
The Qing dynasty, officially the Great Qing, was a Manchu-led imperial dynasty of China and the last imperial dynasty in Chinese history. It emerged from the Later Jin dynasty founded by a Tungusic-speaking ethnic group who became known as the Manchus. The dynasty was officially proclaimed in 1636 in Mukden, and following the Battle of Shanhai Pass it seized control of Beijing in 1644, which is often considered the start of the dynasty's rule in China. Within decades the Qing had consolidated its control over the whole of China proper and Taiwan, and by the mid-18th century it had expanded its rule into Inner Asia. The dynasty lasted until 1912 when it was overthrown in the Xinhai Revolution. In Chinese historiography, the Qing dynasty was preceded by the Ming dynasty and succeeded by the Republic of China. The multiethnic Qing dynasty assembled the territorial base for modern China. It was the largest imperial dynasty in the history of China and in 1790 the fourth-largest empire in world history in terms of territorial size. With 419,264,000 citizens in 1907, it was the most populous country in the world at the time.
The Haijin (海禁) or sea ban was a series of related isolationist policies in China restricting private maritime trading and coastal settlement during most of the Ming dynasty and early Qing dynasty. The policy introduced by the Ming founder Zhu Yuanzhang significantly hampered the growth of China's domestic trade, although the Ming was not able to enforce the policy in full despite official proclamations, and trade continued in forms like smuggling until the late Ming government opened the port of Yuegang for trade. Later, the early Qing dynasty's anti-insurgent "Great Clearance" (1661-1683) also caused considerable devastating effects on communities along the coast, until the Qing seized control of Taiwan and opened coastal ports to foreign trade.
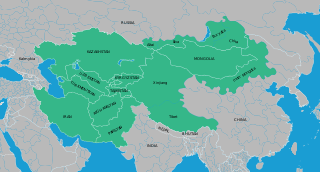
Inner Asia refers to the northern and landlocked regions spanning North, Central and East Asia. It includes parts of western and northeast China, as well as southern Siberia. The area overlaps with some definitions of 'Central Asia', mostly the historical ones, but certain regions that are often included in Inner Asia, such as Manchuria, are not a part of Central Asia by any of its definitions. Inner Asia may be regarded as the western and northern "frontier" of China proper of the former Qin dynasty and as being bounded by East Asia proper, which consists of China proper, Japan and Korea.

Lin Zexu, courtesy name Yuanfu, was a Chinese political philosopher and politician. He was a head of state (Viceroy), Governor General, scholar-official, and under the Daoguang Emperor of the Qing dynasty best known for his role in the First Opium War of 1839–42. He was from Fuzhou, Fujian Province. Lin's forceful opposition to the opium trade was a primary catalyst for the First Opium War. He is praised for his constant position on the "moral high ground" in his fight, but he is also blamed for a rigid approach which failed to account for the domestic and international complexities of the problem. The Emperor endorsed the hardline policies and anti-drugs movement advocated by Lin, but placed all responsibility for the resulting disastrous Opium War onto Lin.

The Ten Great Campaigns were a series of military campaigns launched by the Qing dynasty of China in the mid–late 18th century during the reign of the Qianlong Emperor. They included three to enlarge the area of Qing control in Inner Asia: two against the Dzungars (1755–1757) and the "pacification" of Xinjiang (1758–1759). The other seven campaigns were more in the nature of police actions on frontiers already established: two wars to suppress the Gyalrong of Jinchuan, Sichuan, another to suppress the Taiwanese Aboriginals (1787–88), and four expeditions abroad against the Burmese (1765–1769), the Vietnamese (1788–1789), and the Gurkhas on the border between Tibet and Nepal (1790–1792), with the last counting as two.
The Fragrant Concubine is a figure in Chinese legend who was taken as a consort by the Qianlong Emperor of the Qing dynasty in the 18th century. Although the stories about her are believed to be mythical, they may have been based on an actual concubine from western China who entered the imperial harem in 1760 and received the title "Imperial Consort Rong". Qing Dynasty and Uyghur tellings of the legend of the Fragrant Concubine diverge greatly and her experience represents a powerful symbol for both cultures. The story became very popular during the early 20th century and has since been adapted into several plays, films and books.
Chinese expansionism over the last four millennia has been a central feature throughout the arc of East Asian history. During times when China wielded extensive geopolitical influence over the course of the Han, Tang, Yuan, and Qing eras, the degree of Chinese geopolitical power projection would extend beyond the confines of East Asia and even influence the development and politics further north and west in North Asia, Central Asia, and into parts of South and Southeast Asia as well.
Michel Benoist was a Jesuit scientist who served for thirty years in the court of the Qianlong Emperor during the Qing dynasty, known for his architectural and landscape designs of the Old Summer Palace. Along with Giuseppe Castiglione, Benoist served as one of two Jesuit advisors to the Qianlong Emperor, and transformed parts of the Old Summer Palace into what historian Mark Elliott calls an "imitation of Versailles or Fontainebleau."

