
Isle of Wight County is a county located in the Hampton Roads region of the U.S. state of Virginia. It was named after the Isle of Wight, England, south of the Solent, from where many of its early colonists had come. As of the 2020 census, the population was 38,606. Its county seat is Isle of Wight, an unincorporated community.

John Nash was one of the foremost British architects of the Georgian and Regency eras, during which he was responsible for the design, in the neoclassical and picturesque styles, of many important areas of London. His designs were financed by the Prince Regent and by the era's most successful property developer, James Burton. Nash also collaborated extensively with Burton's son, Decimus Burton.

Courtland is an incorporated town in Southampton County, Virginia, United States. It is the county seat of Southampton County.

Pictou is a town in Pictou County, in the Canadian province of Nova Scotia. Located on the north shore of Pictou Harbour, the town is approximately 10 km north of the larger town of New Glasgow.

James Hoban was an Irish-American architect, best known for designing the White House.

Palladian architecture is a European architectural style derived from the work of the Venetian architect Andrea Palladio (1508–1580). What is today recognised as Palladian architecture evolved from his concepts of symmetry, perspective and the principles of formal classical architecture from ancient Greek and Roman traditions. In the 17th and 18th centuries, Palladio's interpretation of this classical architecture developed into the style known as Palladianism.
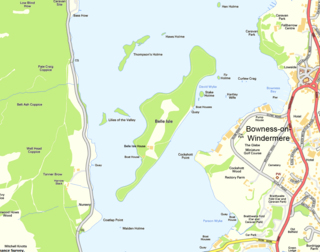
Belle Isle is the largest of 18 islands on Windermere, a mere in the English Lake District, and the only one ever to have been inhabited. It is 1 km in length.

Asher Benjamin was an American architect and author whose work transitioned between Federal architecture and the later Greek Revival architecture. His seven handbooks on design deeply influenced the look of cities and towns throughout New England until the Civil War. Builders also copied his plans in the Midwest and in the South.
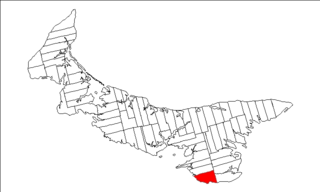
Lot 62 is a township in Queens County, Prince Edward Island, part of St. John's Parish. Lot 62 was awarded to Richard Spry, Esquire in the 1767 Land Lottery, and came to be settled through the efforts of Thomas Douglas, The 5th Earl of Selkirk in 1803. Richard Spry, Esquire, was then Commodore, Commander-in-Chief, Mediterranean Fleet at Gibraltar 1766–1769. Becoming the proprietor, he would be familiar with then the Island of St. John, having first come out to North America in 1754, with the English naval blockade of Ile Royal and the Fortress of Louisbourg in 1756, and then serving off Quebec and in the St. Lawrence into 1759. In 1762, he returned as Commander-in-Chief, North America, quartered in Halifax.

Buildings, sites, districts, and objects in Virginia listed on the National Register of Historic Places:

Goodhue Livingston was an American architect who co-founded the firm of Trowbridge & Livingston. He designed the St. Regis Hotel, the Hayden Planetarium, and numerous buildings listed on the National Register of Historic Places.
Belfast is a rural municipality in Prince Edward Island, Canada. It is located in southeastern Queens County in the townships of Lot 57 and Lot 58.

Samuel Sloan was a Philadelphia-based architect and best-selling author of architecture books in the mid-19th century. He specialized in Italianate villas and country houses, churches, and institutional buildings. His most famous building—the octagonal mansion "Longwood" in Natchez, Mississippi—is unfinished; construction was abandoned during the American Civil War.

Swiss chalet style is an architectural style of Late Historicism, originally inspired by rural chalets in Switzerland and the Alpine (mountainous) regions of Central Europe. The style refers to traditional building designs characterised by widely projecting roofs and facades richly decorated with wooden balconies and carved ornaments. It spread over Germany, Austria-Hungary, Italy, France and Scandinavia during the Belle Époque era.

Frederick Clarke Withers was an English architect in America, especially renowned for his Gothic Revival ecclesiastical designs. For portions of his professional career, he partnered with fellow immigrant Calvert Vaux; both worked in the office of Andrew Jackson Downing in Newburgh, New York, where they began their careers following Downing's accidental death. Withers greatly participated in the introduction of the High Victorian Gothic style to the United States.

Belle Isle Park, known simply as Belle Isle, is a 982-acre island park in Detroit, Michigan, developed in the late 19th century. It consists of Belle Isle, an island in the Detroit River, as well as several surrounding islets. The U.S.-Canada border is in the channel south of Belle Isle.

St Mary on Paddington Green is an Anglican church in the Parish of Little Venice, London, and forms part of Paddington Green conservation area. Today it stands at the junction of Edgware Road and Harrow Road, overlooking the East end of Westway and the approaches to Marylebone Flyover, so seen by tens of thousands of motorists daily.

Second Empire, in the United States and Canada, is an architectural style most popular between 1865 and 1900. Second Empire architecture developed from the redevelopment of Paris under Napoleon III's Second French Empire and looked to French Renaissance precedents. It was characterized by a mansard roof, elaborate ornament, and strong massing and was notably used for public buildings as well as commercial and residential design.
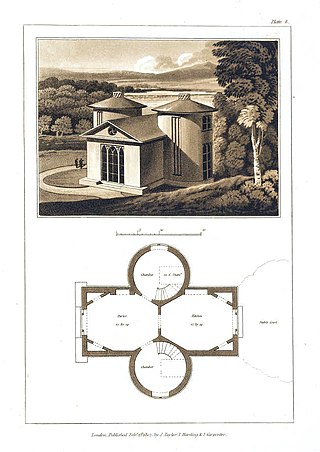
Edward Gyfford or Gifford was a British architect and surveyor known for his two volumes of designs for small buildings that were published in 1806 and 1807. He also produced architectural drawings that were engraved for David Hughson's description of London (1805–1809).

A gatekeeper's lodge or gate lodge is a small, often decorative building, situated at the entrance to the estate of a mansion or country house. Originally intended as the office and accommodation for a gatekeeper who was employed by the landowner to control access to the property, they fell out of use in the early 20th century but surviving examples are often preserved and can sometimes be used as domestic housing.



















