards. The injection of reclaimed water into the water supply distribution system is known as direct potable reuse, however, drinking reclaimed water is not a typical practice. Treated municipal wastewater reuse for irrigation is a long-established practice, especially in arid countries. Reusing wastewater as part of sustainable water management allows water to remain as an alternative water source for human activities. This can reduce scarcity and alleviate pressures on groundwater and other natural water bodies.

The International Water Management Institute (IWMI) is a non-profit international water management research organisation under the CGIAR with its headquarters in Colombo, Sri Lanka, and offices across Africa and Asia. Research at the Institute focuses on improving how water and land resources are managed, with the aim of underpinning food security and reducing poverty while safeguarding the environment.
The Earth Institute is a research institute at Columbia University that was established in 1995. Its stated mission is to address complex issues facing the planet and its inhabitants, with a focus on sustainable development. With an interdisciplinary approach, this includes research in climate change, geology, global health, economics, management, agriculture, ecosystems, urbanization, energy, hazards, and water. The Earth Institute's activities are guided by the idea that science and technological tools that already exist could be applied to greatly improve conditions for the world's poor, while preserving the natural systems that support life on Earth.

Environmental policy is the commitment of an organization or government to the laws, regulations, and other policy mechanisms concerning environmental issues. These issues generally include air and water pollution, waste management, ecosystem management, maintenance of biodiversity, the management of natural resources, wildlife and endangered species. For example, concerning environmental policy, the implementation of an eco-energy-oriented policy at a global level to address the issues of global warming and climate changes could be addressed. Policies concerning energy or regulation of toxic substances including pesticides and many types of industrial waste are part of the topic of environmental policy. This policy can be deliberately taken to influence human activities and thereby prevent undesirable effects on the biophysical environment and natural resources, as well as to make sure that changes in the environment do not have unacceptable effects on humans.

Clean technology, in short cleantech, is any process, product, or service that reduces negative environmental impacts through significant energy efficiency improvements, the sustainable use of resources, or environmental protection activities. Clean technology includes a broad range of technology related to recycling, renewable energy, information technology, green transportation, electric motors, green chemistry, lighting, grey water, and more. Environmental finance is a method by which new clean technology projects can obtain financing through the generation of carbon credits. A project that is developed with concern for climate change mitigation is also known as a carbon project.

Menachem Elimelech is the Sterling Professor of Chemical and Environmental Engineering at Yale University. Elimelech is the only professor from an engineering department at Yale to be awarded the Sterling professorship since its establishment in 1920. Elimelech moved from the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) to Yale University in 1998 and founded Yale's Environmental Engineering program.
The G8 Climate Change Roundtable was formed in January 2005 at the World Economic Forum in Davos, Switzerland. Its purpose was to address the global climate change issue facing governments, business and civil society. The first meeting was held in Gleneagles, Scotland, from 6–8 July 2005, to coincide with the 31st G8 summit.
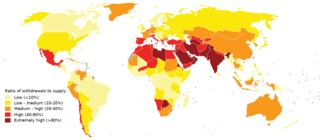
Water scarcity is the lack of fresh water resources to meet the standard water demand. There are two types of water scarcity namely physical water scarcity and economic water scarcity. Physical water scarcity is where there is not enough water to meet all demands, including that needed for ecosystems to function. Arid areas for example Central and West Asia, and North Africa often experience physical water scarcity. Economic water scarcity on the other hand, is the result of lack of investment in infrastructure or technology to draw water from rivers, aquifers, or other water sources, or weak human capacity to meet water demand. Much of Sub-Saharan Africa experience economic water scarcity.

