Related Research Articles

Somatostatin, also known as growth hormone-inhibiting hormone (GHIH) or by several other names, is a peptide hormone that regulates the endocrine system and affects neurotransmission and cell proliferation via interaction with G protein-coupled somatostatin receptors and inhibition of the release of numerous secondary hormones. Somatostatin inhibits insulin and glucagon secretion.
Autocrine signaling is a form of cell signaling in which a cell secretes a hormone or chemical messenger that binds to autocrine receptors on that same cell, leading to changes in the cell. This can be contrasted with paracrine signaling, intracrine signaling, or classical endocrine signaling.

Sertoli cells are a type of sustentacular "nurse" cell found in human testes which contribute to the process of spermatogenesis as a structural component of the seminiferous tubules. They are activated by follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) secreted by the adenohypophysis and express FSH receptor on their membranes.
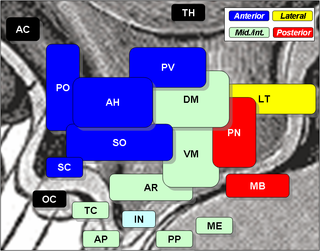
The arcuate nucleus of the hypothalamus (ARH), or ARC, is also known as the infundibular nucleus to distinguish it from the arcuate nucleus of the medulla oblongata in the brainstem. The arcuate nucleus is an aggregation of neurons in the mediobasal hypothalamus, adjacent to the third ventricle and the median eminence. The arcuate nucleus includes several important and diverse populations of neurons that help mediate different neuroendocrine and physiological functions, including neuroendocrine neurons, centrally projecting neurons, and astrocytes. The populations of neurons found in the arcuate nucleus are based on the hormones they secrete or interact with and are responsible for hypothalamic function, such as regulating hormones released from the pituitary gland or secreting their own hormones. Neurons in this region are also responsible for integrating information and providing inputs to other nuclei in the hypothalamus or inputs to areas outside this region of the brain. These neurons, generated from the ventral part of the periventricular epithelium during embryonic development, locate dorsally in the hypothalamus, becoming part of the ventromedial hypothalamic region. The function of the arcuate nucleus relies on its diversity of neurons, but its central role is involved in homeostasis. The arcuate nucleus provides many physiological roles involved in feeding, metabolism, fertility, and cardiovascular regulation.

The endocrine system is a network of glands and organs located throughout the body. It is similar to the nervous system in that it plays a vital role in controlling and regulating many of the body's functions. Endocrine glands are ductless glands of the endocrine system that secrete their products, hormones, directly into the blood. The major glands of the endocrine system include the pineal gland, pituitary gland, pancreas, ovaries, testicles, thyroid gland, parathyroid gland, hypothalamus and adrenal glands. The hypothalamus and pituitary glands are neuroendocrine organs.
Releasing hormones and inhibiting hormones are hormones whose main purpose is to control the release of other hormones, either by stimulating or inhibiting their release. They are also called liberins and statins (respectively), or releasing factors and inhibiting factors. The principal examples are hypothalamic-pituitary hormones that can be classified from several viewpoints: they are hypothalamic hormones, they are hypophysiotropic hormones, and they are tropic hormones.
Growth hormone–releasing hormone (GHRH), also known as somatocrinin among other names in its endogenous form and as somatorelin (INN) in its pharmaceutical form, is a releasing hormone of growth hormone (GH). It is a 44-amino acid peptide hormone produced in the arcuate nucleus of the hypothalamus.
The prolactin receptor (PRLR) is a type I cytokine receptor encoded in humans by the PRLR gene on chromosome 5p13-14. It is the receptor for prolactin (PRL). The PRLR can also bind to and be activated by growth hormone (GH) and human placental lactogen (hPL). The PRLR is expressed in the mammary glands, pituitary gland, and other tissues. It plays an important role in lobuloalveolar development of the mammary glands during pregnancy and in lactation.
Somatostatinomas are a tumor of the delta cells of the endocrine pancreas that produces somatostatin. Increased levels of somatostatin inhibit pancreatic hormones and gastrointestinal hormones. Thus, somatostatinomas are associated with mild diabetes mellitus, steatorrhoea and gallstones, and achlorhydria. Somatostatinomas are commonly found in the head of pancreas. Only ten percent of somatostatinomas are functional tumours [9], and 60–70% of tumours are malignant. Nearly two-thirds of patients with malignant somatostatinomas will present with metastatic disease.
Hormonal therapy in oncology is hormone therapy for cancer and is one of the major modalities of medical oncology, others being cytotoxic chemotherapy and targeted therapy (biotherapeutics). It involves the manipulation of the endocrine system through exogenous or external administration of specific hormones, particularly steroid hormones, or drugs which inhibit the production or activity of such hormones. Because steroid hormones are powerful drivers of gene expression in certain cancer cells, changing the levels or activity of certain hormones can cause certain cancers to cease growing, or even undergo cell death. Surgical removal of endocrine organs, such as orchiectomy and oophorectomy can also be employed as a form of hormonal therapy.

