In human anatomy, the thoracic duct is the larger of the two lymph ducts of the lymphatic system. It is also known as the left lymphatic duct, alimentary duct, chyliferous duct, and Van Hoorne's canal. The other duct is the right lymphatic duct. The thoracic duct carries chyle, a liquid containing both lymph and emulsified fats, rather than pure lymph. Thus when it ruptures, the resulting flood of liquid into the pleural cavity is known as chylothorax.

The jugular venous pressure is the indirectly observed pressure over the venous system via visualization of the internal jugular vein. It can be useful in the differentiation of different forms of heart and lung disease. Classically three upward deflections and two downward deflections have been described.

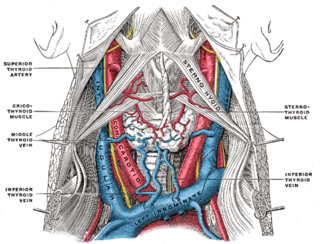
The jugular veins are veins that take deoxygenated blood from the head back to the heart via the superior vena cava.
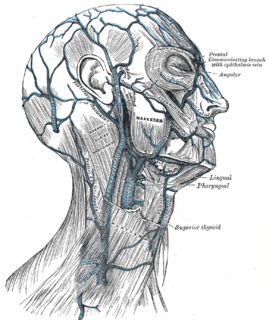
The external jugular vein receives the greater part of the blood from the exterior of the cranium and the deep parts of the face, being formed by the junction of the posterior division of the retromandibular vein with the posterior auricular vein.

The inferior petrosal sinuses are two small sinuses situated on the inferior border of the petrous part of the temporal bone, one on each side. Each inferior petrosal sinus drains the cavernous sinus into the internal jugular vein.
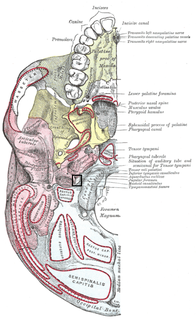
The jugular foramen is a large foramen (opening) in the base of the skull, located behind the carotid canal. It is formed in front by the petrous portion of the temporal bone, and behind by the occipital bone; it is generally larger on the right than on the left side.

The sigmoid sinuses, also known as the pars sigmoid, are venous sinuses within the skull that receive blood from posterior dural venous sinus veins.

The anterior jugular vein is a vein in the neck. It begins near the hyoid bone by the confluence of several superficial veins from the submandibular region.

The transverse sinuses, within the human head, are two areas beneath the brain which allow blood to drain from the back of the head. They run laterally in a groove along the interior surface of the occipital bone. They drain from the confluence of sinuses to the sigmoid sinuses, which ultimately connect to the internal jugular vein. See diagram : labeled under the brain as "SIN. TRANS.".

The pterygoid plexus is a venous plexus of considerable size, and is situated between the temporalis muscle and lateral pterygoid muscle, and partly between the two pterygoid muscles.

The frontal vein begins on the forehead in a venous plexus which communicates with the frontal branches of the superficial temporal vein. The veins converge to form a single trunk, which runs downward near the middle line of the forehead parallel with the vein of the opposite side. The two veins are joined, at the root of the nose, by a transverse branch, called the nasal arch, which receives some small veins from the dorsum of the nose. At the root of the nose the veins diverge, and, each at the medial angle of the orbit, joins the supraorbital vein, to form the angular vein. Occasionally the frontal veins join to form a single trunk, which bifurcates at the root of the nose into the two angular veins.

The occipital vein begins as a plexus at the posterior aspect of the scalp from the external occipital protuberance and superior nuchal line to the back part of the vertex of the skull.

The external vertebral venous plexuses best marked in the cervical region, consist of anterior and posterior plexuses which anastomose freely with each other.

The four plantar metatarsal veins run backward in the metatarsal spaces, communicate, by means of perforating veins, with the veins on the dorsum of the foot, and unite to form the plantar venous arch which lies alongside the plantar arterial arch.

The plantar metatarsal veins run backward in the metatarsal spaces, collect blood from digital veins and communicate, by means of perforating veins, with the veins on the dorsum of the foot, and unite to form the deep plantar venous arch which lies alongside the plantar arterial arch.

The jugular trunk is a lymphatic vessel in the neck. It is formed by vessels that emerge from the superior deep cervical lymph nodes and unite to efferents of the inferior deep cervical lymph nodes.
The suboccipital venous plexus drains deoxygenated blood from the back of the head.
The pharyngeal plexus (venous) is a network of veins beginning in the pharyngeal plexus on the outer surface of the pharynx, and, after receiving some posterior meningeal veins and the vein of the pterygoid canal, end in the internal jugular.
The public domain consists of all the creative work to which no exclusive intellectual property rights apply. Those rights may have expired, been forfeited, expressly waived, or may be inapplicable.

Gray's Anatomy is an English written textbook of human anatomy originally written by Henry Gray and illustrated by Henry Vandyke Carter. Earlier editions were called Anatomy: Descriptive and Surgical, Anatomy of the Human Body and Gray's Anatomy: Descriptive and Applied, but the book's name is commonly shortened to, and later editions are titled, Gray's Anatomy. The book is widely regarded as an extremely influential work on the subject, and has continued to be revised and republished from its initial publication in 1858 to the present day. The latest edition of the book, the 41st, was published in September 2015.