Related Research Articles
Indian epic poetry is the epic poetry written in the Indian subcontinent, traditionally called Kavya. The Ramayana and the Mahabharata, which were originally composed in Sanskrit and later translated into many other Indian languages, and the Five Great Epics of Tamil literature and Sangam literature are some of the oldest surviving epic poems ever written.

The Meitei people, Meetei people, or Manipuri people is an ethnic group native to Manipur. They form the largest and dominant ethnic group of Manipur in Northeast India. They speak Meitei language, one of the 22 official languages of the Indian Republic and the sole official language of Government of Manipur. The Meiteis primarily settled in the Imphal Valley region in modern-day Manipur, though a sizable population has settled in the other Indian states of Assam, Tripura, Nagaland, Meghalaya, and Mizoram. There is also a notable presence of Meitei people in the neighboring countries of Myanmar and Bangladesh. The Meitei ethnic group represents about 53% of Manipur's population.
Odia literature is literature written in the Odia language, mostly from the Indian state of Odisha. The modern Odia language is mostly formed from Tadbhava words with significant Sanskrit (Tatsama) influences, along with loanwords from Desaja, English, Hindustani (Hindi/Urdu), Persian, and Arabic. Its earliest written texts date from around 1000 CE. The earliest Odia newspaper was Utkala Deepika, first published on August 4, 1866.

Manipuri Vaishnavism, also known as Meitei Vaishnavism, is a regional variant of Gaudiya Vaishnavism with a culture-forming role in the north-eastern Indian state of Manipur.

Meitei literature, also known as Manipuri literature, is literature written in the Meitei language of Manipur. An ancient institution of learning, the Luwang Nonghumsang, later known as the Pandit Loishang, collected sources of indigenous Meitei knowledge and philosophy until the 18th century. Writing by Meiteis is assumed to go back to the Kingdom of Kangleipak in the early 12th century. The Meitei script is a Brahmic abugida. It is known only from the Puya manuscripts discovered in the first half of the 20th century. Manuscripts of the 18th and 19th centuries were written using the Bengali alphabet. The existence of the Meitei script in the 15th-century hinges on the authenticity of an inscription dated to the reign of Senbi Kiyamba. The first printed Manipuri book, Manipurer Itihas, appeared in 1890 from the Baptist Mission Press, Calcutta. Though the kings of Manipur had established contact with the British from the middle of the eighteenth century onward the real impact of the contact came much later. Johnstone Middle English School, based on the western system of education, was started in 1885 at Imphal, and in 1891 Manipur lost its independence to the British. British domination facilitated the introduction of new systems in the civil, political and educational spheres, which hastened the process of modernization in Manipur, exposed as it was to new ideas and influences.

Padma Shri Ashangbam Minaketan Singh is regarded as the founder of Modern Manipuri literature. He was born as the only child to Ashangbam Jivan Singh and Medhabati Devi on 2 May 1906. His grandfather Ashang Kut, also known as Ashangbam Phura Hongba, served as an Officer in The Maharaja of Manipur's army. In March 1891 he played a part in the assassination of British officials and was thereby sentenced for transportation on charge of murder. He was sentenced twenty five years of life imprisonment at Kalapani Jail, which is located in the Andaman and Nicobar Islands, India.

Khumanthem Ningol Nameirakpam Ongbi Ibemni Devi was an Indian singer of traditional music, known for her expertise in the Khongjom Praba genre of Manipuri music. The Government of India honoured Ibemni Devi in 2012, with the fourth highest civilian award of Padma Shri.
Elangbam Nilakanta Singh (1927-2000) was an Indian poet and critic, considered by many as one of the pioneers of modern Meitei literature. A recipient of the Sahitya Akademi Award in 1987, Nilakanta Singh was honored by the Government of India, in 2000, with the fourth highest Indian civilian award of Padma Shri.
Ningthoukhongjam Khelchandra Singh was an Indian writer, lexicographer and historian, known as the author of Manipuri to Manipuri and English, the first modern general dictionary in Meitei language, which was published in 1964. He was a fellow of the Sahitya Akademi and Sangeet Natak Akademi. The Government of India awarded him the fourth highest civilian honour of Padma Shri in 1987.