Water resources are natural resources of water that are potentially useful for humans, for example as a source of drinking water supply or irrigation water. 97% of the water on Earth is salt water and only three percent is fresh water; slightly over two-thirds of this is frozen in glaciers and polar ice caps. The remaining unfrozen freshwater is found mainly as groundwater, with only a small fraction present above ground or in the air. Natural sources of fresh water include surface water, under river flow, groundwater and frozen water. Artificial sources of fresh water can include treated wastewater and desalinated seawater. Human uses of water resources include agricultural, industrial, household, recreational and environmental activities.
Water supply and sanitation in Israel are intricately linked to the historical development of Israel. Because rain falls only in the winter, and largely in the northern part of the country, irrigation and water engineering are considered vital to the country's economic survival and growth. Large scale projects to desalinate seawater, direct water from rivers and reservoirs in the north, make optimal use of groundwater, and reclaim flood overflow and sewage have been undertaken. Among them is the National Water Carrier, carrying water from the country's biggest freshwater lake, the Sea of Galilee, to the northern part of the Negev desert through channels, pipes and tunnels. Israel's water demand today outstrips available conventional water resources. Thus, in an average year, Israel relies for about half of its water supply on unconventional water resources, including reclaimed water and desalination. A particularly long drought in 1998–2002 had prompted the government to promote large-scale seawater desalination. In 2022, 85% of the country's drinkable water was produced through desalination of saltwater and brackish water.
WREN is a major non-profit organization registered in the United Kingdom with charitable status and affiliated to UNESCO, the Deputy Director General of which is its honorary President. It has a Governing Council, an Executive Committee and a Director General. It maintains links with many United Nations, governmental and non-governmental organisations.
Environmentally sustainable design is the philosophy of designing physical objects, the built environment, and services to comply with the principles of ecological sustainability and also aimed at improving the health and comfort of occupants in a building. Sustainable design seeks to reduce negative impacts on the environment, the health and well-being of building occupants, thereby improving building performance. The basic objectives of sustainability are to reduce the consumption of non-renewable resources, minimize waste, and create healthy, productive environments.

Water resource policy, sometimes called water resource management or water management, encompasses the policy-making processes and legislation that affect the collection, preparation, use, disposal, and protection of water resources. Water is a necessity for all forms of life as well as industries on which humans are reliant, like technology development and agriculture. This global need for clean water access necessitates water resource policy to determine the means of supplying and protecting water resources. Water resource policy varies by region and is dependent on water availability or scarcity, the condition of aquatic systems, and regional needs for water. Since water basins do not align with national borders, water resource policy is also determined by international agreements, also known as hydropolitics. Water quality protection also falls under the umbrella of water resource policy; laws protecting the chemistry, biology, and ecology of aquatic systems by reducing and eliminating pollution, regulating its usage, and improving the quality are considered water resource policy. When developing water resource policies, many different stakeholders, environmental variables, and considerations have to be taken to ensure the health of people and ecosystems are maintained or improved. Finally, ocean zoning, coastal, and environmental resource management are also encompassed by water resource management, like in the instance of offshore wind land leasing.
The water, energy and food security nexus according to the Food And Agriculture Organisation of the United Nations (FAO), means that water security, energy security and food security are very much linked to one another, meaning that the actions in any one particular area often can have effects in one or both of the other areas.

Environmental issues in the United Arab Emirates (UAE) are caused by the exploitation of natural resources, rapid population growth, and high energy demand. The continuing temperature rise caused by global warming contributes to UAE's water scarcity, drought, rising sea level, and aridity. The countryside of the UAE, characterized with its great arid land, infrequent precipitation, and high temperatures are already facing long-term aridity. This precondition is very vulnerable to the effects of climate change and contributes to worsening water scarcity, quality, and water contamination.
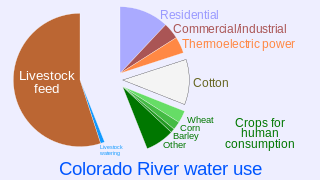
Water scarcity in the United States is a result of increasing changes to the Earth's climate and increasing population levels, and includes issues of both the amount of water that is available and the quality of that water. Water scarcity is one most often associated with developing countries, but not absent from first world countries. Most recently, the United States has seen many environmental issues which have exacerbated the clean water crisis in several states. The most recent incident occurred in February 2023 with the derailment of a train in Ohio that led to the release of toxic chemicals into the environment. This however is not the only incident which has affected water in the U.S., as past incidents such as the flood in Jackson, Mississippi have also greatly impact the availability of water. Both the incident of September 2022 in Jackson, and the lead water crisis in Flint have been due to old water treatment infrastructure greatly impacting communities which are majority black. Despite this, access to potable water is not the only issue, as many states, especially those in the western U.S., have seen droughts leaving many without running water. It's observed that more than 50% of the U.S. has experienced drought conditions in recent years, and this problem will only worsen, as it is estimated that 40 out of 50 states will experience water shortages in the next 10 years.











