
A frigate is a type of warship. In different eras, the roles and capabilities of ships classified as frigates have varied.

The Battle of Trafalgar was a naval engagement that took place on 21 October 1805 between the British Royal Navy and the combined fleets of the French and Spanish Navies during the War of the Third Coalition of the Napoleonic Wars (1803–1815).

During the 18th and 19th centuries, a sloop-of-war was a warship of the British Royal Navy with a single gun deck that carried up to 18 guns. The rating system of the Royal Navy covered all vessels with 20 or more guns; thus, the term encompassed all unrated warships, including gun-brigs and cutters. In technical terms, even the more specialised bomb vessels and fire ships were classed by the Royal Navy as sloops-of-war, and in practice these were employed in the role of a sloop-of-war when not carrying out their specialised functions.

HMS Bellerophon, known to sailors as the "Billy Ruffian", was a ship of the line of the Royal Navy. A third-rate of 74 guns, she was launched in 1786. Bellerophon served during the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars, mostly on blockades or convoy escort duties. She fought in three fleet actions: the Glorious First of June (1794), the Battle of the Nile (1798) and the Battle of Trafalgar (1805). While the ship was on blockade duty in 1815, Napoleon boarded Bellerophon so he could surrender to the ship's captain, ending 22 years of almost continuous war between Britain and France.

The Battle of Pulo Aura was a minor naval engagement of the Napoleonic Wars, fought on 14 February 1804, in which a large convoy of Honourable East India Company (HEIC) East Indiamen, well-armed merchant ships, intimidated, drove off and chased away a powerful French naval squadron. Although the French force was much stronger than the British convoy, Commodore Nathaniel Dance's aggressive tactics persuaded Contre-Admiral Charles-Alexandre Durand Linois to retire after only a brief exchange of shot. Dance then chased the French warships until his convoy was out of danger, whereupon he resumed his passage toward British India. Linois later claimed that the unescorted British merchant fleet was defended by eight ships of the line, a claim criticised by contemporary officers and later historians.

HMS Speedy was a 14-gun Speedy-class brig of the British Royal Navy. Built during the last years of the American War of Independence, she served with distinction during the French Revolutionary Wars.

Neptune was a Bucentaure-class 80-gun ship of the line of the French Navy. Built during the last years of the French Revolutionary Wars she was launched at the beginning of the Napoleonic Wars. Her brief career with the French included several major battles, though she spent the last 12 years of her life under the Spanish flag.

The Battle of Santa Cruz de Tenerife was an amphibious assault by the Royal Navy on the Spanish port city of Santa Cruz de Tenerife in the Canary Islands. Launched by Rear-Admiral Horatio Nelson on 22 July 1797, the assault was defeated, and on 25 July the remains of the landing party withdrew under a truce, having lost several hundred men. Nelson himself had been wounded in the arm, which was subsequently partially amputated: a stigma that he carried to his grave as a constant reminder of his failure.

HMS Anson was a ship of the Royal Navy, launched at Plymouth on 4 September 1781. Originally a 64-gun third rate ship of the line, she fought at the Battle of the Saintes.
William Prowse CB was an officer of the Royal Navy, who saw service during the American War of Independence, and the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars. Rising from humble origins and joining the navy as an able seaman, he had a highly active career, serving under some of the most famous naval commanders of the age of sail, and participating in some of their greatest victories. He was at Grenada and Martinique under Byron and Rodney, the Glorious First of June under Howe; and commanded ships at Cape St Vincent under Jervis, Cape Finisterre under Calder and Trafalgar under Nelson. He finished his career by serving with distinction in the Mediterranean, and died with the rank of Rear-Admiral.
Vice-Admiral Sir Thomas Dundas KCB was an officer of the Royal Navy, who saw service during the American War of Independence, and the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars. An effective frigate captain he made a number of small captures, but did not see action in any major fleet clashes, until he was present at the Battle of Trafalgar in 1805. He played an important role in relaying signals before the battle, and in towing dismasted British ships to safety afterwards. He had a largely uneventful career thereafter, rising through the ranks and eventually dying a vice-admiral.

