Related Research Articles
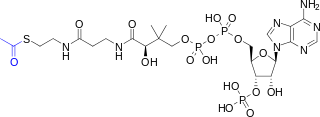
Acetyl-CoA is a molecule that participates in many biochemical reactions in protein, carbohydrate and lipid metabolism. Its main function is to deliver the acetyl group to the citric acid cycle to be oxidized for energy production.

Anabolism is the set of metabolic pathways that construct macromolecules like DNA or RNA from smaller units. These reactions require energy, known also as an endergonic process. Anabolism is the building-up aspect of metabolism, whereas catabolism is the breaking-down aspect. Anabolism is usually synonymous with biosynthesis.
In chemistry, racemization is a conversion, by heat or by chemical reaction, of an optically active compound into a racemic form. This creates a 1:1 molar ratio of enantiomers and is referred to as a racemic mixture. Plus and minus forms are called Dextrorotation and levorotation. The D and L enantiomers are present in equal quantities, the resulting sample is described as a racemic mixture or a racemate. Racemization can proceed through a number of different mechanisms, and it has particular significance in pharmacology as different enantiomers may have different pharmaceutical effects.

Thiamine pyrophosphate (TPP or ThPP), or thiamine diphosphate (ThDP), or cocarboxylase is a thiamine (vitamin B1) derivative which is produced by the enzyme thiamine diphosphokinase. Thiamine pyrophosphate is a cofactor that is present in all living systems, in which it catalyzes several biochemical reactions.
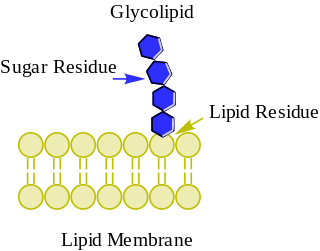
Glycolipids are lipids with a carbohydrate attached by a glycosidic (covalent) bond. Their role is to maintain the stability of the cell membrane and to facilitate cellular recognition, which is crucial to the immune response and in the connections that allow cells to connect to one another to form tissues. Glycolipids are found on the surface of all eukaryotic cell membranes, where they extend from the phospholipid bilayer into the extracellular environment.

Malate dehydrogenase (EC 1.1.1.37) (MDH) is an enzyme that reversibly catalyzes the oxidation of malate to oxaloacetate using the reduction of NAD+ to NADH. This reaction is part of many metabolic pathways, including the citric acid cycle. Other malate dehydrogenases, which have other EC numbers and catalyze other reactions oxidizing malate, have qualified names like malate dehydrogenase (NADP+).
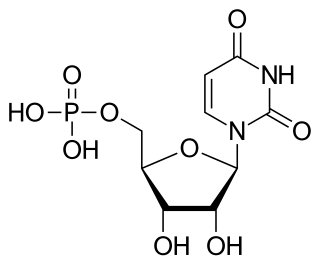
Uridine monophosphate (UMP), also known as 5′-uridylic acid, is a nucleotide that is used as a monomer in RNA. It is an ester of phosphoric acid with the nucleoside uridine. UMP consists of the phosphate group, the pentose sugar ribose, and the nucleobase uracil; hence, it is a ribonucleotide monophosphate. As a substituent or radical its name takes the form of the prefix uridylyl-. The deoxy form is abbreviated dUMP. Covalent attachment of UMP is called uridylylation.

