
Whiplash, whose formal term is whiplash associated disorders (WAD), is a range of injuries to the neck caused by or related to a sudden distortion of the neck associated with extension, although the exact injury mechanisms remain unknown. The term "whiplash" is a colloquialism. "Cervical acceleration–deceleration" (CAD) describes the mechanism of the injury, while WAD describes the subsequent injuries and symptoms.

A stretcher, gurney, litter, or pram is an apparatus used for moving patients who require medical care. A basic type must be carried by two or more people. A wheeled stretcher is often equipped with variable height frames, wheels, tracks, or skids.

A splint is defined as "a rigid or flexible device that maintains in position a displaced or movable part; also used to keep in place and protect an injured part" or as "a rigid or flexible material used to protect, immobilize, or restrict motion in a part". Splints can be used for injuries that are not severe enough to immobilize the entire injured structure of the body. For instance, a splint can be used for certain fractures, soft tissue sprains, tendon injuries, or injuries awaiting orthopedic treatment. A splint may be static, not allowing motion, or dynamic, allowing controlled motion. Splints can also be used to relieve pain in damaged joints. Splints are quick and easy to apply and do not require a plastering technique. Splints are often made out of some kind of flexible material and a firm pole-like structure for stability. They often buckle or Velcro together.

An orthopedic cast, or simply cast, is a shell, frequently made from plaster or fiberglass, that encases a limb to stabilize and hold anatomical structures—most often a broken bone, in place until healing is confirmed. It is similar in function to a splint.

A spinal board, is a patient handling device used primarily in pre-hospital trauma care. It is designed to provide rigid support during movement of a person with suspected spinal or limb injuries. They are most commonly used by ambulance staff, as well as lifeguards and ski patrollers. Historically, backboards were also used in an attempt to "improve the posture" of young people, especially girls.

A vacuum mattress, or vacmat, is a medical device used for the immobilisation of patients, especially in case of a vertebra, pelvis or limb trauma. It is also used for manual transportation of patients for short distances. It was invented by Loed and Haederlé, who called it "shell" mattress.
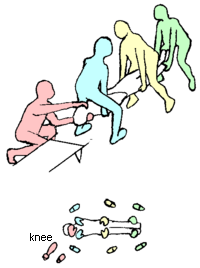
Casualty lifting is the first step of casualty movement, an early aspect of emergency medical care. It is the procedure used to put the casualty on a stretcher.

Vehicle extrication is the process of removing a patient from a vehicle who has been involved in a motor vehicle collision. Patients who have not already exited a crashed vehicle may be medically or physically trapped and may be pinned by wreckage or simply unable to exit a vehicle.

A cervical collar, also known as a neck brace, is a medical device used to support and immobilize a person's neck. It is also applied by emergency personnel to those who have had traumatic head or neck injuries, although they should not be routinely used in prehospital care. They can also be used to treat chronic medical conditions.

The scoop stretcher is a device used specifically for moving injured people. It is ideal for carrying casualties with possible spinal injuries.

A cervical fracture, commonly called a broken neck, is a fracture of any of the seven cervical vertebrae in the neck. Examples of common causes in humans are traffic collisions and diving into shallow water. Abnormal movement of neck bones or pieces of bone can cause a spinal cord injury, resulting in loss of sensation, paralysis, or usually death soon thereafter, primarily via compromising neurological supply to the respiratory muscles and innervation to the heart.
Outdoor emergency care (OEC) was first developed by the National Ski Patrol in the 1980s for certification in first aid, and other pre-hospital care and treatment for possible injuries in non-urban settings. Outdoor emergency care technicians provide care at ski resorts, wilderness settings, white-water excursions, mountain bike events, and in many other outdoor environments.
A traction splint most commonly refers to a splinting device that uses straps attaching over the pelvis or hip as an anchor, a metal rod(s) to mimic normal bone stability and limb length, and a mechanical device to apply traction to the limb.

A litter is a stretcher designed to be used where there are physical obstacles that impair movement, including other hazards such as, in confined spaces, on slopes or uneven terrain, or in densely forested areas. Typically it is shaped to accommodate an adult in a face up position and it is used in search and rescue operations. The person is strapped into the basket, making safe evacuation possible. The person generally is further protected by a cervical collar and sometimes a long spine board, so as to immobilize the person and prevent further injury.
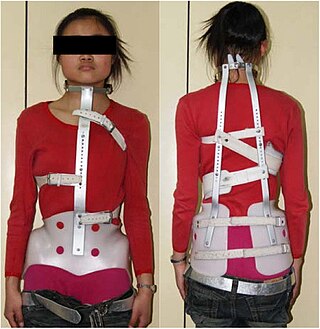
The Milwaukee brace, also known as a cervico-thoraco-lumbo-sacral orthosis or CTLSO, is a back brace most often used in the treatment of spinal curvatures in children but also, more rarely, in adults to prevent collapse of the spine and associated pain and deformity. It is a full-torso brace that extends from the pelvis to the base of the skull. It was originally designed by Blount and Schmidt in 1946 for postoperative care when surgery required long periods of immobilization.
Grady straps are a specific strapping configuration used in full body spinal immobilization.

In sports medicine, helmet removal is the practice of removing the helmet of someone who has just experienced a sports injury in order to better facilitate first aid. Obvious causes include head and neck injury, or both, with no immediate means of excluding neck injury in the athlete who may be unable to give a history.

Airtraq is a fibreoptic intubation device used for indirect tracheal intubation in difficult airway situations. It is designed to enable a view of the glottic opening without aligning the oral with the pharyngeal, and laryngeal axes as an advantage over direct endotracheal intubation and allows for intubation with minimal head manipulation and positioning.

Spinal precautions, also known as spinal immobilization and spinal motion restriction, are efforts to prevent movement of the spine in those with a risk of a spine injury. This is done as an effort to prevent injury to the spinal cord. It is estimated that 2% of people with blunt trauma will have a spine injury.

Basic airway management is a concept and set of medical procedures performed to prevent and treat airway obstruction and allow for adequate ventilation to a patient's lungs. This is accomplished by clearing or preventing obstructions of airways. Airway obstructions can occur in both conscious and unconscious individuals. They can also be partial or complete. Airway obstruction is commonly caused by the tongue, the airways itself, foreign bodies or materials from the body itself, such as blood or vomit. Contrary to advanced airway management, basic airway management technique do not rely on the use of invasive medical equipment and can be performed with less training. Medical equipment commonly used includes oropharyngeal airway, nasopharyngeal airway, bag valve mask, and pocket mask. Airway management is a primary consideration in cardiopulmonary resuscitation, anaesthesia, emergency medicine, intensive care medicine and first aid.

















