
The Cessna AT-17 Bobcat or Cessna Crane is a twin-engine advanced trainer aircraft designed and made in the United States, and used during World War II to bridge the gap between single-engine trainers and larger multi-engine combat aircraft. The commercial version was the Model T-50, from which the military versions were developed.

The Curtiss Robin, introduced in 1928, was a high-wing monoplane built by the Curtiss-Robertson Airplane Manufacturing Company. The J-1 version was flown by Wrongway Corrigan who crossed the Atlantic after being refused permission.

The Fairchild Model 24, also called the Fairchild Model 24 Argus and UC-61 Forwarder, is a four-seat, single-engine monoplane light transport aircraft designed by the Fairchild Aviation Corporation in the 1930s. It was adopted by the United States Army Air Corps as UC-61 and also by the Royal Air Force. The Model 24 was itself a development of previous Fairchild models and became a successful civil and military utility aircraft.

The Monocoupe 90 was a two-seat, light cabin airplane built by Donald A. Luscombe for Monocoupe Aircraft. The first Monocoupe was built in an abandoned church in Davenport, Iowa, and first flew on April 1, 1927. Various models were in production until the late 1940s.

The Aeronca L was a 1930s American cabin monoplane designed and built, in small numbers, by Aeronca Aircraft. It differed significantly from other Aeronca planes by the use of radial engines, streamlining, and a cantilever low wing.

The Arrow Sport was a two-seat sporting biplane aircraft built in the United States in the 1920s and 1930s.

The Culver Dart was a 1930s American two-seat light monoplane aircraft produced by the Dart Aircraft Company.

The Harlow PJC-2 was a 1930s American four-seat cabin monoplane, designed by Max Harlow.

The Travel Air 2000/3000/4000 were open-cockpit biplane aircraft produced in the United States in the late 1920s by the Travel Air Manufacturing Company. During the period from 1924–1929, Travel Air produced more aircraft than any other American manufacturer, including over 1,000 biplanes. While an exact number is almost impossible to ascertain due to the number of conversions and rebuilds, some estimates for Travel Air as a whole range from 1,200 to nearly 2,000 aircraft.

The Meyers OTW was a 1930s United States training biplane designed by Allen Meyers and built by his Meyers Aircraft Company from 1936 to 1944.

The Ryan S-C (Sports-Coupe) was an American three-seat cabin monoplane designed and built by the Ryan Aeronautical Company. At least one was impressed into service with the United States Army Air Forces as the L-10.

The Rearwin Sportster is a 1930s American two-seat, high-winged, cabin monoplane designed and built by Rearwin Aircraft & Engines for sport/touring use.

The Davis D-1 is an American light two-seat parasol-winged monoplane of the late 1920s.
The St. Louis C2 Cardinal family are a series of light sport monoplanes built by the St. Louis Aircraft Corporation during the peak of the Lindbergh Boom after the Spirit of St. Louis flight of 1927.

The Fahlin SF-2 Plymocoupe was a high-wing, cantilever type, prototype experimental airplane produced in 1935.
Swen (Sven) Swanson was a Swedish aircraft designer. He designed aircraft for various aviation companies in the United States and also designed prototype and experimental airplanes. He was known as an innovative aircraft designer. He later worked in partnership with Ole Fahlin. Swanson started designing airplanes while in his teens and by the time he was in college he had designed his third airplane. He founded the Swanson Aircraft Company Inc. and became its chief engineer and president. While working for his own company he designed and built the Swanson W-15 Coupe. He has been described as a "brilliant man of great capabilities and extreme modesty".

The Swanson Coupe Model W-15 was a high-wing, cantilever-type monoplane produced in 1931 by Swedish aircraft designer and manufacturer Swen Swanson. Its design was considered innovative and the aircraft was viewed as part of a trend of producing safe and economical airplanes, which would appeal especially to automobile drivers. The Swanson Coupe was also designed to function as trainer aircraft.

The Command-Aire 3C3 and similar 4C3 and 5C3 are American three-seat open cockpit utility, training and touring biplanes developed by Command-Aire in the late 1920s and early 1930s.

The Gee Bee Model A was an American two-seat open cockpit single-bay biplane developed by the Granville Brothers that first flew in 1929.
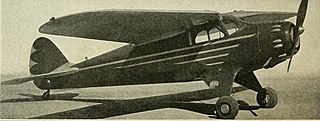
The Swanson-Fahlin SF-1 was a high wing, two seat cabin aircraft with a small radial engine, designed in the United States and first flown in 1934. Only one was built.


