The Trafalgar campaign was a long and complicated series of fleet manoeuvres carried out by the combined French and Spanish fleets; and the opposing moves of the Royal Navy during much of 1805. These were the culmination of French plans to force a passage through the English Channel, and so achieve a successful invasion of the United Kingdom. The plans were extremely complicated and proved to be impractical. Much of the detail was due to the personal intervention of Napoleon, who as a soldier rather than a sailor failed to consider the effects of weather, difficulties in communication, and the Royal Navy. Despite limited successes in achieving some elements of the plan the French commanders were unable to follow the main objective through to execution. The campaign, which took place over thousands of miles of ocean, was marked by several naval engagements, most significantly at the Battle of Trafalgar on 21 October, where the combined fleet was decisively defeated, and from which the campaign takes its name. A final mopping up action at the Battle of Cape Ortegal on 4 November completed the destruction of the combined fleet, and secured the supremacy of the Royal Navy at sea.

The Battle of Diamond Rock took place between 31 May and 2 June 1805 during the Napoleonic Wars, when a Franco-Spanish force dispatched under Captain Julien Cosmao was able to retake Diamond Rock, at the entrance to the bay leading to Fort-de-France, from the British forces that had occupied it over a year before.

The Java campaign of 1806–1807 was a minor campaign during the Napoleonic Wars by British Royal Navy forces against a naval squadron of the Kingdom of Holland, a client state of the French Empire, based on the island of Java in the Dutch East Indies. Seeking to eliminate any threat to valuable British merchant convoys passing through the Malacca Straits, Rear-Admiral Sir Edward Pellew determined in early 1806 that the Dutch naval forces based at Java, which included several ships of the line and three frigates, had to be defeated to ensure British dominance in the region. Lacking the forces to effect an invasion of the Dutch colony, Pellew instead sought to isolate and blockade the Dutch squadron based at Batavia in preparation for raids specifically targeting the Dutch ships with his main force.
Vice-Admiral James Wilkes Maurice was an officer of the Royal Navy during the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars. Unlike his contemporaries who won fame commanding ships, Maurice gained accolades for his command of a number of island fortresses.

Neptuno was an 80-gun Neptuno-class ship of the line of the Spanish Navy. She was built in 1795 and took part in the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars. She fought with the Franco-Spanish fleet in the battle of Trafalgar, and was wrecked in its aftermath.
HMS Aeolus was a 32-gun Amphion-class fifth-rate frigate of the Royal Navy. She was launched in 1801 and served in the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars, and the War of 1812.

A ship's boat is a utility boat carried by a larger vessel. Ship's boats have always provided transport between the shore and other ships. Other work done by such boats has varied over time, as technology has changed. In the age of sail, especially for warships, an important role was the collection of drinking water. The use of radio, followed by telex, e-mail, etc. has reduced and then replaced the need for written communications to be delivered. A large enough boat may be needed to carry an anchor to some distance away from the ship, so as to kedge out of a harbour or away from a hazard – and also to recover such an anchor afterwards. Warships have always used their boats as an extension to their military role. This includes the provision of a means of escape for the crews of fireships, the landing of troops, or the "cutting out" raids that were used by the Royal Navy, especially during the Napoleonic Wars. All these requirements competed with the need to be able to stow the boats on board in a way that did not interfere with the normal operation of the ship.

HMS Aigle was a 36-gun, fifth-rate frigate of the Royal Navy. Ordered on 15 September 1799 and built at Bucklers Hard shipyard, she was launched 23 September 1801. More than fifty of her crew were involved in the Easton Massacre when she visited Portland in April 1803 to press recruits. Her captain and three other officers stood trial for murder but were acquitted. Much of Aigle's career as a frigate was spent trying to keep the English Channel free of enemy warships and merchant vessels. On 22 March 1808, she was first into the action against two large French frigates, compelling one to seek the shelter of the Île de Groix batteries and forcing the other onto the shore.
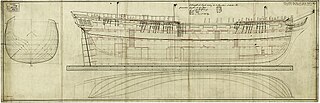
HMS Beaulieu was a 40-gun fifth-rate frigate of the Royal Navy. The ship was laid down in 1790 as a speculative build by the shipwright Henry Adams and purchased by the Royal Navy in June of the same year. Built to the dimensions of a merchant ship, Beaulieu was broader, with more storage capacity, than a standard frigate; though may not have had good sailing qualities. The frigate was commissioned in January 1793 by Lord Northesk and sent to serve on the Leeward Islands Station. She participated in the capture of Martinique in February 1794, and then was similarly present at the capture of the island of Saint Lucia in April. The frigate also took part in the initial stages of the invasion of Guadeloupe. Later in the year the ship's crew was beset by yellow fever and much depleted. Beaulieu was sent to serve on the North America Station to allow them to recuperate, returning to the Leeward Islands in 1795. In the following two years the ship found success in prizetaking and briefly took part in more operations at Saint Lucia. She returned to Britain at the end of 1796.















