Related Research Articles

Appalachia is a geographic region located in the central and southern sections of the Appalachian Mountains of the eastern United States. Its boundaries stretch from the western Catskill Mountains of New York into Pennsylvania, continuing on through the Blue Ridge Mountains and Great Smoky Mountains into northern Georgia, Alabama, and Mississippi, with West Virginia being the only state in which the entire state is within the boundaries of Appalachia. In 2021, the region was home to an estimated 26.3 million people, of whom roughly 80% were white.

Don Carlos Buell was a United States Army officer who fought in the Seminole War, the Mexican–American War, and the American Civil War. Buell led Union armies in two great Civil War battles—Shiloh and Perryville. The nation was angry at his failure to defeat the outnumbered Confederates after Perryville, or to secure East Tennessee. Historians generally concur that he was a brave and industrious master of logistics, but was too cautious and too rigid to meet the great challenges he faced in 1862. Buell was relieved of field command in late 1862 and made no more significant military contributions until his resignation in 1864.

The Battle of Perryville, also known as the Battle of Chaplin Hills, was fought on October 8, 1862, in the Chaplin Hills west of Perryville, Kentucky, as the culmination of the Confederate Heartland Offensive during the American Civil War. Confederate Gen. Braxton Bragg's Army of Mississippi initially won a tactical victory against primarily a single corps of Maj. Gen. Don Carlos Buell's Union Army of the Ohio. The battle is considered a strategic Union victory, sometimes called the Battle for Kentucky, since Bragg withdrew to Tennessee soon thereafter. The Union retained control of the critical border state of Kentucky for the remainder of the war.

Lieutenant-General Leonidas Polk was an American Confederate military officer, a bishop of the Episcopal Diocese of Louisiana and founder of the Protestant Episcopal Church in the Confederate States of America, which separated from the Episcopal Church of the United States of America. He was a planter in Maury County, Tennessee, and a first cousin twice removed of President James K. Polk. He resigned his ecclesiastical position to become a major-general in the Confederate States Army, when he was called "Sewanee's Fighting Bishop". His official portrait at the University of the South depicts him as a bishop with his army uniform hanging nearby. He is often erroneously referred to as "Leonidas K. Polk" but he had no middle name and never signed any documents as such.
The Army of the Ohio was the name of two Union armies in the American Civil War. The first army became the Army of the Cumberland and the second army was created in 1863.

Charles Champion Gilbert was a United States Army officer during the Mexican–American War and the American Civil War.
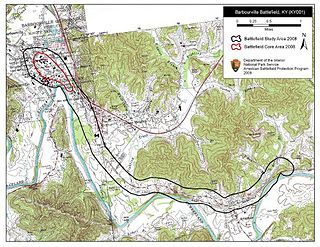
The Battle of Barbourville was one of the early engagements of the American Civil War. It took place on September 19, 1861, in Knox County, Kentucky during the campaign known as the Kentucky Confederate Offensive. The battle is considered the first Confederate victory in the commonwealth, and threw a scare into Federal commanders, who rushed troops to central Kentucky to try to repel the invasion, which was finally stopped at the Battle of Camp Wildcat in October.

Perryville Battlefield State Historic Site is a 745-acre (3.01 km2) park near Perryville, Kentucky. The park continues to expand with purchases of parcels by the Office of Kentucky Nature Preserves' Kentucky Heritage Land Conservation Fund and the American Battlefield Trust. An interpretive museum is located near the site where many Confederate soldiers killed in the Battle of Perryville were buried. Monuments, interpretive signage, and cannons also mark notable events during the battle. The site became part of the Kentucky State Park System in 1936.

The Confederate Heartland Offensive, also known as the Kentucky Campaign, was an American Civil War campaign conducted by the Confederate States Army in Tennessee and Kentucky where Generals Braxton Bragg and Edmund Kirby Smith tried to draw neutral Kentucky into the Confederacy by outflanking Union troops under Major General Don Carlos Buell. Though they scored some successes, notably a tactical win at Perryville, they soon retreated, leaving Kentucky primarily under Union control for the rest of the war.
The following Confederate Army units and commanders fought in the Battle of Perryville of the American Civil War. The Union order of battle is listed separately.

The Union Monument in Perryville is an historic monument located by the visitor center of the Perryville Battlefield State Historic Site, in the vicinity of Perryville, Kentucky, in Boyle County, Kentucky. It was built in 1928, sixty-six years after the Battle of Perryville, the bloodiest battle in Kentucky history, on October 8, 1862. There were 16,000 Union soldiers at the Battle of Perryville, with 4,276 combined killed, captured, wounded, and missing.
19th Indiana Battery Light Artillery was an artillery battery that served in the Union Army during the American Civil War. It was often referred to as Harris' Battery.

