The Ajanta Caves are 30 rock-cut Buddhist cave monuments dating from the second century BCE to about 480 CE in Aurangabad district of Maharashtra state in India. Ajanta Caves are a UNESCO World Heritage Site. Universally regarded as masterpieces of Buddhist religious art, the caves include paintings and rock-cut sculptures described as among the finest surviving examples of ancient Indian art, particularly expressive paintings that present emotions through gesture, pose and form.
The Ellora Caves are a UNESCO World Heritage Site in Aurangabad district, Maharashtra, India. It is one of the largest rock-cut Hindu temple cave complexes in the world, with artwork dating from the period 600–1000 AD, also including several Buddhist and Jain caves. The complex is a leading example of Indian rock-cut architecture, and several are not strictly "caves" in that they have no roof. Cave 16 features the largest single monolithic rock excavation in the world, the Kailash temple, a chariot-shaped monument dedicated to the god Shiva. The Kailash temple excavation also features sculptures depicting various Hindu deities as well as relief panels summarizing the two major Hindu epics.

Ratnagiri district is a district in the state of Maharashtra, India. The administrative headquarter of the district is located in the town of Ratnagiri. The district is 11.33% urban. The district is bounded by the Arabian Sea to the west, Sindhudurg district to the south, Raigad district to the north and Satara, Sangli and Kolhapur districts to the east. This district is part of Konkan division.
Vihāra generally refers to a Buddhist temple or Buddhist monastery for Buddhist renunciates, mostly in the Indian subcontinent. The concept is ancient and in early Pali texts, it meant any arrangement of space or facilities for dwellings. The term evolved into an architectural concept wherein it refers to living quarters for monks with an open shared space or courtyard, particularly in Buddhism. The term is also found in Jain monastic literature, usually referring to temporary refuge for wandering monks or nuns during the annual Indian monsoons. In modern Jainism, the monks continue to wander from town to town except during the rainy season (chaturmasya), and the term "vihara" refers to their wanderings.

A chaitya, chaitya hall, chaitya-griha, refers to a shrine, sanctuary, temple or prayer hall in Indian religions. The term is most common in Buddhism, where it refers to a space with a stupa and a rounded apse at the end opposite the entrance, and a high roof with a rounded profile. Strictly speaking, the chaitya is the stupa itself, and the Indian buildings are chaitya halls, but this distinction is often not observed. Outside India, the term is used by Buddhists for local styles of small stupa-like monuments in Nepal, Cambodia, Indonesia and elsewhere. In Thailand a stupa itself, not a stupa hall, is called a chedi, a local Thai word derived from the Pali Cetiya. In the historical texts of Jainism and Hinduism, including those relating to architecture, chaitya refers to a temple, sanctuary or any sacred monument.

The Karla Caves, Karli Caves, Karle Caves or Karla Cells, are a complex of ancient Buddhist Indian rock-cut caves at Karli near Lonavala, Maharashtra. It is just 10.9 Kilometers away from Lonavala. Other caves in the area are Bhaja Caves, Patan Buddhist Cave, Bedse Caves and Nasik Caves. The shrines were developed over the period – from the 2nd century BCE to the 5th century CE. The oldest of the cave shrines is believed to date back to 160 BCE, having arisen near a major ancient trade route, running eastward from the Arabian Sea into the Deccan.

The Bagh Caves are a group of nine rock-cut monuments, situated among the southern slopes of the Vindhya Range in Bagh town of Dhar district in Madhya Pradesh in central India. These monuments are located at a distance of 97 km from Dhar town. These are renowned for mural paintings by master painters of ancient India. The caves are examples of Indian rock-cut architecture, rather than naturally formed.

Furus also known as Phuroos or Furoos is a village in Khed,Ratnagiri district, Maharashtra state in Western India. The 2011 Census of India recorded a total of 3255 residents in the village with total area 1062.35 hectares. It is predominantly populated by Konkani Muslims along with Hindu and Buddhist. Furus is believed to be named by Persians who came here to trade in horses. The main language spoken in Furus is Kokni, a blend of Bankoti, Sangameshwari and Marathi infused with words of Arabic, Urdu and Persian origin.

Mahad ( [məɦaːɖ]) is a city in Raigad district situated in the North Konkan region of Maharashtra state, India. It is located 108.5 km (67.4 mi) from District Headquarters Alibag, and 167 km (104 mi) from Mumbai. Mahad is known for Raigad Fort, the capital of the Maratha Empire in Shivaji Maharaj's era and the revolutionary Mahad Satyagraha launched by at Chavdar Tale in the wake of modern India.