The Khamba Thoibi Sheireng, also spelled as the Khamba Thoibi Seireng, is a 1940 Meitei language classical epic poem based on the ancient love story of Khuman prince Khamba and Moirang princess Thoibi of Moirang kingdom of Ancient Kangleipak. It is the magnum opus of Hijam Anganghal, the "Bard of Samurou". It is regarded as the national epic of the Manipuris. It is regarded as the greatest of all the epic poems in Meitei literature, with 39,000 verses, thereby being the third longest Indian epic poem, next to the Mahabharata and the Ramayana.

Meitei mythology or Manipuri mythology is a collection of myths, belonging to the religious and cultural traditions of the Meitei people, the predominant ethnic group of Manipur. It is associated with traditional Meitei religion (Sanamahism). Meitei myths are a part of Meitei culture and explain various natural phenomena, how the human civilization developed, and the reasons of many things happening. Most of the Meitei legends are found in the Meitei language texts.
Meitei Chanu is a Meitei language poem by Lamabam Kamal. It was first published in a magazine, with the same name, called Meitei Chanu (magazine) in the year 1924. It was republished in the author's book of his collection of poems called "Lei Pareng" in the year 1929. Its central theme is the reconfiguration of the identity of the Meitei people. The poem bountifully reflects the poet's love of his motherland and its heritage.

In Meitei mythology and folklore, the epic cycles of incarnations in Moirang is a cyclic epic of seven incarnations of two divine lovers in the kingdom of Moirang in the realm of Ancient Kangleipak.

The ancient legend of Khuyol Haoba and Yaithing Konu is one of the epic cycles of incarnations of Meitei mythology and folklore, that is originated from Moirang kingdom of Ancient Kangleipak. It concerns the fateful love of Khuyol Haoba, an orphan man, for the beautiful Yaithing Konu. Khuyol Haoba was the son of late Khundouremba, a court official of Moirang. Yaithing Konu was the daughter of Luwang Huiningsumba, an influential nobleman of Moirang.

The ancient legend of Kadeng Thangjahanba and Tonu Laijinglembi is one of the epic cycles of incarnations of Meitei mythology and folklore, that is originated from Moirang kingdom of Ancient Kangleipak. It concerns the fateful love of Kadeng Thangjahanba, a skilled blacksmith, for the beautiful Tonu Laijinglembi. Kadeng Thangjahanba was a highly talented and skilful royal chief metalsmith appointed by King Laijing Ningthou Punsiba of Moirang. Tonu Laijinglembi was the only daughter of Laijing Lakpa, a favourite nobleman of the King of Moirang.

The Mahabharata is one of the epics of Sanskrit literature that is translated as well as literarily adapted into Meitei language, thereby creating a space for Hindu literature within the granary of Meitei literature.

The Khoirentak tiger was a vicious monster in Meitei mythology that lived in Khoirentak a kom village.
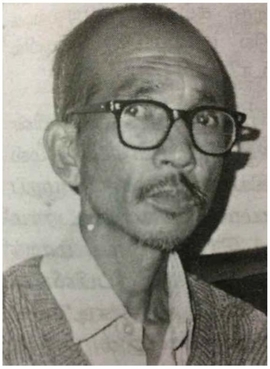
Nongthombam Shri Biren, better known shortly as Shri Biren or Sri Biren, and also spelled as Shribiren or Sribiren, was an Indian editor, poet, playwright, social reformer, teacher and short story writer of works in Meitei literature. His writings are characterised by the wrath and the mood of the loss of hope and confidence. He was active in writing in the 1960s and the 1970s. Most of his writings are predominant with the "iconoclastic extreme anger and questioning of everything in life". He was considered to be an angry young man of the 1970s, for his poem, Tangkhul Hui. He was known for portraying the lives of people in a metaphysical and philosophical way, protesting against the existing socio-political systems and institutions and attempting to break them, using symbolism and allegory as tools, as evident in "The Two Doors". He was bestowed with the Manipur State Kala Academy Award, the Central Sahitya Akademi Award and the Jamini Sundar Gold Medal for his poetry and short stories. Unfortunate to the Meitei literature is that he died at an early age, suffering from Parkinson's disease.
References
- ↑ L. Kamal Singh. Sahitya Akademi. 2000. p. 12. ISBN 8126008563 . Retrieved 16 August 2015.
- ↑ Burningvoices. "Khwairakpam Chaoba Singh". Archived from the original on 8 July 2011.
- ↑ Datta, Amaresh (1988). Encyclopedia of Indian Literature Volume 1. Sahitya Akademi. pp. 1145–1153. ISBN 8126011947 . Retrieved 16 August 2015.