The 125th Illinois Volunteer Infantry was an infantry regiment from Illinois that served in the Union Army during the American Civil War. Soon after mustering into Federal service in September 1862, the regiment fought at Perryville. After being stationed at Nashville, Tennessee, the unit briefly fought at Chickamauga and served in the Chattanooga and Knoxville campaigns in 1863. The regiment participated in the Atlanta campaign in 1864, where it took heavy losses at Kennesaw Mountain. It also fought at Peachtree Creek and Jonesborough. At the end of 1864, it served during Sherman's March to the Sea and in 1865 the unit fought in the Carolinas campaign. The regiment participated in the Grand Review of the Armies before being mustered out of service in June 1865.
Don Whitehead was an American journalist. He was awarded the Medal of Freedom. He won the 1950 George Polk Award for wire service reporting.

The Battle of Augusta was an engagement during the American Civil War that took place on September 27, 1862, in Augusta, Kentucky, between the Bracken County Home Guard (Union) and the Confederate Second Kentucky Cavalry Regiment under command of Colonel Basil W. Duke, a brother-in-law of John H. Morgan. The skirmish resulted in a victory for the Confederacy but the number of Confederate casualties and lack of ammunition for his artillery caused Colonel Duke to abandon plans to cross over the Ohio River into Ohio. A result of the fighting was that twenty buildings were set on fire and destroyed.
The 1st Tennessee Infantry Regiment was an infantry regiment in the Confederate States Army during the Civil War, and was successively commanded by Colonels George Maney and Hume R. Field.

The 9th Texas Infantry Regiment was a unit of Confederate States Army infantry volunteers organized in December 1861 that fought during the American Civil War. The regiment fought at Shiloh, Perryville, and Stones River in 1862, Chickamauga in 1863, the Atlanta Campaign, Allatoona, and Nashville in 1864, and Spanish Fort and Fort Blakeley in 1865. The remaining 87 officers and men surrendered to Federal forces in May 1865. Two of the regiment's commanding officers were promoted brigadier general.

The Battle of Riggins Hill was a minor engagement in western Tennessee during the American Civil War. A Confederate raiding force under Colonel Thomas Woodward captured Clarksville, Tennessee, threatening Union shipping on the Cumberland River. Several Union regiments led by Colonel William Warren Lowe advanced from nearby Fort Donelson and drove off the Confederates after a struggle lasting less than an hour. The action occurred during the Confederate Heartland Offensive but only affected the local area.

Barrett's Missouri Battery was an artillery battery that served in the Confederate States Army during the American Civil War. After entering Confederate service on April 1, 1862, the unit was armed with two 6-pounder smoothbore cannons and two 12-pounder howitzers and was commanded by Captain Overton W. Barrett. It was present during the Siege of Corinth, but saw no action. During the Battle of Perryville in October 1862, Barrett's battery provided artillery support for a Confederate brigade. After spending the next several months moving around Tennessee, the battery supported a Confederate attack during the Battle of Stones River in December. The 1863 Chickamauga campaign brought light action for the unit, which also fought in the Battle of Missionary Ridge. When the Confederates retreated after the Missionary Ridge fighting, Barrett's battery was part of the Confederate rear guard at the Battle of Ringgold Gap, earning the praise of Patrick R. Cleburne. Rearmed with four 12-pounder howitzers, the unit was action in the 1864 Atlanta campaign as part of the Confederate reserve artillery, although two of the cannons were lost to attrition. On April 16, 1865, the battery ceased to exist when its flag, cannons, and most of its members were captured during the Battle of Columbus, Georgia. As of January 2021, its battle flag is part of the collection of the Missouri State Museum.

The 20th Louisiana Infantry Regiment was a unit of volunteers recruited in Louisiana that fought in the Confederate States Army during the American Civil War. The unit began its existence as the 6th Louisiana Battalion in September 1861. The battalion was augmented to regimental strength in January 1862 at New Orleans and served during the war in the Western Theater of the American Civil War. The regiment fought at Shiloh, Farmington, and Perryville in 1862. After being reduced in numbers, the regiment was consolidated with the 13th Louisiana Infantry Regiment and served at Stones River, Jackson, Chickamauga, and Missionary Ridge in 1863. The 13th-20th Consolidated Louisiana fought at Resaca, New Hope Church, Ezra Church, and Nashville in 1864. The consolidation with the 13th Louisiana was discontinued in February 1865 and the regiment was re-consolidated with other units. It fought its final battle at Spanish Fort one month before surrendering in May 1865.
References
- ↑ "Kenneth W. Noe". Auburn University. Retrieved 3 February 2021.