The International Union of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology (IUBMB) is an international non-governmental organisation concerned with biochemistry and molecular biology. Formed in 1955 as the International Union of Biochemistry (IUB), the union has presently 79 member countries and regions. The Union is devoted to promoting research and education in biochemistry and molecular biology throughout the world, and gives particular attention to localities where the subject is still in its early development.
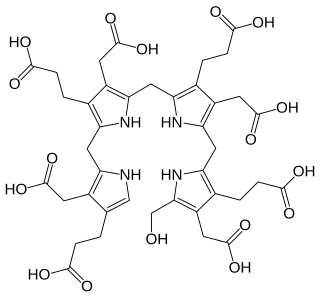
Hydroxymethylbilane, also known as preuroporphyrinogen, is an organic compound that occurs in living organisms during the synthesis of porphyrins, a group of critical substances that include haemoglobin, myoglobin, and chlorophyll. The name is often abbreviated as HMB.
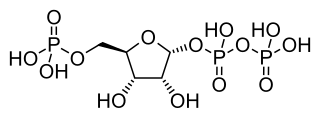
Phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate (PRPP) is a pentose phosphate. It is a biochemical intermediate in the formation of purine nucleotides via inosine-5-monophosphate, as well as in pyrimidine nucleotide formation. Hence it is a building block for DNA and RNA. The vitamins thiamine and cobalamin, and the amino acid tryptophan also contain fragments derived from PRPP. It is formed from ribose 5-phosphate (R5P) by the enzyme ribose-phosphate diphosphokinase:
Enzyme catalysis is the increase in the rate of a process by an "enzyme", a biological molecule. Most enzymes are proteins, and most such processes are chemical reactions. Within the enzyme, generally catalysis occurs at a localized site, called the active site.
Palmitoyl-CoA is an acyl-CoA thioester. It is an "activated" form of palmitic acid and can be transported into the mitochondrial matrix by the carnitine shuttle system, and once inside can participate in beta-oxidation. Alternatively, palmitoyl-CoA is used as a substrate in the biosynthesis of sphingosine.

Dihydroorotase is an enzyme which converts carbamoyl aspartic acid into 4,5-dihydroorotic acid in the biosynthesis of pyrimidines. It forms a multifunctional enzyme with carbamoyl phosphate synthetase and aspartate transcarbamoylase. Dihydroorotase is a zinc metalloenzyme.

Orotic aciduria is a disease caused by an enzyme deficiency, resulting in a decreased ability to synthesize pyrimidines. It was the first described enzyme deficiency of the de novo pyrimidine synthesis pathway.

Nucleotidyltransferases are transferase enzymes of phosphorus-containing groups, e.g., substituents of nucleotidylic acids or simply nucleoside monophosphates. The general reaction of transferring a nucleoside monophosphate moiety from A to B, can be written as:
Metabolic intermediates are compounds produced during the conversion of substrates into final products in biochemical reactions within cells.
Donald Herman Voet was an American biochemist who was emeritus associate professor of chemistry at the University of Pennsylvania. His laboratory used x-ray crystallography to understand structure-function relationships in proteins. He and his wife, Judith G. Voet, are authors of biochemistry text books that are widely used in undergraduate and graduate curricula.

NADH dehydrogenase (ubiquinone) 1 beta subcomplex, 3, 12kDa is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NDUFB3 gene. NADH dehydrogenase (ubiquinone) 1 beta subcomplex, 3, 12kDa is an accessory subunit of the NADH dehydrogenase (ubiquinone) complex, located in the mitochondrial inner membrane. It is also known as Complex I and is the largest of the five complexes of the electron transport chain. Mutations in this gene contribute to mitochondrial complex I deficiency.

Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecular Level is a biochemistry textbook written by Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet and Charlotte W. Pratt. Published by John Wiley & Sons, it is a common undergraduate biochemistry textbook.
Charlotte W. Pratt is an American biochemist and author. She is the co-author with Judith G. Voet and Donald Voet of the popular standard biochemistry textbook Fundamentals of Biochemistry.
References
- ↑ Press, Jaques Cattell (1982). "American men and women of science: The physical and biological sciences".
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - 1 2 "Project Kaleidoscope: Judith G. Voet". Project Kaleidoscope. 8 May 2000. Archived from the original on 5 June 2011. Retrieved 18 January 2010.
- ↑ Buehler, Lukas K. (January 2, 2000). "Reviews of books by Donald Voet, Judith Voet". Lukas K. Buehler. Retrieved 18 January 2010.
- 1 2 Wood, E.J. (1 October 1999). "Book review: Biochemistry in a nutshell - Fundamentals of Biochemistry by Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet and Charlotte W. Pratt". Trends in Biochemical Sciences. 24 (10): 409–410. doi:10.1016/S0968-0004(99)01447-4.
- 1 2 "Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Education (BAMBED), a Journal for University, College, and High School Educators by Judith G. Voet1 and Donald H. Voet2, BAMBED Co-Editors-in-Chief" (PDF). Protein Databank Newsletter (38). RCSB PDB: 5. Summer 2008. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2023-01-27. Retrieved 2021-10-11.
- ↑ "Penn Chemistry: Faculty Donald Voet". The Trustees of the University of Pennsylvania. 2005. Archived from the original on 11 September 2007. Retrieved 18 January 2010.