Formic acid, systematically named methanoic acid, is the simplest carboxylic acid, and has the chemical formula H2CO2. It is an important intermediate in chemical synthesis and occurs naturally, most notably in some ants. The word "formic" comes from the Latin word for ant, formica, referring to its early isolation by the distillation of ant bodies. Esters, salts, and the anion derived from formic acid are called formates. Industrially, formic acid is produced from methanol.

Methyl formate, also called methyl methanoate, is the methyl ester of formic acid. The simplest example of an ester, it is a colorless liquid with an ethereal odour, high vapor pressure, and low surface tension. It is a precursor to many other compounds of commercial interest.

Formamide, also known as methanamide, is an amide derived from formic acid. It is a clear liquid which is miscible with water and has an ammonia-like odor. It is chemical feedstock for the manufacture of sulfa drugs, other pharmaceuticals, herbicides, pesticides and the manufacture of hydrocyanic acid. It has been used as a softener for paper and fiber. It is a solvent for many ionic compounds. It has also been used as a solvent for resins and plasticizers.
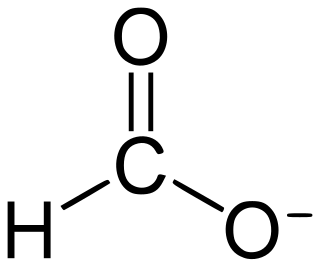
Formate is the anion derived A formate (compound) is a salt or ester of formic acid.

Ethyl formate is an ester formed when ethanol reacts with formic acid. Ethyl formate has the characteristic smell of rum and is also partially responsible for the flavor of raspberries. It occurs naturally in the body of ants and in the stingers of bees.
The Tishchenko reaction is an organic chemical reaction that involves disproportionation of an aldehyde in the presence of an alkoxide. The reaction is named after Russian organic chemist Vyacheslav Tishchenko, who discovered that aluminium alkoxides are effective catalysts for the reaction.
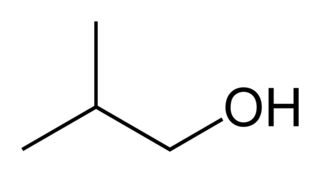
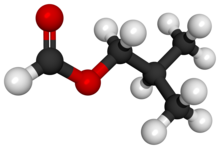
Isobutanol (IUPAC nomenclature: 2-methylpropan-1-ol) is an organic compound with the formula (CH3)2CHCH2OH (sometimes represented as i-BuOH). This colorless, flammable liquid with a characteristic smell is mainly used as a solvent either directly or as its esters. Its isomers, the other butanols, include n-butanol, 2-butanol, and tert-butanol, all of which are important industrially.
Isobutyl nitrite, C4H9NO2, is an alkyl nitrite, an ester of isobutanol and nitrous acid. Its chemical structure is (CH3)2CH-CH2-ONO.

n-Butyl acetate, also known as butyl ethanoate, is an ester that is a colorless, flammable liquid at room temperature. It is found in many types of fruit, where along with other chemicals, it imparts characteristic flavors and has a sweet smell of banana or apple. It is used as a synthetic fruit flavoring in foods such as candy, ice cream, cheeses, and baked goods. Butyl acetate is often used as a high-boiling solvent of moderate polarity. It is also used as a solvent in nail polish along with ethyl acetate.

The chemical compound isobutyl acetate, also known as 2-methylpropyl ethanoate or β-methylpropyl acetate, is a common solvent. It is produced from the esterification of isobutanol with acetic acid. It is used as a solvent for lacquer and nitrocellulose. Like many esters it has a fruity or floral smell at low concentrations and occurs naturally in raspberries, pears and other plants. At higher concentrations the odor can be unpleasant and may cause symptoms of central nervous system depression such as nausea, dizziness and headache.

tert-Butyl acetate, t-butyl acetate or TBAc is a colorless flammable liquid with a camphor- or blueberry-like smell. It is used as a solvent in the production of lacquers, enamels, inks, adhesives, thinners and industrial cleaners. It has recently gained EPA volatile organic compound (VOC) exempt status.

Sodium formate, HCOONa, is the sodium salt of formic acid, HCOOH. It usually appears as a white deliquescent powder.
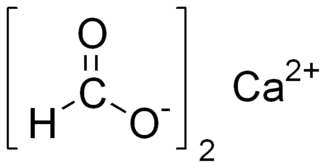
Calcium formate is the calcium salt of formic acid. It is also known as E238. Under this E number it is used as an animal feed preservative within EU, but not in foods intended for people.
The molecular formula C5H10O2 (molar mass: 102.13 g/mol) may refer to:
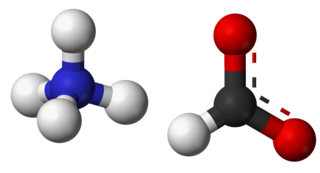
Ammonium formate, NH4HCO2, is the ammonium salt of formic acid. It is a colorless, hygroscopic, crystalline solid.
The Cl−-formate exchanger, otherwise known as Pendrin encoded by the SLC26A4 gene, is a transport protein present in the kidney, where it functions in the renal chloride reabsorption. It is also present in vascular smooth muscle and cardiac muscle.

Potassium formate, HCO2K, HCOOK, or CHKO2, is the potassium salt of formic acid. This strongly hygroscopic white solid is an intermediate in the formate potash process for the production of potassium. Potassium formate has also been studied as a potential environmentally friendly deicing salt for use on roads. It has also been suggested for use in a less corrosive liquid desiccant. A 52% solution of potassium formate has a freezing point of −60 °C (−76 °F).

Acmella oleracea is a species of flowering herb in the family Asteraceae. Common names include toothache plant, paracress, Sichuan buttons, buzz buttons, tingflowers and electric daisy. Its native distribution is unclear, but it is likely derived from a Brazilian Acmella species. It is grown as an ornamental and attracts fireflies when in bloom. It is used as a medicinal remedy in various parts of the world. A small, erect plant, it grows quickly and bears gold and red inflorescences. It is frost-sensitive but perennial in warmer climates.
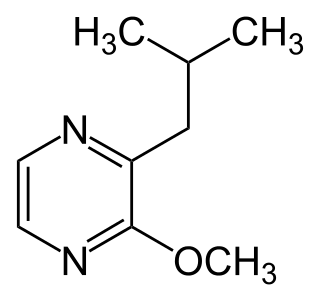
3-Isobutyl-2-methoxypyrazine is a methoxypyrazine that is very similar to isopropyl methoxy pyrazine except that the alkyl side-group contains an isobutyl group attached to the carbon alpha to the methoxy sidegroup instead of an isopropyl side-group at that same carbon position.