Isomerases are a general class of enzymes that convert a molecule from one isomer to another. Isomerases facilitate intramolecular rearrangements in which bonds are broken and formed. The general form of such a reaction is as follows:
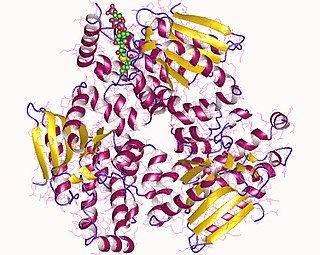
Enoyl-CoA-(∆) isomerase (EC 5.3.3.8, also known as dodecenoyl-CoA- isomerase, 3,2-trans-enoyl-CoA isomerase, ∆3 ,∆2 -enoyl-CoA isomerase, or acetylene-allene isomerase, is an enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of cis- or trans-double bonds of coenzyme A bound fatty acids at gamma-carbon to trans double bonds at beta-carbon as below:
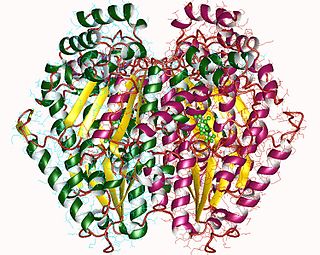
Glucose-6-phosphate isomerase (GPI), alternatively known as phosphoglucose isomerase/phosphoglucoisomerase (PGI) or phosphohexose isomerase (PHI), is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the GPI gene on chromosome 19. This gene encodes a member of the glucose phosphate isomerase protein family. The encoded protein has been identified as a moonlighting protein based on its ability to perform mechanistically distinct functions. In the cytoplasm, the gene product functions as a glycolytic enzyme that interconverts glucose-6-phosphate (G6P) and fructose-6-phosphate (F6P). Extracellularly, the encoded protein functions as a neurotrophic factor that promotes survival of skeletal motor neurons and sensory neurons, and as a lymphokine that induces immunoglobulin secretion. The encoded protein is also referred to as autocrine motility factor (AMF) based on an additional function as a tumor-secreted cytokine and angiogenic factor. Defects in this gene are the cause of nonspherocytic hemolytic anemia, and a severe enzyme deficiency can be associated with hydrops fetalis, immediate neonatal death and neurological impairment. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2014]

Triose-phosphate isomerase is an enzyme that catalyzes the reversible interconversion of the triose phosphate isomers dihydroxyacetone phosphate and D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate.

Triosephosphate isomerase deficiency is a rare autosomal recessive metabolic disorder which was initially described in 1965.

Isopentenyl pyrophosphate isomerase, also known as Isopentenyl-diphosphate delta isomerase, is an isomerase that catalyzes the conversion of the relatively un-reactive isopentenyl pyrophosphate (IPP) to the more-reactive electrophile dimethylallyl pyrophosphate (DMAPP). This isomerization is a key step in the biosynthesis of isoprenoids through the mevalonate pathway and the MEP pathway.
In enzymology, an isopiperitenol dehydrogenase (EC 1.1.1.223) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a 5-carboxymethyl-2-hydroxymuconate Delta-isomerase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an aconitate Δ-isomerase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a cholestenol Δ-isomerase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a L-dopachrome isomerase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a methylitaconate Δ-isomerase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a muconolactone Δ-isomerase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a polyenoic fatty acid isomerase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a Prostaglandin-A1 Δ-isomerase (EC 5.3.3.9) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Ribose-5-phosphate isomerase (Rpi) encoded by the RPIA gene is an enzyme that catalyzes the conversion between ribose-5-phosphate (R5P) and ribulose-5-phosphate (Ru5P). It is a member of a larger class of isomerases which catalyze the interconversion of chemical isomers. It plays a vital role in biochemical metabolism in both the pentose phosphate pathway and the Calvin cycle. The systematic name of this enzyme class is D-ribose-5-phosphate aldose-ketose-isomerase.

In enzymology, a steroid Δ5-isomerase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a vinylacetyl-CoA Delta-isomerase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
(-)-Isopiperitenone reductase (EC 1.3.1.82) is an enzyme with systematic name (+)-cis-isopulegone:NADP+ oxidoreductase. It catalyses the following chemical reaction:

In enzymology, a xylose isomerase is an enzyme that catalyzes the interconversion of D-xylose and D-xylulose. This enzyme belongs to the family of isomerases, specifically those intramolecular oxidoreductases interconverting aldoses and ketoses. The isomerase has now been observed in nearly a hundred species of bacteria. Xylose-isomerases are also commonly called fructose-isomerases due to their ability to interconvert glucose and fructose. The systematic name of this enzyme class is D-xylose aldose-ketose-isomerase. Other names in common use include D-xylose isomerase, D-xylose ketoisomerase, and D-xylose ketol-isomerase.








