
Oshtemo Charter Township is a charter township of Kalamazoo County in the U.S. state of Michigan. The 2010 census recorded a population of 21,705, up from 17,003 at the 2000 census. The township was organized in 1839.

The Toms River is a 41.7-mile-long (67.1 km) freshwater river and estuary in Ocean County, New Jersey in the United States.

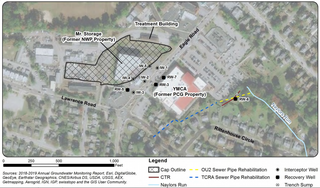
Naylors Run is a 4.6-mile-long (7.4 km) tributary of Cobbs Creek in Haverford and Upper Darby Township, Pennsylvania, United States.
The Laurel Park, Inc. site, also known as Hunters Mountain Dump, or Murtha's Dump to locals, is a capped landfill that occupies approximately 20 acres (81,000 m2) of a 35-acre (140,000 m2) parcel of land in Naugatuck, Connecticut. The landfill has been in existence since the late 1940s, and several industries disposed of solvents, oils, hydrocarbons, chemical and liquid sludge, chemical solids, tires, and rubber products there. The facility continued to operate as a municipal landfill until 1987. It was owned and operated by Terrence and Howard Murtha.
Havertown Superfund is a 13-acre polluted groundwater site in Havertown, Pennsylvania contaminated by the dumping of industrial waste by National Wood Preservers from 1947 to 1991. The state first became aware of the pollution in 1962 and initiated legal action against the owners in 1973 to force them to cleanup the site. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) ranked the site the eighth worst cleanup project in the United States. The site was added to the National Priorities List in 1983 and designated as a Superfund cleanup site in the early 1990s. Remediation and monitoring efforts are ongoing and the EPA transferred control of the site to the Pennsylvania Department of Environmental Protection in 2013.

