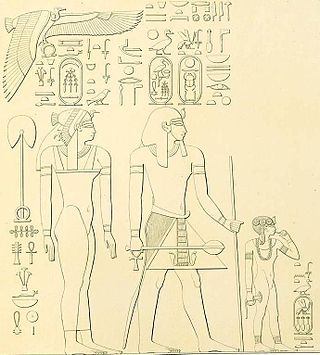
Ahmose was an Ancient Egyptian queen in the Eighteenth Dynasty. She was the Great Royal Wife of the dynasty's third pharaoh, Thutmose I, and the mother of the queen and pharaoh Hatshepsut. Her name means "Born of the Moon".
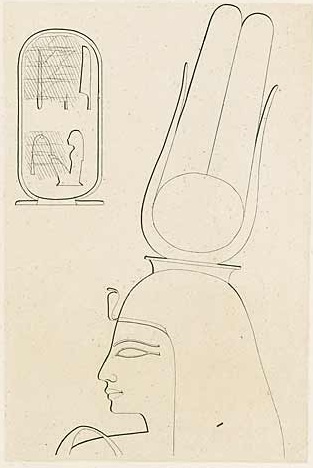
Tey was the Great Royal Wife of Kheperkheprure Ay, who was the penultimate pharaoh of Ancient Egypt's Eighteenth Dynasty. She also had been the wet nurse of Nefertiti.

Sitre or Tia-Sitre, was the Great Royal Wife of Pharaoh Ramesses I of Egypt and mother of Seti I.

Bintanath was the firstborn daughter and later Great Royal Wife of the Egyptian Pharaoh Ramesses II.

Meritamen was a daughter and later Great Royal Wife of Pharaoh Ramesses the Great.

Ahmose-Meritamun was a Queen of Egypt during the early Eighteenth Dynasty. She was both the older sister and the wife of Pharaoh Amenhotep I. She died fairly young and was buried in tomb TT358 in Deir el-Bahari.
Iput I was a queen of ancient Egypt, a daughter of King Unas, the last king of the Fifth Dynasty of Egypt. She married Teti, the first Pharaoh of the Sixth Dynasty of Egypt. Their son was Pepi I Meryre. She possibly ruled as regent for her son Pepi I.

Ankhesenpepi II or Ankhesenmeryre II was a queen consort during the Sixth Dynasty of Egypt. She was the wife of Kings Pepi I and Merenre Nemtyemsaf I, and the mother of Pepi II. She likely served as regent during the minority of her son. She was buried in a pyramid in Saqqara.

Iaret was a Great Royal Wife from the middle of the Eighteenth Dynasty of Ancient Egypt.

Ahmose-Henuttamehu was a princess and queen of the late 17th-early 18th dynasties of Egypt.
Nubwenet was an ancient Egyptian queen consort, a wife of Pharaoh Pepi I of the 6th dynasty.
Nedjeftet is a queen mentioned on reliefs discovered near the pyramid complex of Pepi I. She was a wife of Pepi. Her name was also that of the 20th nome, later known as the Herakleopolis nome, in Upper Egypt; it is possible her family came from there and the marriage was to strengthen the king's position as opposed to the local lords.
Meritites IV was a queen consort from the Sixth Dynasty. She was believed to be a wife of Pepi I Meryre, but her title of King's Daughter of his body of Pepy-Mennefer (s3t-niswt-nt-kht.f-ppy-mn-nfr) is now understood to indicate that she was a daughter of Pepi I Meryre and wife of a king Neferkare, presumably Pepi II. One more evidence for that theory is that her name means "Beloved of her father".

Isetnofret was a royal woman of Ancient Egypt and, as the Great Royal Wife of Pharaoh Merenptah, she became Isetnofret II.
Tabiry was a Nubian queen dated to the Twenty-fifth Dynasty of Egypt.
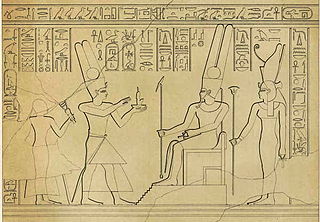
Abar was a Nubian queen of the Kingdom of Kush dated to the Twenty-fifth Dynasty of Egypt. She is known from a series of stela found in Sudan and Egypt. Her appearances mark her as the niece of King Alara of Nubia, married to King Piye and the mother of King Taharqa.

Takahatenamun was a Nubian queen dated to the Twenty-fifth Dynasty of Egypt.

Naparaye was a Nubian queen dated to the Twenty-fifth Dynasty of Egypt.

Bunefer was an ancient Egyptian queen from the 4th or 5th dynasty. It is not known which king she was married to. Bunefer was buried in tomb G 8408 in the Central Field of the Giza Necropolis.
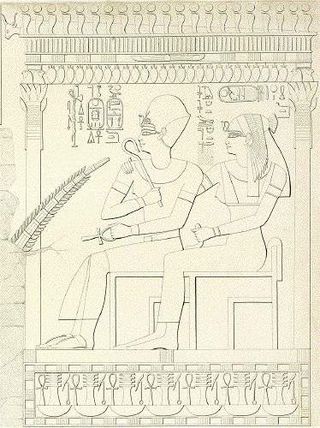
Merytre-Hatshepsut was the Great Royal Wife of Pharaoh Thutmose III after the death of Queen Satiah. She was the mother of Pharaoh Amenhotep II.