The growth-hormone-releasing hormone receptor (GHRHR) is a G-protein-coupled receptor that binds growth hormone-releasing hormone. The GHRHR activates a Gs protein that causes a cascade of cAMP via adenylate cyclase. GHRHR is distinct from the growth hormone secretagogue receptor, where growth hormone releasing peptides act to release growth hormone.

G protein-coupled estrogen receptor 1 (GPER), also known as G protein-coupled receptor 30 (GPR30), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GPER gene. GPER binds to and is activated by the female sex hormone estradiol and is responsible for some of the rapid effects that estradiol has on cells.

Hypothalamic–pituitary hormones are hormones that are produced by the hypothalamus and pituitary gland. Although the organs in which they are produced are relatively small, the effects of these hormones cascade throughout the body. They can be classified as a hypothalamic–pituitary axis of which the adrenal, gonadal, thyroid, somatotropic, and prolactin axes are branches.
Hormonal regulation occurs at every stage of development. A milieu of hormones simultaneously affects development of the fetus during embryogenesis and the mother, including human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) and progesterone (P4).
EPI-001 is the first inhibitor of the androgen receptor amino-terminal domain. The single stereoisomer of EPI-001, EPI-002, is a first-in-class drug that the USAN council assigned a new stem class "-aniten" and the generic name "ralaniten". This distinguishes the anitens novel molecular mechanism from anti androgens that bind the C-terminus ligand-binding domain and have the stem class "lutamide". EPI-001 and its stereoisomers and analogues were discovered by Marianne Sadar and Raymond Andersen, who co-founded the pharmaceutical company ESSA Pharma Inc for the clinical development of anitens for the treatment of castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC).
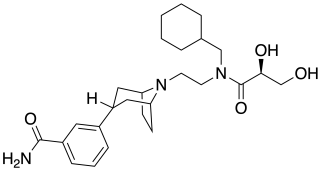
Axelopran is a drug which is under development by Theravance Biopharma and licensed to Glycyx for all indications. It acts as a peripherally acting μ-opioid receptor antagonist and also acts on κ-, and δ-opioid receptors, with similar affinity for the μ- and κ-opioid receptors and about an order of magnitude lower affinity for the δ-opioid receptor. Recent data suggests that μ-opioid antagonists have a direct effect on overall survival in patients with advanced cancer.
A hormone-sensitive cancer, or hormone-dependent cancer, is a type of cancer that is dependent on a hormone for growth and/or survival. Examples include breast cancer, which is dependent on estrogens like estradiol, and prostate cancer, which is dependent on androgens like testosterone.
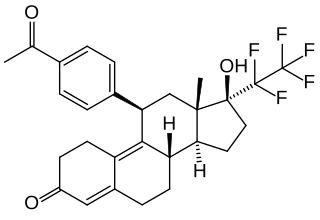
Lonaprisan is a synthetic, steroidal antiprogestogen which was under development by Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals for the treatment of endometriosis, dysmenorrhea, and breast cancer but was discontinued. It is a potent and highly selective silent antagonist of the progesterone receptor (PR). The drug reached phase II clinical trials prior to its discontinuation.

ERX-11, also known as ERα coregulator-binding modulator-11, is a novel antiestrogen and experimental hormonal antineoplastic agent which is being researched for the potential treatment of estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer. It is not a competitive antagonist of the estrogen receptor (ER) like conventional antiestrogens such as tamoxifen or fulvestrant; instead of binding to the ligand-binding site of the ER, ERX-11 interacts with a different part of the ERα and blocks protein–protein interactions of the ERα with coregulators that are necessary for the receptor to act and regulate gene expression. It was designed to bind to the coregulator binding region of the ERα and inhibit the ERα/coactivator interaction, although its precise binding site and mode of action have yet to be fully elucidated and understood. Nonetheless, it is clear that ERX-11 binds within the AF-2 domain of the ERα.
Endocrine therapy is a common treatment for estrogen receptor positive breast cancer. However, resistance to this therapy can develop, leading to relapse and progression of disease. This highlights the need for new strategies to combat this resistance.
References
- ↑ Annunziata M, Grande C, Scarlatti F, et al. (June 2009). "The growth hormone-releasing hormone (GHRH) antagonist JV-1-36 inhibits proliferation and survival of human ectopic endometriotic stromal cells (ESCs) and the T HESC cell line". Fertil. Steril. 94 (3): 841–849. doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2009.03.093 . PMID 19524226.