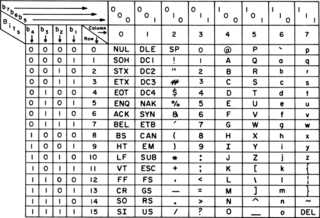
ASCII, abbreviated from American Standard Code for Information Interchange, is a character encoding standard for electronic communication. ASCII codes represent text in computers, telecommunications equipment, and other devices. Because of technical limitations of computer systems at the time it was invented, ASCII has just 128 code points, of which only 95 are printable characters, which severely limited its scope. Modern computer systems have evolved to use Unicode, which has millions of code points, but the first 128 of these are the same as the ASCII set.

Scroll Lock is a lock key on most IBM-compatible computer keyboards.

A text editor is a type of computer program that edits plain text. Such programs are sometimes known as "notepad" software. Text editors are provided with operating systems and software development packages, and can be used to change files such as configuration files, documentation files and programming language source code.
TECO, short for Text Editor & Corrector, is both a character-oriented text editor and a programming language, that was developed in 1962 for use on Digital Equipment Corporation computers, and has since become available on PCs and Unix. Dan Murphy developed TECO while a student at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT).

A terminal emulator, or terminal application, is a computer program that emulates a video terminal within some other display architecture. Though typically synonymous with a shell or text terminal, the term terminal covers all remote terminals, including graphical interfaces. A terminal emulator inside a graphical user interface is often called a terminal window.
Cut, copy, and paste are essential commands of modern human–computer interaction and user interface design. They offer an interprocess communication technique for transferring data through a computer's user interface. The cut command removes the selected data from its original position, and the copy command creates a duplicate; in both cases the selected data is kept in temporary storage called the clipboard. Clipboard data is later inserted wherever a paste command is issued. The data remains available to any application supporting the feature, thus allowing easy data transfer between applications.

A computer terminal is an electronic or electromechanical hardware device that can be used for entering data into, and transcribing data from, a computer or a computing system. The teletype was an example of an early-day hard-copy terminal and predated the use of a computer screen by decades. Starting in the mid-1970s with machines such as the Sphere 1, Sol-20, and Apple I, terminal circuitry began to be integrated into personal and workstation computer systems, with the computer handling character generation and sometimes outputting to a basic CRT display such as a consumer TV.

In computing, a keyboard shortcut also known as hotkey is a series of one or several keys to quickly invoke a software program or perform a preprogrammed action. This action may be part of the standard functionality of the operating system or application program, or it may have been written by the user in a scripting language. Some integrated keyboards also include pointing devices; the definition of exactly what counts as a "key" sometimes differs.

In computing, text-based user interfaces (TUI), is a retronym describing a type of user interface (UI) common as an early form of human–computer interaction, before the advent of bitmapped displays and modern conventional graphical user interfaces (GUIs). Like modern GUIs, they can use the entire screen area and may accept mouse and other inputs. They may also use color and often structure the display using box-drawing characters such as ┌ and ╣. The modern context of use is usually a terminal emulator.

The VT50 is a CRT-based computer terminal that was introduced by Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC) in July 1974. It provided a display with 12 rows and 80 columns of upper-case text, and used an expanded set of control characters and forward-only scrolling based on the earlier VT05. DEC documentation of the era refers to the terminals as the DECscope, a name that was otherwise almost never seen.
On personal computers with numeric keypads that use Microsoft operating systems, such as Windows, many characters that do not have a dedicated key combination on the keyboard may nevertheless be entered using the Alt code. This is done by pressing and holding the Alt key, then typing a number on the keyboard's numeric keypad that identifies the character and then releasing Alt.

The Gold key is a computer keyboard key used as a prefix to invoke a variety of single-key editing and formatting functions. Usually located in the top-left position of the numeric keypad on platforms such as the VT100, it is the signature element of a consistent user interface implemented by Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC) across multiple product lines.
Key rollover is the ability of a computer keyboard to correctly handle several simultaneous keystrokes. A keyboard with n-key rollover (NKRO) can correctly detect input from each key on the keyboard at the same time, regardless of how many other keys are also being pressed. Keyboards that lack full rollover will register an incorrect keystroke when certain combinations of keys are pressed simultaneously. Rollover has applications for stenotype, electronic music keyboards, gaming, and touch-typing generally.
Control-C is a common computer command. It is generated by pressing the C key while holding down the Ctrl key on most computer keyboards.

GNU Emacs is a free software text editor. It was created by GNU Project founder Richard Stallman, based on the Emacs editor developed for Unix operating systems. GNU Emacs has been a central component of the GNU project and a flagship project of the free software movement. Its tag line is "the extensible self-documenting text editor."

A computer keyboard is a peripheral input device modeled after the typewriter keyboard which uses an arrangement of buttons or keys to act as mechanical levers or electronic switches. Replacing early punched cards and paper tape technology, interaction via teleprinter-style keyboards have been the main input method for computers since the 1970s, supplemented by the computer mouse since the 1980s.
Emacs, originally named EMACS, is a family of text editors that are characterized by their extensibility. The manual for the most widely used variant, GNU Emacs, describes it as "the extensible, customizable, self-documenting, real-time display editor". Development of the first Emacs began in the mid-1970s, and work on GNU Emacs, directly descended from the original, is ongoing; its latest version is 29.1, released July 2023.
The POSIX terminal interface is the generalized abstraction, comprising both an application programming interface for programs, and a set of behavioural expectations for users of a terminal, as defined by the POSIX standard and the Single Unix Specification. It is a historical development from the terminal interfaces of BSD version 4 and Seventh Edition Unix.
The Hazeltine 2000 is one of the first general-purpose "smart" computer terminals, introduced in October 1970 at a price of $2,995. While earlier terminal systems included "smart" editing features, notably the IBM 2260, the Hazeltine 2000 was the first that used a standard RS-232 interface and sent its control sequences in the data stream. It could be attached to any contemporary minicomputer or mainframe that had a serial port and used ASCII-standard character sets.

The Hazeltine 1500 was a popular smart terminal introduced by Hazeltine Corporation in April 1977 at a price of $1,125. Using a microprocessor and semiconductor random access memory, it implemented the basic features of the earlier Hazeltine 2000 in a much smaller and less expensive system, less than half the price. It came to market just as the microcomputer revolution was taking off, and the 1500 was very popular among early hobbyist users.