Dorney Road Landfill is a 27-acre (11 ha) municipal and industrial landfill in Upper Macungie Township and Longswamp Township, Pennsylvania that was polluted with toxic waste from 1952 to 1978. The site is surrounded by rural residences and farmland. The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) added the site to the Superfund National Priorities List in 1984. The site was remediated and removed from the National Priorities List in 2018.
In 1990, the Allied Paper, Inc./Portage Creek/Kalamazoo River in southwestern Michigan was declared by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) to be a Superfund site – in other words, an abandoned industrial site containing significant amounts of toxic waste. The EPA and companies responsible for the waste in this area, which includes a three-mile section of Portage Creek as well as part of the Kalamazoo River, into which it flows, are currently involved in an effort to reduce the amount of toxic waste at the site, which is contaminated by PCBs from paper mills and other factories.
The former Operating Industries Inc. Landfill is a Superfund site located in Monterey Park, California at 900 N Potrero Grande Drive. From 1948 to 1984, the landfill accepted 30 million tons of solid municipal waste and 300 million US gallons (1,100,000 m3) of liquid chemicals. Accumulating over time, the chemical waste polluted the air, leached into groundwater, and posed a fire hazard, spurring severely critical public health complaints. Recognizing OII Landfill's heavy pollution, EPA placed the financial responsibility of the dump's clean-up on the main waste-contributing companies, winning hundreds of millions of dollars in settlements for the protection of human health and the environment.
Kauffman & Minteer Inc. (K&M) was an industrial transportation company that operated from 1960 to 1981 in Burlington County, New Jersey. After cleaning their trucks, they dumped the waste water into a nearby lagoon that was not properly lined. The lagoon flooded and the waste water containing chemicals, migrated over to wetlands, causing damage to vegetation and seeping into underground drinking water. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) got involved in 1989 and conducted a few remediation attempts but the extent of the damage is hard to determine as the different underground pathways of water are unpredictable. The site is currently an active superfund site that is closely monitored by the EPA.
The A.O. Polymer manufacturing site is located in Sparta Township, New Jersey. This facility created special polymers, plastics, and resins. It was also used for reclaiming spent solvents. The facility's poor waste handling led to serious contamination of the ground. It also contaminated the water in the ground with volatile organic compounds. The site has been a threat to the Allentown aquifer, which provides drinking water to over 5,000 people. Initial clean ups started with getting rid of old drums and contaminants from their original disposal area. The company took them and decided to dispose of them elsewhere, thus not fixing the problem. Primary cleanups of the site were ongoing as of 2008. The EPA has been using water pumps to remove contaminants from the water in the ground. A soil extraction system has been put at their disposal to remove harmful contamination within the soil as well. All wells in the affected areas have been closed.
Bog Creek Farm, located in Howell Township, New Jersey, is a designated Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) Superfund site. Lying on 12 acres of land, Bog Creek Farm is home to several hazardous and life-threatening contamination beginning in 1973 and continuing for a year. Over a decade later, actions began to take place to clean and restore the contaminated soil and water. Bog Creek Farm is situated near several other farms that house horses, growing crops and flowers, and livestock. Less than a mile down the road lies Allaire State Park, a park used by golfers, hunters, and fisherman.
Price Landfill is a 26-acre site located in Pleasantville, Egg Harbor Township, Atlantic County, New Jersey. Price Landfill is also known as Price Sanitary Landfill, Prices Pit, Price Landfill No.1 and Price Chemical Dump. The United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA) added Price Landfill to the Superfund National Priorities List on September 20, 1983, because of the hazardous chemicals found on the site and in the groundwater. The site was originally owned by Mr. Charles Price and was used to mine sand and gravel, which was shut down in 1968. The site was then turned into a private landfill in 1969 and then a commercial solid waste landfill in 1971. At this point the landfill was used to dispose of liquid waste by companies, specifically Atlantic City Electric Company. The liquid waste consisted of industrial chemicals, oils and greases/sludges, septic tank and sewer wastes, which were disposed on the site for 8 years, ending altogether in 1976, but in the meantime, having contaminated the groundwater, soil, air, and nearby creeks, specifically Absecon Creek. Chemicals dumped on the site are believed to be 1,2-Dichloroethane, arsenic, benzene, chloroform, lead, and vinyl chloride, all of which contaminated the groundwater, soil, air, and nearby creeks. The USEPA originally got involved in 1982 by beginning to correct the damage. Currently the USEPA states that they are continuing to monitor and treat the groundwater and land, and that hazards to humans are controlled.
Adams Plating, also known as Adam's Plating, is a 1-acre (0.40-hectare) Superfund site in Lansing Charter Township near Lansing, Michigan.
Forest Waste Products is a 120-acre (49-hectare) Superfund site in Forest Township northwest of Otisville, Michigan.
Thermo-Chem, Inc., also referred to as Thermo-Chem, is a 50-acre Superfund site located in Egelston Township near Muskegon, Michigan.
The G&H Industrial Landfill is a Superfund site located in Shelby Charter Township near Utica, Michigan. The 60-acre (24-hectare) landfill, with about 10 to 20 acres of adjacent property, operated as a waste oil recovery facility from 1955 to 1967. From 1955 to 1974 the site was used as an industrial and municipal landfill. Contaminated soil, surface water, and groundwater with hazardous chemicals have been left behind as a result of the disposal of waste solvents, waste oil and paint sludge. Operation and maintenance activities are ongoing following the cleanup.
Michigan Disposal Service, also known as Kalamazoo City Dump, Kalamazoo City Landfill, Dispose-O-Waste and the Cork Street Landfill, is a 68-acre Superfund site in Kalamazoo, Michigan. Davis Creek is adjacent to the site. It is one of six Superfund sites in the Kalamazoo River watershed.

Ohio River Park is a Superfund Site located in Neville Island, Pennsylvania. Between the 1920s-1970s, the Site was used for municipal waste, pesticide manufacturing, coke sludge disposal, cement manufacturing disposal, and pesticide waste. In 1977, Neville Land Company donated the Site to Allegheny County who started developing the Site as a community park. In 1979, Allegheny County found various hazardous contaminants on the Site. On August 30, 1990, the Site was determined to be a Superfund Site due to VOCs, SVOCs, inorganics, and pesticides being present in the surface soil, subsurface soil, surface water, river sediment, and groundwater. Soil remediation began in February 1998 and ended in September 1999. Today, Ohio River Park has the Robert Morris University Island Sports Center and Coraopolis Bridge on top of it. Additionally, benzene continues to be monitored because it is still present in the Site's groundwater.
The Ott/Story/Cordova Chemical Co. is a 20-acre superfund site that is located in Dalton township in the US State of Michigan.