The Canton System served as a means for Qing China to control trade with the West within its own country by focusing all trade on the southern port of Canton. The protectionist policy arose in 1757 as a response to a perceived political and commercial threat from abroad on the part of successive Chinese emperors.

Pamela Kyle Crossley is a historian of modern China, northern Asia, and global history and is the Charles and Elfriede Collis Professor of History, Dartmouth College. She is a founding appointment of the Dartmouth Society of Fellows.

The Puning Temple, commonly called the Big Buddha Temple, is a Buddhist temple complex in Chengde, Hebei province, China. It was built in 1755 during the reign of the Qianlong Emperor in the Qing dynasty. It is near the Chengde Mountain Resort and alongside the equally famed Putuo Zongcheng Temple. Puning is one of the "Eight Outer Temples" of Chengde.

The Dzungar people are the many Mongol Oirat tribes who formed and maintained the Dzungar Khanate in the 17th and 18th centuries. Historically, they were one of the major tribes of the Four Oirat confederation. They were also known as the Eleuths or Ööled, from the Qing dynasty euphemism for the hated word "Dzungar", and as the "Kalmyks". In 2010, 15,520 people claimed "Ööled" ancestry in Mongolia. An unknown number also live in China, Russia and Kazakhstan.

The Battle of Ty-ho Bay was a significant naval engagement in 1855 involving the United Kingdom and United States against Chinese pirates. The action off Tai O, Hong Kong was to rescue captured merchant vessels, held by a fleet of armed war-junks. British and American forces defeated the pirates in one of the last major battles between Chinese pirate fleets and western navies. It was also one of the first joint operations undertaken by British and American forces.

Migration to Xinjiang is both an ongoing and historical movement of people, often sponsored by various states who controlled the region, including the Han dynasty, Qing dynasty, Republic of China and People's Republic of China.

The Dzungar genocide was the mass extermination of the Mongol Dzungar people by the Qing dynasty. The Qianlong Emperor ordered the genocide after the rebellion in 1755 by Dzungar leader Amursana against Qing rule, after the dynasty first conquered the Dzungar Khanate with Amursana's support. The genocide was perpetrated by Manchu generals of the Qing army, supported by Turkic oasis dwellers who rebelled against Dzungar rule.
Anti-Mongol sentiment has been prevalent throughout history, often perceiving the Mongols to be barbaric and uncivilized people with a lack of intelligence or civilized culture.

The imperial hunt of the Qing dynasty was an annual rite of the emperors of China during the Qing dynasty (1636–1912). It was first organized in 1681 by the Kangxi Emperor at the imperial hunting grounds at Mulan (modern-day Weichang Manchu and Mongol Autonomous County, near what would become the summer residence of the Qing emperors at Chengde. Starting in 1683 the event was held annually at Mulan during the autumn, lasting up to a month. The Qing dynasty hunt was a synthesis of earlier Chinese and Inner Asian hunting traditions, particularly those of the Manchus and Mongols. The emperor himself participated in the hunt, along with thousands of soldiers, imperial family members, and government officials.
The New Qing History is a historiographical school that gained prominence in the United States in the mid-1990s by offering a wide-ranging revision of history of the Manchu-led Qing dynasty of China. Orthodox historians tend to emphasize the power of the Han people to "sinicize" their conquerors in their thought and institutions. In the 1980s and early 1990s, American scholars began to learn Manchu and took advantage of newly opened Chinese- and Manchu-language archives. This research found that the Manchu rulers were savvy in manipulating their subjects and from the 1630s through at least the 18th century, emperors developed a sense of Manchu identity and used traditional Han Chinese culture and Confucian models to rule, while blending with models from other ethnic groups across the vast empire, including those from northern China, the Eurasian Steppe, and Inner Asia.
Evelyn Sakakida Rawski is Distinguished University Professor in the Department of History of the University of Pittsburgh and a scholar in Chinese and Inner Asian history. She was born in Honolulu, Hawaii, United States of Japanese-American ancestry. She served as president of the Association for Asian Studies in 1995–1996.
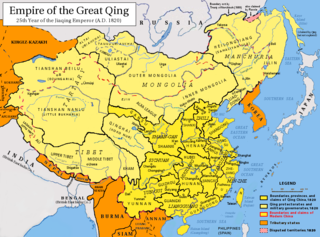
The Qing dynasty in Inner Asia was the expansion of the Qing dynasty's realm in Inner Asia in the 17th and the 18th century AD, including both Inner Mongolia and Outer Mongolia, both Manchuria and Outer Manchuria, Tibet, Qinghai and Xinjiang.












