The International Bank for Reconstruction and Development (IBRD) is an international financial institution, established in 1944 and headquartered in Washington, D.C., United States; it is the lending arm of World Bank Group. The IBRD offers loans to middle-income developing countries. It is the first of five member institutions that compose the World Bank Group. The initial mission of the IBRD in 1944, was to finance the reconstruction of European nations devastated by World War II. The IBRD and its concessional lending arm, the International Development Association (IDA), are collectively known as the World Bank as they share the same leadership and staff.

The European Bank for Reconstruction and Development is an international financial institution founded in 1991. As a multilateral developmental investment bank, the EBRD uses investment as a tool to build market economies.

The Inter-American Development Bank is an international financial institution headquartered in Washington, D.C., United States of America, and serving as the largest source of development financing for Latin America and the Caribbean. Established in 1959, the IDB supports Latin American and Caribbean economic development, social development and regional integration by lending to governments and government agencies, including State corporations.

An export credit agency or investment insurance agency is a private or quasi-governmental institution that acts as an intermediary between national governments and exporters to issue export insurance solutions and guarantees for financing. The financing can take the form of credits or credit insurance and guarantees or both, depending on the mandate the ECA has been given by its government. ECAs can also offer credit or cover on their own account. This does not differ from normal banking activities. Some agencies are government-sponsored, others private, and others a combination of the two.

The African Development Bank Group (AfDB) or Banque Africaine de Développement (BAD) is a multilateral development finance institution headquartered in Abidjan, Ivory Coast, since September 2014. The AfDB is a financial provider to African governments and private companies investing in the regional member countries (RMC).

The Nordic Investment Bank (NIB) is an international financial institution founded in 1975 by the five Nordic countries. In 2005, the three Baltic states also became members of the Bank. NIB’s headquarters are located in Helsinki, Finland. NIB acquires the funds for its lending by borrowing on the international capital markets.
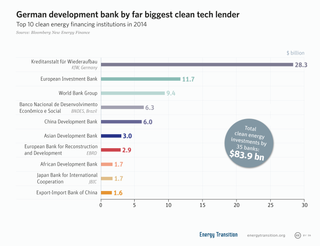
Development financial institution (DFI), also known as a Development bank, is a financial institution that provides risk capital for economic development projects on a non-commercial basis.

FMO is a Dutch development bank structured as a bilateral private-sector international financial institution based in the Hague, the Netherlands. FMO manages funds for the Ministries of Foreign Affairs and Economic Affairs of the Dutch government to maximize the development impact of private sector investments. It is licensed as a bank and supervised by the Dutch Central Bank.

The Black Sea Trade and Development Bank (BSTDB) is an international development finance institution serving the eleven member founding countries of the Black Sea Economic Cooperation, a regional economic organization. It supports economic development and regional cooperation by providing loans, guarantees, and equity for development projects and trade transactions. BSTDB supports both public and private enterprises in member countries and does not attach political conditionality to its financing.
This is a list of international organizations in which Canada has membership.
AccessBank Liberia (ABL), is a microfinance commercial bank in Liberia. It is one of the commercial banks licensed by the Central Bank of Liberia, the national banking regulator.

Climate finance consists of funding processes for investments related to climate change mitigation and adaptation. The term has been used in a narrower sense to refer to transfers of public resources from developed to developing countries, in light of their UN Climate Convention obligations to provide "new and additional financial resources". In a wider sense, the term refers to all financial flows relating to climate change mitigation and adaptation.

The New Development Bank (NDB), formerly referred to as the BRICS Development Bank, is a multilateral development bank established by the BRICS states (Brazil, Russia, India, China and South Africa). According to the Agreement on the NDB, "the Bank shall support public or private projects through loans, guarantees, equity participation and other financial instruments." Moreover, the NDB "shall cooperate with international organizations and other financial entities, and provide technical assistance for projects to be supported by the Bank."

The Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank (AIIB) is a multilateral development bank and international financial institution that aims to collectively improve economic and social outcomes in Asia. It is the world's second largest multi-lateral development institution. Headquartered in Beijing, China, the bank currently has 109 members, including 14 prospective members from around the world. The breakdown of the 109 members by continents are as follows: 42 in Asia, 26 in Europe, 22 in Africa, 9 in Oceania, 8 in South America, and 2 in North America. The bank started operation after the agreement entered into force on 25 December 2015, after ratifications were received from 10 member states holding a total number of 50% of the initial subscriptions of the Authorized Capital Stock.

The World Bank is an international financial institution that provides loans and grants to the governments of low- and middle-income countries for the purpose of pursuing capital projects. The World Bank is the collective name for the International Bank for Reconstruction and Development (IBRD) and International Development Association (IDA), two of five international organizations owned by the World Bank Group. It was established along with the International Monetary Fund at the 1944 Bretton Woods Conference. After a slow start, its first loan was to France in 1947. In the 1970s, it focused on loans to developing world countries, shifting away from that mission in the 1980s. For the last 30 years, it has included NGOs and environmental groups in its loan portfolio. Its loan strategy is influenced by the United Nations' Sustainable Development Goals, as well as environmental and social safeguards.
The European Long-Term Investors Association (ELTI) aisbl represent a European-wide network of National Promotional Banks and Institutions (NPBIs). As of May 2020, the association gathers 31 European long-term financial institutions from 23 Member States across the European Union and Turkey.

The Sustainable Development Investment Partnership (SDIP) is an international public-private partnership which aims to use blended finance to support sustainable infrastructure investments in developing countries. The SDIP thus brings together public, private and philanthropic entities to work towards the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) set out by the United Nations. The SDIP was launched at the United Nations Conference on Financing for Development in Addis Ababa in July 2015 with 20 founding members, which has since risen to 42. The World Economic Forum and OECD were founding partners and provide institutional support. SDIP's inaugural meeting took place in Geneva, Switzerland on 15 September 2015.

Vilius Šapoka is a former Minister of Finance in Republic of Lithuania and Governor of the European Investment Bank for the Republic of Lithuania.

Jānis Reirs is a Latvian politician who served as Minister of Finance in the first Kariņš cabinet from 2019 until 2022, as well as Minister for Welfare in the Kučinskis cabinet from 2016 until 2019 and Minister of Finance in the second Straujuma cabinet.

Kashf Foundation is a non-profit organization, founded by Roshaneh Zafar in 1996. Kashf is regarded as the first microfinance institution (MFI) of Pakistan that uses village banking methodology in microcredit to alleviate poverty by providing affordable financial and non-financial services to low income households - particularly for women, to build their capacity and enhance their economic role. With headquarters in Lahore, Punjab, Kashf has regional offices in five major cities and over 200 branches across the Pakistan.