Indian rock-cut architecture is more various and found in greater abundance in that country than any other form of rock-cut architecture around the world. Rock-cut architecture is the practice of creating a structure by carving it out of solid natural rock. Rock that is not part of the structure is removed until the only rock left makes up the architectural elements of the excavated interior. Indian rock-cut architecture is mostly religious in nature.

Bhaja Caves are a group of 22 rock-cut caves dating back to the 2nd century BC located off the Mumbai - Pune expressway near the city of Pune, India. The caves are 400 feet above the village of Bhaja, on an important ancient trade route running from the Arabian Sea eastward into the Deccan Plateau. The inscriptions and the cave temple are protected as a Monument of National Importance, by the Archaeological Survey of India per Notification No. 2407-A. It belongs to the Early Buddhist schools in Maharashtra. The caves have a number of stupas, one of their significant features. The most prominent excavation is its chaitya, a good example of the early development of this form from wooden architecture, with a vaulted horseshoe ceiling. Its vihara has a pillared verandah in front and is adorned with unique reliefs. These caves are notable for their indications of the awareness of wooden architecture. The carvings prove that tabla – a percussion instrument – was used in India for at least 2300 years, disproving the centuries-held belief that the tabla was introduced to India by outsiders or from Turko-Arab. The carving shows a woman playing tabla and another woman, performing dance.

The Barabar Hill Caves are the oldest surviving rock-cut caves in India, dating from the Maurya Empire, some with Ashokan inscriptions, located in the Makhdumpur region of Jehanabad district, Bihar, India, 24 km (15 mi) north of Gaya.
Kondivali is a small village in Khed Taluka of Ratnagiri district in Maharashtra, India. The village is also known as 'Kondvil'. The main languages spoken here are Marathi and Konkani.

The Aurangabad caves, are twelve rock-cut Buddhist shrines located on a hill running roughly east to west, close to the city of Aurangabad, Maharashtra. The first reference to the Aurangabad Caves is in the great chaitya of Kanheri Caves. The Aurangabad Caves were dug out of comparatively soft basalt rock during the 6th and 7th century.

The Shivneri Caves are artificial caves dug for Buddhist monks circa the 1st century CE. These are now famous tourist attractions located on Shivneri Hill, about 2 km Southwest of Junnar, India. Other caves around the city of Junnar are: Manmodi Caves, Lenyadri, and the Tulja Caves.
Nenavali Caves, also Khadsamble Caves, are located at Sudhagad at Raigad, India. This is group of 37 Buddhist caves about 35 km from Pali, carved in first century B.C.

Panhalakaji Caves are situated in the Ratnagiri district of Maharashtra state, about 160 km south of Mumbai. This cave complex has around 30 Buddhist and Hindu caves. The Hinayana sect began carving caves in 3rd century AD, beginning with the stupa in the current Cave 5. The caves have inscriptions in Brahmi and Devanagari script. In the 10–11th century AD another Buddhist group, a Vajrayana sect, established cave 10 with their deities Akshobhya and Mahachandaroshana; and strengthened their practice in that region. Shiva and Ganpatya worshiping started at the site during Silahara rule. There are total 29 caves out of which 28 are situated on the right bank of mou tain stream Kotjai.

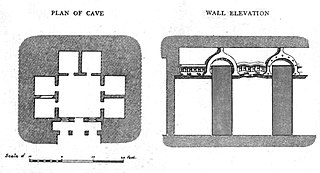
The Guntupalle or Guntupalli Group of Buddhist Monuments is located near Kamavarapukota, Eluru district, in the state of Andhra Pradesh in India. It is around 40 km away from Eluru. The rock-cut part of the site has two Buddhist caves, a chaitya hall and a large group of stupas. The chaitya hall has a rare carved stone entrance replicating wooden architecture, a simpler version of that at the Lomas Rishi Cave.

Yerphal Caves, also Yerphale Caves, are a small group of Buddhist caves located near Umbraj, Maharashtra, India. The caves were only discovered recently, in 1979. It is located not far from the Karad Caves.

The Khapra Kodiya Caves are part of the Junagadh Buddhist Cave Group. They are the oldest of the caves in the group. The caves, on the basis of scribbles and short cursive letters on the wall, are dated to 3rd-4th century BCE during the Emperor Ashoka's rule and are the plainest of all the caves in the groups. These caves are also known as Khangar Mahal. They were carved in rock during the reign of Emperor Ashoka and are considered the earliest monastic settlement in the area. These caves are along the edge of the ancient Sudarshan Lake and a little outside Uparkot fort, to the north.